跳转指针算法是一种针对并行算法的设计技术,该并行算法对指针结构(例如数组或链表)进行操作。此算法通常用于确定有根树的森林的根。
在跳转指针算法中,我们对一棵树进行预处理,以便可以回答查询以找到树中任何节点的任何父级,时间复杂度为O(log n) 。
跳转指针算法最多将log 2 n个指针关联到树的每个顶点。这些指针之所以称为跳转指针,是因为它们向上跳转到树的根节点。对于处理树的任何节点,该算法存储一个长度为l的跳线数组,其中l = log2(depth(v)) 。该数组的第i个元素指向节点v的第2个父元素。这种数据结构帮助我们从任何给定节点跳到树的中间。当要求算法处理查询以找到树中任何节点的任何父节点时,我们将使用这些指针反复跳到树上。跳转次数最多为log n ,因此在树中找到任何节点的父节点的任何问题都可以用O(log n)时间复杂度来回答。
在跳转指针中,有一个从节点N到N的第j个父节点的指针,用于
j = 1、2、4、8,…,依此类推。因此,我们存储每个节点的第2个父节点。
跳转指针算法基本上适用于动态编程的方法,在该方法中,我们使用预先计算的结果来查找下一个结果。通过执行一些简单的计算,我们可以计算出一个数学公式,对于任何节点k, k的第2 j个父级等于k的2 j-1个父级的第2 j-1个父级。
该公式的简要说明在下面的“算法”部分中给出。
该算法最常见的用途是解决需要查找O(log n)时间复杂度的任何节点的祖先的查询。
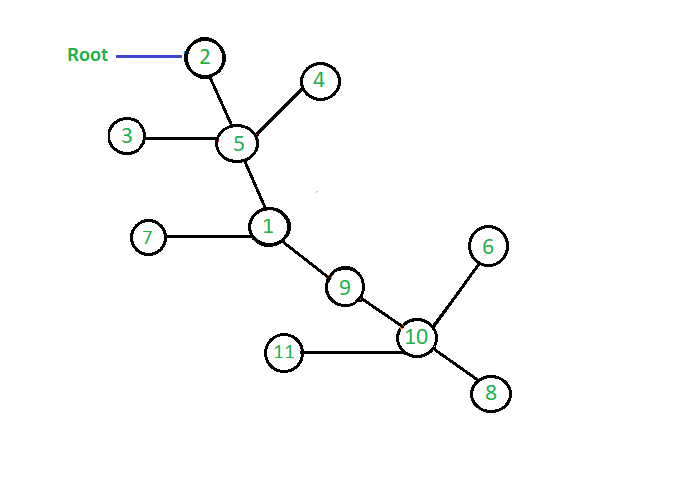
图来实现跳转指针算法:
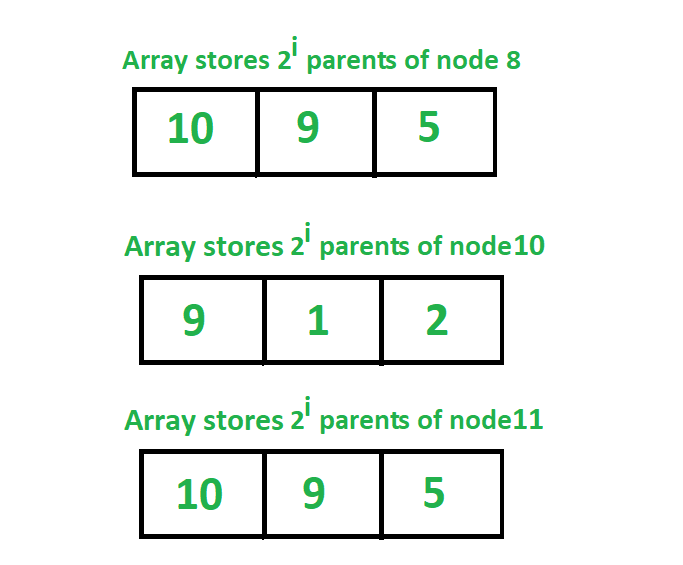
存储所有节点的第2个第i个父节点的跳转数组的表示形式:
例子:
Input: 0th parent of node 2
Output: 0th parent of node 2 is = 2
Input: 2th parent of node 4
Output: 2th parent of node 4 is = 2
Input: 3rd parent of node 8
Output: 3rd parent of node 8 is = 1
算法:
这是实现跳转指针算法以查找图中任何节点的任何父代的算法。我们使用动态规划确定跳跃矩阵。在这里,我们将根节点表示为R,并且最初假定根节点的父级为0,这意味着该节点没有父级。现在看曲线图和阵列在上述图中所示,我们可以很容易地理解上面的公式来确定2 i各自节点的父第。如果我们看一下值为8的节点,我们可以看到它的第2 0个父级是10 ,现在要找到它的第2 1个父级,我们看到它的第2 1个父级是值为2的节点的第2 0个父级,在这里10是8的2 0父级,这意味着节点8的2 1父级是8的2 0父级的2 0父级。类似地,我们还可以看到节点8的第2 2个父级是5,它是节点8的第2 1个父级的第2 1个父级,即节点2的第2 1个父级的值为9 。
因此,在这种方式,我们可以计算出跳指针数组的所有节点来存储他们的2个第i个父母。
下面是伪代码来计算跳转指针矩阵商店2 I中的所有树中的节点的父第。
jump[k][j] = it points 2^jth parent of k
= 2^j-1th parent of (2^j-1th parent of k)
= jump[jump[i][j-1][j-1]
实现:下面是实现上述算法的代码,以查找O(logn)时间复杂度的任何节点的任何父节点。
C++
// C++ program to implement Jump pointer algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
int R = 0;
// n -> it represent total number of nodes
// len -> it is the maximum length of array
// to hold parent of each node.
// In worst case, the highest value of
// parent a node can have is n-1.
// 2 ^ len <= n-1
// len = O(log2n)
int getLen(int n)
{
int len = (int)(log(n) / log(2)) + 1;
return len;
}
// jump represent 2D matrix to hold parent of node in jump matrix
// here we pass reference of 2D matrix so that the change made
// occur directly to the original matrix
// len is same as defined above
// n is total nodes in graph
void set_jump_pointer(vector >& jump,
