给定大小为N的数组arr []和整数K。任务是找到子阵列的数量,以使每个子阵列具有恰好K个不同的元素。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {2, 1, 2, 1, 6}, K = 2
Output: 7
{2, 1}, {1, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 6}, {2, 1, 2},
{1, 2, 1} and {2, 1, 2, 1} are the only valid subarrays.
Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, K = 1
Output: 5
方法:直接对具有完全不同的K个整数的子数组进行计数是很困难的,但是要找到至多具有K个不同的整数的子数组的计数是容易的。因此,我们的想法是找到最多具有K个不同整数的子数组的数量,将其设为C(K) ,并将最多具有(K – 1)个不同整数的子数组的数量,设为C(K – 1)最后求出它们的差C(K)– C(K – 1) ,这是必需的答案。
通过滑动窗口技术,可以轻松计算最多包含K个不同元素的子数组的数量。这个想法是继续扩大窗口的右边界,直到窗口中的不同元素的数量小于或等于K,并且当窗口中的不同元素的数量超过K时,开始从左侧缩小窗口直到计数小于或等于K为止。同样对于每次扩展,将子数组计数为右–左+ 1 ,其中右和左是当前窗口的边界。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
#include Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
public class GfG {
// Function to return the count of subarrays
// with at most K distinct elements using
// the sliding window technique
private static int atMostK(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
// To store the result
int count = 0;
// Left boundary of window
int left = 0;
// Right boundary of window
int right = 0;
// Map to keep track of number of distinct
// elements in the current window
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
// Loop to calculate the count
while (right < n) {
// Calculating the frequency of each
// element in the current window
map.put(arr[right],
map.getOrDefault(arr[right], 0) + 1);
// Shrinking the window from left if the
// count of distinct elements exceeds K
while (map.size() > k) {
map.put(arr[left], map.get(arr[left]) - 1);
if (map.get(arr[left]) == 0)
map.remove(arr[left]);
left++;
}
// Adding the count of subarrays with at most
// K distinct elements in the current window
count += right - left + 1;
right++;
}
return count;
}
// Function to return the count of subarrays
// with exactly K distinct elements
private static int exactlyK(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
// Count of subarrays with exactly k distinct
// elements is equal to the difference of the
// count of subarrays with at most K distinct
// elements and the count of subararys with
// at most (K - 1) distinct elements
return (atMostK(arr, n, k)
- atMostK(arr, n, k - 1));
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 1, 2, 1, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
int k = 2;
System.out.print(exactlyK(arr, n, k));
}
} Python
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
# Function to return the count of subarrays
# with at most K distinct elements using
# the sliding window technique
def atMostK(arr, n, k):
# To store the result
count = 0
# Left boundary of window
left = 0
# Right boundary of window
right = 0
# Map to keep track of number of distinct
# elements in the current window
map = {}
# Loop to calculate the count
while(right < n):
if arr[right] not in map:
map[arr[right]] = 0
# Calculating the frequency of each
# element in the current window
map[arr[right]] += 1
