给定两个正整数N和S ,任务是计算在N个硬币上执行S翻转操作时可能产生的唯一结果的数量。
例子:
Input: N = 3, S = 4
Output: 3
Explanation: Considering the intiial configuration of coins to be “HHH”, then the possible combinations of 4 flips are:
- Flipping the 1st and 2nd coins once and the third coin twice modifies the configuration to “TTH”.
- Flipping the 1st and 3rd coins once and the 2nd coin twice modifies the configuration to “THT”.
- Flipping the 2nd and 3rd coins once and the 1st coin twice modifies the configuration to “HTT”.
The above three combinations are unique. Therefore, the total count is 3.
Input: N = 3, S = 6
Output: 4
天真的方法:可以通过使用递归状态定义为的递归来解决该问题:
- 考虑到F(N,S)表示当掷出N个硬币且掷骰总数等于S时唯一结果的数量。
- 然后, F(N,S)也可以表示为1次翻转或2次翻转的所有组合的总和,即
F(N, S) = F(N – 1, S – 1) + F(N – 1, S – 2)
- 这个递推关系基础案例是F(K,K),其值是1对所有(K> 1)。
- 下表显示了F(N,S)= F(N – 1,S – 1)+ F(N – 1,S – 2)的分布,其中F(K,K)= 1 。
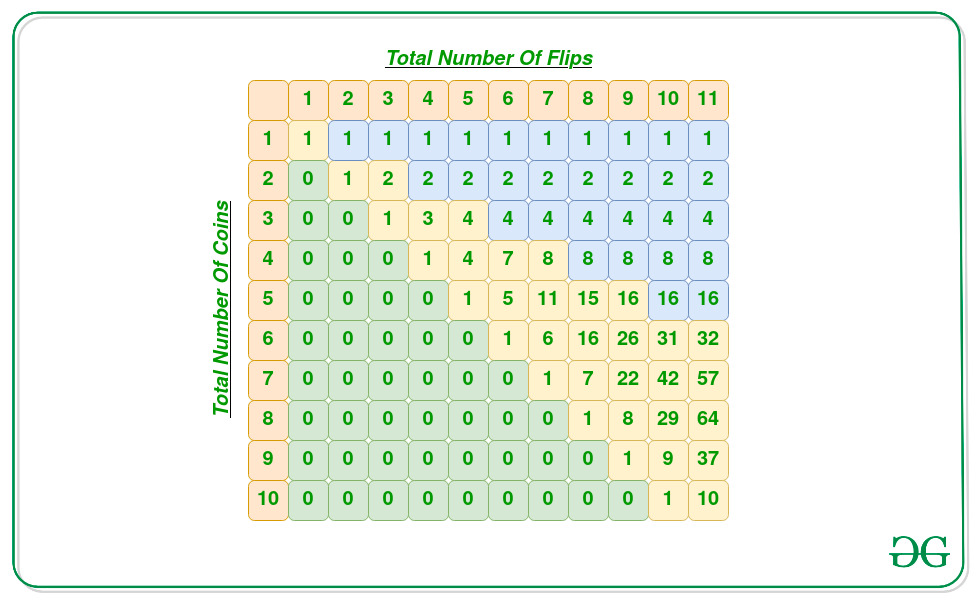
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 声明一个函数,例如numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N,S) ,该函数分别将允许的硬币和翻转次数作为参数,并执行以下步骤:
- 如果S的值小于N ,则从函数返回0 。
- 如果N的值为S或1 ,则从函数返回1 ,因为这是唯一组合之一。
- 递归地返回两个递归状态的和:
return numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N – 1, S – 1) + numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N – 1, S – 2)
- 完成上述步骤后,打印由numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N,S)函数返回的值作为结果的结果数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// S flips are performed on N coins
int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int N, int S)
{
// Base Cases
if (S < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1 || N == S)
return 1;
// Recursive Calls
return (numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N - 1, S - 1)
+ numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N - 1, S - 2));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 3, S = 4;
cout << numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// S flips are performed on N coins
static int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int N, int S)
{
// Base Cases
if (S < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1 || N == S)
return 1;
// Recursive Calls
return (numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N - 1, S - 1)
+ numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N - 1, S - 2));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int N = 3, S = 4;
System.out.println(numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S));
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Function to recursively count the
# number of unique outcomes possible
# S flips are performed on N coins
def numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S):
# Base Cases
if (S < N):
return 0
if (N == 1 or N == S):
return 1
# Recursive Calls
return (numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N - 1, S - 1) +
numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N - 1, S - 2))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N, S = 3, 4
print (numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// S flips are performed on N coins
static int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int N, int S)
{
// Base Cases
if (S < N)
return 0;
if (N == 1 || N == S)
return 1;
// Recursive Calls
return (numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N - 1, S - 1) +
numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N - 1, S - 2));
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main()
{
int N = 3, S = 4;
Console.WriteLine(numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Dimensions of the DP table
#define size 1001
// Stores the dp states
int ans[size][size] = { 0 };
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// by performing S flips on N coins
int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int n, int s)
{
// Base Case
if (s < n)
ans[n][s] = 0;
else if (n == 1 || n == s)
ans[n][s] = 1;
// If the count for the current
// state is not calculated, then
// calculate it recursively
else if (!ans[n][s]) {
ans[n][s] = numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 1)
+ numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 2);
}
// Otherwise return the
// already calculated value
return ans[n][s];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 5, S = 8;
cout << numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Dimensions of the DP table
static int size = 100;
static int [][]ans = new int[size][size];
static void initialize()
{
// Stores the dp states
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
ans[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// by performing S flips on N coins
static int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int n, int s)
{
// Base Case
if (s < n)
ans[n][s] = 0;
else if (n == 1 || n == s)
ans[n][s] = 1;
// If the count for the current
// state is not calculated, then
// calculate it recursively
else if (ans[n][s] == 0) {
ans[n][s] = numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 1)
+ numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 2);
}
// Otherwise return the
// already calculated value
return ans[n][s];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
initialize();
int N = 5, S = 8;
System.out.println(numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S));
}
}
// This code is contributed by SURENDRA_GANGWAR.Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Dimensions of the DP table
size = 100
# Stores the dp states
ans = [[0 for i in range(size)]
for j in range(size)]
# Function to recursively count the
# number of unique outcomes possible
# by performing S flips on N coins
def numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n, s):
# Base Case
if (s < n):
ans[n][s] = 0;
elif (n == 1 or n == s):
ans[n][s] = 1;
# If the count for the current
# state is not calculated, then
# calculate it recursively
elif(ans[n][s] == 0):