int* node, int len, int n)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= len; j++)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
jump[node[i]][j] = jump[jump[node[i]][j - 1]][j - 1];
}
// c -> it represent child
// p -> it represent parent
// i -> it represent node number
// p=0 means the node is root node
// here also we pass reference of 2D matrix
// and depth vector so that the change made
// occur directly to the original matrix and original vector
void constructGraph(vector >& jump,
int* node, int* isNode, int c, int p, int i)
{
// enter the node in node array
// it stores all the nodes in the graph
node[i] = c;
// to confirm that no child node have 2 parents
if (isNode == 0) {
isNode = 1;
// make parent of x as y
jump[0] = p;
}
return;
}
// function to jump to Lth parent of any node
void jumpPointer(vector >& jump,
int* isNode, int x, int L)
{
int j = 0, n = x, k = L;
// to check if node is present in graph or not
if (isNode[x] == 0) {
cout << "Node is not present in graph " << endl;
return;
}
// in this loop we decrease the value of L by L/2 and
// increment j by 1 after each iteration, and check for set bit
// if we get set bit then we update x with jth parent of x
// as L becomes less than or equal to zero means
// we have jumped to Lth parent of node x
while (L > 0) {
// to check if last bit is 1 or not
if (L & 1)
x = jump[x][j];
// use of shift operator to make
// L = L/2 after every iteration
L = L >> 1;
j++;
}
cout << k << "th parent of node " << n
<< " is = " << x << endl;
return;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// n represent number of nodes
int n = 11;
// initialization of parent matrix
// suppose max range of a node is up to 1000
// if there are 1000 nodes than also
// length of jump matrix will not exceed 10
vector > jump(1000, vector(10));
// node array is used to store all nodes
int* node = new int[1000];
// isNode is an array to check whether
// a node is present in graph or not
int* isNode = new int[1000];
// memset function to initialize isNode array with 0
memset(isNode, 0, 1000 * sizeof(int));
// function to calculate len
// len -> it is the maximum length of
// array to hold parent of each node.