# Shrinking the window from left if the
# count of distinct elements exceeds K
while(len(map) > k):
if arr[left] not in map:
map[arr[left]] = 0
map[arr[left]] -= 1
if map[arr[left]] == 0:
del map[arr[left]]
left += 1
# Adding the count of subarrays with at most
# K distinct elements in the current window
count += right - left + 1
right += 1
return count
# Function to return the count of subarrays
# with exactly K distinct elements
def exactlyK(arr, n, k):
# Count of subarrays with exactly k distinct
# elements is equal to the difference of the
# count of subarrays with at most K distinct
# elements and the count of subararys with
# at most (K - 1) distinct elements
return (atMostK(arr, n, k) -
atMostK(arr, n, k - 1))
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [2, 1, 2, 1, 6]
n = len(arr)
k = 2
print(exactlyK(arr, n, k))
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GfG {
// Function to return the count of subarrays
// with at most K distinct elements using
// the sliding window technique
private static int atMostK(int[] arr, int n, int k)
{
// To store the result
int count = 0;
// Left boundary of window
int left = 0;
// Right boundary of window
int right = 0;
// Map to keep track of number of distinct
// elements in the current window
Dictionary map
= new Dictionary();
// Loop to calculate the count
while (right < n) {
// Calculating the frequency of each
// element in the current window
if (map.ContainsKey(arr[right]))
map[arr[right]] = map[arr[right]] + 1;
else
map.Add(arr[right], 1);
// Shrinking the window from left if the
// count of distinct elements exceeds K
while (map.Count > k) {
if (map.ContainsKey(arr[left])) {
map[arr[left]] = map[arr[left]] - 1;
if (map[arr[left]] == 0)
map.Remove(arr[left]);
}
left++;
}
// Adding the count of subarrays with at most
// K distinct elements in the current window
count += right - left + 1;
right++;
}
return count;
}
// Function to return the count of subarrays
// with exactly K distinct elements
private static int exactlyK(int[] arr, int n, int k)
{
// Count of subarrays with exactly k distinct
// elements is equal to the difference of the
// count of subarrays with at most K distinct
// elements and the count of subararys with
// at most (K - 1) distinct elements
return (atMostK(arr, n, k)
- atMostK(arr, n, k - 1));
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 2, 1, 2, 1, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
int k = 2;
Console.Write(exactlyK(arr, n, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar C++
// C++ program to calculate number
// of subarrays with distinct elemnts of size k
#include
#include Java
// Java program to calculate number
// of subarrays with distinct elemnts of size k
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int subarraysWithKDistinct(int A[], int K)
{
// declare a map for the frequency
HashMap mapp = new HashMap<>();
int begin = 0, end = 0, prefix = 0, cnt = 0;
int res = 0;
// traverse the array
while (end < A.length)
{
// increase the frequency