ans[n][s] = (numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1, s - 1) +
numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1, s - 2))
# Otherwise return the
# already calculated value
return ans[n][s];
# Driver Code
N = 5
S = 8
print(numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S))
# This code is contributed by rag2127C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Dimensions of the DP table
static int size = 100;
static int [,]ans = new int[size, size];
static void initialize()
{
// Stores the dp states
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
ans[i, j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// by performing S flips on N coins
static int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int n, int s)
{
// Base Case
if (s < n)
ans[n, s] = 0;
else if (n == 1 || n == s)
ans[n, s] = 1;
// If the count for the current
// state is not calculated, then
// calculate it recursively
else if (ans[n, s] == 0)
{
ans[n, s] = numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 1) +
numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 2);
}
// Otherwise return the
// already calculated value
return ans[n,s];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string []args)
{
initialize();
int N = 5, S = 8;
Console.WriteLine(numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkThon输出:
3时间复杂度: O(2 N )
辅助空间: O(N)
高效方法:还可以通过存储递归状态来优化上述方法,因为它包含重叠的子问题。因此,这个想法是使用记忆来存储重复的状态。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个二维数组,例如维数为N * M的dp [] [] ,以使dp [i] [j]使用i个硬币和j个翻转次数存储可能的结果数。
- 声明一个函数,例如numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N,S) ,该函数分别将允许的硬币数量和翻转数作为参数,并执行以下步骤:
- 如果S的值小于N ,则将dp [N] [S]的值更新为0并从函数返回此值。
- 如果N的值为S或1 ,则将dp [N] [S]的值更新为1并从函数返回此值,因为这是唯一组合之一。
- 如果DP的值[n]是已计算出的[S],然后从该函数返回值DP [N] [S]。
- 递归更新两个递归状态的dp [N] [S]之和的值,如下所示,并从函数返回该值。
dp[N][S] = numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N – 1, S – 1) + numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N – 1, S – 2)
- 完成上述步骤后,打印由numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N,S)函数返回的值作为结果的结果数。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Dimensions of the DP table
#define size 1001
// Stores the dp states
int ans[size][size] = { 0 };
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// by performing S flips on N coins
int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int n, int s)
{
// Base Case
if (s < n)
ans[n][s] = 0;
else if (n == 1 || n == s)
ans[n][s] = 1;
// If the count for the current
// state is not calculated, then
// calculate it recursively
else if (!ans[n][s]) {
ans[n][s] = numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 1)
+ numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 2);
}
// Otherwise return the
// already calculated value
return ans[n][s];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 5, S = 8;
cout << numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Dimensions of the DP table
static int size = 100;
static int [][]ans = new int[size][size];
static void initialize()
{
// Stores the dp states
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
ans[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// by performing S flips on N coins
static int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int n, int s)
{
// Base Case
if (s < n)
ans[n][s] = 0;
else if (n == 1 || n == s)
ans[n][s] = 1;
// If the count for the current
// state is not calculated, then
// calculate it recursively
else if (ans[n][s] == 0) {
ans[n][s] = numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 1)
+ numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 2);
}
// Otherwise return the
// already calculated value
return ans[n][s];
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
initialize();
int N = 5, S = 8;
System.out.println(numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S));
}
}
// This code is contributed by SURENDRA_GANGWAR.
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Dimensions of the DP table
size = 100
# Stores the dp states
ans = [[0 for i in range(size)]
for j in range(size)]
# Function to recursively count the
# number of unique outcomes possible
# by performing S flips on N coins
def numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n, s):
# Base Case
if (s < n):
ans[n][s] = 0;
elif (n == 1 or n == s):
ans[n][s] = 1;
# If the count for the current
# state is not calculated, then
# calculate it recursively
elif(ans[n][s] == 0):
ans[n][s] = (numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1, s - 1) +
numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1, s - 2))
# Otherwise return the
# already calculated value
return ans[n][s];
# Driver Code
N = 5
S = 8
print(numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S))
# This code is contributed by rag2127
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Dimensions of the DP table
static int size = 100;
static int [,]ans = new int[size, size];
static void initialize()
{
// Stores the dp states
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
ans[i, j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Function to recursively count the
// number of unique outcomes possible
// by performing S flips on N coins
static int numberOfUniqueOutcomes(int n, int s)
{
// Base Case
if (s < n)
ans[n, s] = 0;
else if (n == 1 || n == s)
ans[n, s] = 1;
// If the count for the current
// state is not calculated, then
// calculate it recursively
else if (ans[n, s] == 0)
{
ans[n, s] = numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 1) +
numberOfUniqueOutcomes(n - 1,
s - 2);
}
// Otherwise return the
// already calculated value
return ans[n,s];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string []args)
{
initialize();
int N = 5, S = 8;
Console.WriteLine(numberOfUniqueOutcomes(N, S));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkThon
输出:
15时间复杂度: O(N * S)
辅助空间: O(N * S)