int len = getLen(n);
// R stores root node
R = 2;
// construction of graph
// here 0 represent that the node is root node
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 2, 0, 0);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 5, 2, 1);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 3, 5, 2);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 4, 5, 3);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 1, 5, 4);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 7, 1, 5);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 9, 1, 6);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 10, 9, 7);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 11, 10, 8);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 6, 10, 9);
constructGraph(jump, node, isNode, 8, 10, 10);
// function to pre compute jump matrix
set_jump_pointer(jump, node, len, n);
// query to jump to parent using jump pointers
// query to jump to 1st parent of node 2
jumpPointer(jump, isNode, 2, 0);
// query to jump to 2nd parent of node 4
jumpPointer(jump, isNode, 4, 2);
// query to jump to 3rd parent of node 8
jumpPointer(jump, isNode, 8, 3);
// query to jump to 5th parent of node 20
jumpPointer(jump, isNode, 20, 5);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program to implement
# Jump pointer algorithm
import math
# Initialization of parent matrix
# suppose max range of a node is
# up to 1000 if there are 1000 nodes
# than also length of jump matrix
# will not exceed 10
jump = [[0 for j in range(10)]
for i in range(1000)]
# Node array is used to store all nodes
node = [0 for i in range(1000)]
# isNode is an array to check whether
# a node is present in graph or not
isNode = [0 for i in range(1000)]
# n -> it represent total number of nodes
# len -> it is the maximum length of array
# to hold parent of each node.
# In worst case, the highest value of
# parent a node can have is n-1.
# 2 ^ len <= n-1
# len = O(log2n)
def getLen(n):
len = int((math.log(n)) //
(math.log(2))) + 1
return len
# jump represent 2D matrix to hold parent
# of node in jump matrix here we pass
# reference of 2D matrix so that the
# change made occur directly to the
# original matrix len is same as
# defined above n is total nodes
# in graph
def set_jump_pointer(len, n):
global jump, node
for j in range(1,len + 1):
for i in range(0, n):
jump[node[i]][j] = jump[jump[node[i]][j - 1]][j - 1]
# c -> it represent child
# p -> it represent parent
# i -> it represent node number
# p=0 means the node is root node
# here also we pass reference of
# 2D matrix and depth vector so
# that the change made occur
# directly to the original matrix
# and original vector
def constructGraph(c, p, i):
global jump, node, isNode
# Enter the node in node array
# it stores all the nodes in the graph
node[i] = c
# To confirm that no child node
# have 2 parents
if (isNode == 0):
isNode = 1
# Make parent of x as y
jump[0] = p
return
# function to jump to Lth parent
# of any node
def jumpPointer(x, L):
j = 0
n = x
k = L
global jump, isNode
# To check if node is present in
# graph or not
if (isNode[x] == 0):
print("Node is not present in graph ")
return
# In this loop we decrease the value
# of L by L/2 and increment j by 1
# after each iteration, and check
# for set bit if we get set bit
# then we update x with jth parent
# of x as L becomes less than or
# equal to zero means we have
# jumped to Lth parent of node x
while (L > 0):
# To check if last bit is 1 or not
if ((L & 1)!=0):
x = jump[x][j]
# Use of shift operator to make
# L = L/2 after every iteration
L = L >> 1
j += 1
print(str(k) + "th parent of node " +
str(n) + " is = " + str(x))
return
# Driver code
if __name__=="__main__":
# n represent number of nodes
n = 11
# Function to calculate len
# len -> it is the maximum length of
# array to hold parent of each node.
len = getLen(n)
# R stores root node
R = 2
# Construction of graph
# here 0 represent that
# the node is root node
constructGraph(2, 0, 0)
constructGraph(5, 2, 1)
constructGraph(3, 5, 2)
constructGraph(4, 5, 3)
constructGraph(1, 5, 4)
constructGraph(7, 1, 5)
constructGraph(9, 1, 6)
constructGraph(10, 9, 7)
constructGraph(11, 10, 8)
constructGraph(6, 10, 9)
constructGraph(8, 10, 10)
# Function to pre compute jump matrix
set_jump_pointer(len, n)
# Query to jump to parent using jump pointers
# query to jump to 1st parent of node 2
jumpPointer(2, 0)
# Query to jump to 2nd parent of node 4
jumpPointer(4, 2)
# Query to jump to 3rd parent of node 8
jumpPointer(8, 3)
# Query to jump to 5th parent of node 20
jumpPointer(20, 5)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_560th parent of node 2 is = 2
2th parent of node 4 is = 2
3th parent of node 8 is = 1
Node is not present in graph