if(mapp.containsKey(A[end]))
{
mapp.put(A[end], mapp.get(A[end]) + 1);
}
else
{
mapp.put(A[end], 1);
}
if (mapp.get(A[end]) == 1)
{
cnt++;
}
end++;
if (cnt > K)
{
if(mapp.containsKey(A[begin]))
{
mapp.put(A[begin], mapp.get(A[begin]) - 1);
}
else
{
mapp.put(A[begin], -1);
}
begin++;
cnt--;
prefix = 0;
}
// loop until mapp[A[begin]] > 1
while (mapp.get(A[begin]) > 1)
{
if(mapp.containsKey(A[begin]))
{
mapp.put(A[begin], mapp.get(A[begin]) - 1);
}
else
{
mapp.put(A[begin], -1);
}
begin++;
prefix++;
}
if (cnt == K)
{
res += prefix + 1;
}
}
// return the final count
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 1, 2, 1, 6 };
int k = 2;
// Function call
System.out.println(subarraysWithKDistinct(arr, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07 Python3
# Python3 program to calculate number of
# subarrays with distinct elemnts of size k
def subarraysWithKDistinct(A, K):
# Declare a map for the frequency
mapp = {}
begin, end, prefix, cnt = 0, 0, 0, 0
res = 0
# Traverse the array
while (end < len(A)):
# Increase the frequency
mapp[A[end]] = mapp.get(A[end], 0) + 1
if (mapp[A[end]] == 1):
cnt += 1
end += 1
if (cnt > K):
mapp[A[begin]] -= 1
begin += 1
cnt -= 1
prefix = 0
# Loop until mapp[A[begin]] > 1
while (mapp[A[begin]] > 1):
mapp[A[begin]] -= 1
begin += 1
prefix += 1
if (cnt == K):
res += prefix + 1
# Return the final count
return res
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [ 2, 1, 2, 1, 6 ]
k = 2
# Function call
print (subarraysWithKDistinct(arr, k))
# This code is contributed by Mohit kumarC#
// C# program to calculate number
// of subarrays with distinct elemnts of size k
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static int subarraysWithKDistinct(List A, int K)
{
// declare a map for the frequency
Dictionary mapp = new Dictionary();
int begin = 0, end = 0, prefix = 0, cnt = 0;
int res = 0;
// traverse the array
while (end < A.Count)
{
// increase the frequency
if(mapp.ContainsKey(A[end]))
{
mapp[A[end]]++;
}
else{
mapp[A[end]] = 1;
}
if (mapp[A[end]] == 1) {
cnt++;
}
end++;
if (cnt > K)
{
if(mapp.ContainsKey(A[begin]))
{
mapp[A[begin]]--;
}
else{
mapp[A[begin]] = -1;
}
begin++;
cnt--;
prefix = 0;
}
// loop until mapp[A[begin]] > 1
while (mapp[A[begin]] > 1)
{
mapp[A[begin]]--;
begin++;
prefix++;
}
if (cnt == K)
{
res += prefix + 1;
}
}
// return the final count
return res;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
List arr = new List(new int[] { 2, 1, 2, 1, 6 });
int k = 2;
// Function call
Console.Write(subarraysWithKDistinct(arr, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019 输出
7时间复杂度: O(N)
空间复杂度: O(N)
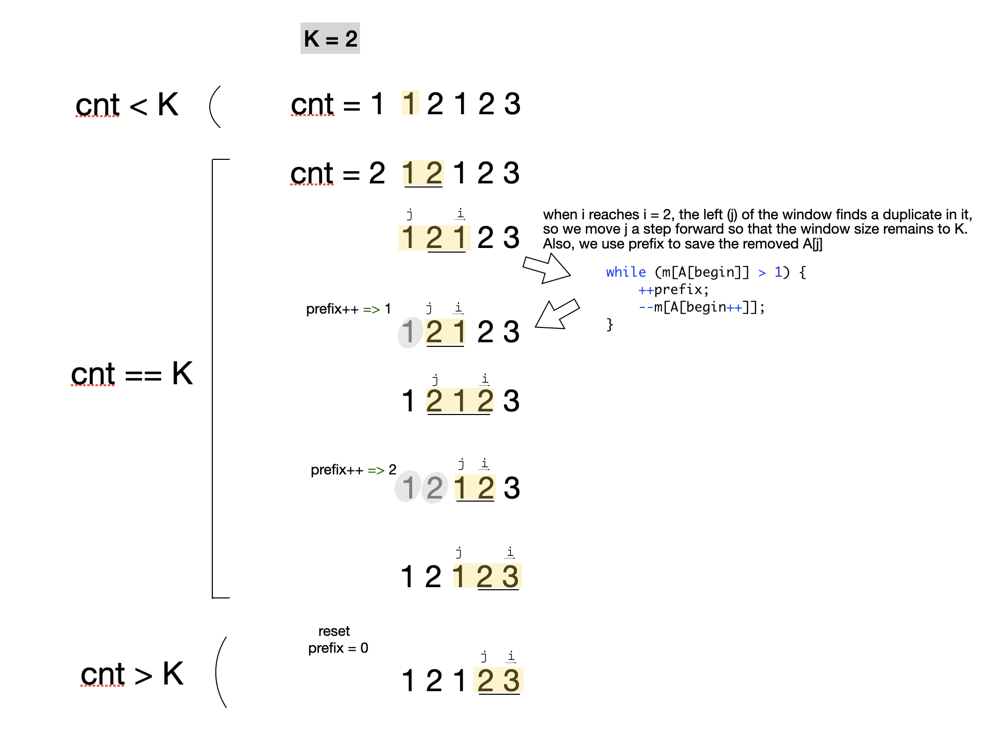
另一种方法:当您移动右光标时,请继续跟踪我们是否已达到K个不同整数的计数,如果是,则处理左光标,这是处理左光标的方式:
- 检查左光标指向的元素是否在窗口中重复,如果是,我们将其删除,并使用变量(例如前缀)记录我们已从窗口中删除了元素)。保持此过程,直到将窗口大小从减小到恰好为K。现在,我们可以将有效商品数组的数量计算为res + = prefix;
- 在处理完左光标和所有内容之后,外循环将继续,右光标将向前移动,然后窗口大小将超过K,我们可以简单地将窗口的最左边的元素删除并将前缀重置为0。然后继续。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to calculate number
// of subarrays with distinct elemnts of size k
