给定一个加权有向图和图中的目标顶点,找到所有顶点到目标顶点的最短距离。
输入 :
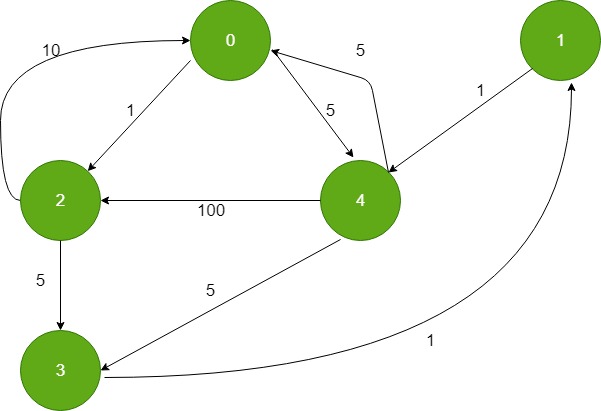
1
输出: 0 6 10 7 5
0到0的距离:0
0 与 1 的距离:1+5 = 6 (1->4->0)
0 与 2 的距离:10 (2->0)
0 与 3 的距离:1+1+5 = 7 (3->1->4->0)
0 到 4 的距离:5 (4->0)
处理方法:问题类似于Dijkstra的问题。思路是使用Dijkstra的算法。为了找到从所有顶点到给定目标顶点的最短距离,我们反转有向图的所有边,并在 dijkstra 算法中使用目标顶点作为源顶点。由于现在所有边都被反转,因此计算从目标顶点到所有其他顶点的最短距离类似于计算从所有顶点到给定目标顶点的最短距离。
反转边缘后,图形如下所示:
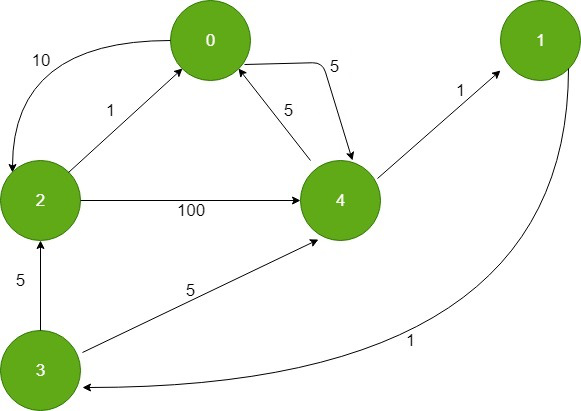
现在在 Dijkstra 算法中计算作为源顶点的目标顶点的最短距离。
下面是上述方法的实现:
CPP
// C++ implementation for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
// iPair ==> Integer Pair
typedef pair iPair;
// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices
// In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex
// and weight pair for every edge
list >* adj;
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an reverse edge to graph
void addEdgeRev(int u, int v, int w);
// prints shortest distance from all
// vertex to the given destination vertex
void shortestPath(int s);
};
// Allocates memory for adjacency list
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdgeRev(int u, int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u, w));
}
// Prints shortest distance from all vertex to
// the given destination vertex
void Graph::shortestPath(int dest)
{
// Create a priority queue to store vertices that
// are being preprocessed. This is weird syntax in C++.
// Refer below link for details of this syntax
// https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/implement-min-heap-using-stl/
priority_queue, greater > pq;
// Create a vector for distances and initialize all
// distances as infinite (INF)
vector dist(V, INF);
// Insert destination itself in priority queue and initialize
// its distance as 0.
pq.push(make_pair(0, dest));
dist[dest] = 0;
/* Looping till priority queue becomes empty (or all
distances are not finalized) */
while (!pq.empty()) {
// The first vertex in pair is the minimum distance
// vertex, extract it from priority queue.
// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
// has to be done this way to keep the vertices
// sorted distance (distance must be first item
// in pair)
int u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
// 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex
list >::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i) {
// Get vertex label and weight of current adjacent
// of u.
int v = (*i).first;
int weight = (*i).second;
// If there is shorted path to v through u.
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight) {
// Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pq.push(make_pair(dist[v], v));
}
}
}
// Print shortest distances stored in dist[]
printf("Destination Vertex Distance "
"from all vertex\n");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t\t %d\n", i, dist[i]);
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
int main()
{
// create the graph given in above figure
int V = 5;
Graph g(V);
// adding edges in reverse direction
g.addEdgeRev(0, 2, 1);
g.addEdgeRev(0, 4, 5);
g.addEdgeRev(1, 4, 1);
g.addEdgeRev(2, 0, 10);
g.addEdgeRev(2, 3, 5);
g.addEdgeRev(3, 1, 1);
g.addEdgeRev(4, 0, 5);
g.addEdgeRev(4, 2, 100);
g.addEdgeRev(4, 3, 5);
g.shortestPath(0);
return 0;
} Python3
from queue import PriorityQueue
INF = int(0x3f3f3f3f)
# This class represents a directed graph using
# adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V: int) -> None:
self.V = V
# No. of vertices
# In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex
# and weight pair for every edge
self.adj = [[] for _ in range(V)]
def addEdgeRev(self, u: int, v: int, w: int) -> None:
self.adj[v].append((u, w))
# Prints shortest distance from all vertex to
# the given destination vertex
def shortestPath(self, dest: int) -> None:
# Create a priority queue to store vertices that
# are being preprocessed. This is weird syntax in C++.
# Refer below link for details of this syntax
# https:# www.geeksforgeeks.org/implement-min-heap-using-stl/
pq = PriorityQueue()
# Create a vector for distances and initialize all
# distances as infinite (INF)
dist = [INF for _ in range(V)]
# Insert destination itself in priority queue and initialize
# its distance as 0.
pq.put((0, dest))
dist[dest] = 0
# Looping till priority queue becomes empty (or all
# distances are not finalized) */
while not pq.empty():
# The first vertex in pair is the minimum distance
# vertex, extract it from priority queue.
# vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
# has to be done this way to keep the vertices
# sorted distance (distance must be first item
# in pair)
u = pq.get()[1]
# 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex
for i in self.adj[u]:
# Get vertex label and weight of current adjacent
# of u.
v = i[0]
weight = i[1]
# If there is shorted path to v through u.
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight):
# Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight
pq.put((dist[v], v))
# Print shortest distances stored in dist[]
print("Destination Vertex Distance from all vertex")
for i in range(V):
print("{} \t\t {}".format(i, dist[i]))
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# create the graph given in above figure
V = 5
g = Graph(V)
# adding edges in reverse direction
g.addEdgeRev(0, 2, 1)
g.addEdgeRev(0, 4, 5)
g.addEdgeRev(1, 4, 1)
g.addEdgeRev(2, 0, 10)
g.addEdgeRev(2, 3, 5)
g.addEdgeRev(3, 1, 1)
g.addEdgeRev(4, 0, 5)
g.addEdgeRev(4, 2, 100)
g.addEdgeRev(4, 3, 5)
g.shortestPath(0)
# This code is contributed by sanjeev2552输出:
Destination Vertex Distance from all vertex
0 0
1 6
2 10
3 7
4 5 如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。