#include
#include Java
// Java program to calculate number
// of subarrays with distinct elemnts of size k
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int subarraysWithKDistinct(int A[], int K)
{
// declare a map for the frequency
HashMap mapp = new HashMap<>();
int begin = 0, end = 0, prefix = 0, cnt = 0;
int res = 0;
// traverse the array
while (end < A.length)
{
// increase the frequency
if(mapp.containsKey(A[end]))
{
mapp.put(A[end], mapp.get(A[end]) + 1);
}
else
{
mapp.put(A[end], 1);
}
if (mapp.get(A[end]) == 1)
{
cnt++;
}
end++;
if (cnt > K)
{
if(mapp.containsKey(A[begin]))
{
mapp.put(A[begin], mapp.get(A[begin]) - 1);
}
else
{
mapp.put(A[begin], -1);
}
begin++;
cnt--;
prefix = 0;
}
// loop until mapp[A[begin]] > 1
while (mapp.get(A[begin]) > 1)
{
if(mapp.containsKey(A[begin]))
{
mapp.put(A[begin], mapp.get(A[begin]) - 1);
}
else
{
mapp.put(A[begin], -1);
}
begin++;
prefix++;
}
if (cnt == K)
{
res += prefix + 1;
}
}
// return the final count
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 1, 2, 1, 6 };
int k = 2;
// Function call
System.out.println(subarraysWithKDistinct(arr, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
Python3
# Python3 program to calculate number of
# subarrays with distinct elemnts of size k
def subarraysWithKDistinct(A, K):
# Declare a map for the frequency
mapp = {}
begin, end, prefix, cnt = 0, 0, 0, 0
res = 0
# Traverse the array
while (end < len(A)):
# Increase the frequency
mapp[A[end]] = mapp.get(A[end], 0) + 1
if (mapp[A[end]] == 1):
cnt += 1
end += 1
if (cnt > K):
mapp[A[begin]] -= 1
begin += 1
cnt -= 1
prefix = 0
# Loop until mapp[A[begin]] > 1
while (mapp[A[begin]] > 1):
mapp[A[begin]] -= 1
begin += 1
prefix += 1
if (cnt == K):
res += prefix + 1
# Return the final count
return res
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [ 2, 1, 2, 1, 6 ]
k = 2
# Function call
print (subarraysWithKDistinct(arr, k))
# This code is contributed by Mohit kumar
C#
// C# program to calculate number
// of subarrays with distinct elemnts of size k
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
static int subarraysWithKDistinct(List A, int K)
{
// declare a map for the frequency
Dictionary mapp = new Dictionary();
int begin = 0, end = 0, prefix = 0, cnt = 0;
int res = 0;
// traverse the array
while (end < A.Count)
{
// increase the frequency
if(mapp.ContainsKey(A[end]))
{
mapp[A[end]]++;
}
else{
mapp[A[end]] = 1;
}
if (mapp[A[end]] == 1) {
cnt++;
}
end++;
if (cnt > K)
{
if(mapp.ContainsKey(A[begin]))
{
mapp[A[begin]]--;
}
else{
mapp[A[begin]] = -1;
}
begin++;
cnt--;
prefix = 0;
}
// loop until mapp[A[begin]] > 1
while (mapp[A[begin]] > 1)
{
mapp[A[begin]]--;
begin++;
prefix++;
}
if (cnt == K)
{
res += prefix + 1;
}
}
// return the final count
return res;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
List arr = new List(new int[] { 2, 1, 2, 1, 6 });
int k = 2;
// Function call
Console.Write(subarraysWithKDistinct(arr, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019
输出
7