Graph 在 JavaScript 中的实现
在本文中,我们将在 JavaScript 中实现 Graph 数据结构。图是非线性数据结构。图G包含一组顶点V和一组边E 。图在计算机科学中有很多应用。
图基本上分为两大类:
- 有向图(有向图) ——边有方向的地方。
- 无向图——边不代表任何有向图
有多种表示图形的方法:-
- 邻接矩阵
- 邻接表
还有其他几种方法,例如关联矩阵等,但这两种是最常用的。有关邻接矩阵和列表的说明,请参阅图形及其表示。
在本文中,我们将使用邻接表来表示图,因为在大多数情况下,它比其他表示具有一定的优势。
现在让我们看一个 Graph 类的例子——
JavaScript
// create a graph class
class Graph {
// defining vertex array and
// adjacent list
constructor(noOfVertices)
{
this.noOfVertices = noOfVertices;
this.AdjList = new Map();
}
// functions to be implemented
// addVertex(v)
// addEdge(v, w)
// printGraph()
// bfs(v)
// dfs(v)
}JavaScript
// add vertex to the graph
addVertex(v)
{
// initialize the adjacent list with a
// null array
this.AdjList.set(v, []);
}JavaScript
// add edge to the graph
addEdge(v, w)
{
// get the list for vertex v and put the
// vertex w denoting edge between v and w
this.AdjList.get(v).push(w);
// Since graph is undirected,
// add an edge from w to v also
this.AdjList.get(w).push(v);
}JavaScript
// Prints the vertex and adjacency list
printGraph()
{
// get all the vertices
var get_keys = this.AdjList.keys();
// iterate over the vertices
for (var i of get_keys)
{
// great the corresponding adjacency list
// for the vertex
var get_values = this.AdjList.get(i);
var conc = "";
// iterate over the adjacency list
// concatenate the values into a string
for (var j of get_values)
conc += j + " ";
// print the vertex and its adjacency list
console.log(i + " -> " + conc);
}
}JavaScript
// Using the above implemented graph class
var g = new Graph(6);
var vertices = [ 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F' ];
// adding vertices
for (var i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
g.addVertex(vertices[i]);
}
// adding edges
g.addEdge('A', 'B');
g.addEdge('A', 'D');
g.addEdge('A', 'E');
g.addEdge('B', 'C');
g.addEdge('D', 'E');
g.addEdge('E', 'F');
g.addEdge('E', 'C');
g.addEdge('C', 'F');
// prints all vertex and
// its adjacency list
// A -> B D E
// B -> A C
// C -> B E F
// D -> A E
// E -> A D F C
// F -> E C
g.printGraph();JavaScript
// function to performs BFS
bfs(startingNode)
{
// create a visited object
var visited = {};
// Create an object for queue
var q = new Queue();
// add the starting node to the queue
visited[startingNode] = true;
q.enqueue(startingNode);
// loop until queue is empty
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// get the element from the queue
var getQueueElement = q.dequeue();
// passing the current vertex to callback function
console.log(getQueueElement);
// get the adjacent list for current vertex
var get_List = this.AdjList.get(getQueueElement);
// loop through the list and add the element to the
// queue if it is not processed yet
for (var i in get_List) {
var neigh = get_List[i];
if (!visited[neigh]) {
visited[neigh] = true;
q.enqueue(neigh);
}
}
}
}JavaScript
// prints
// BFS
// A B D E C F
console.log("BFS");
g.bfs('A');JavaScript
// Main DFS method
dfs(startingNode)
{
var visited = {};
this.DFSUtil(startingNode, visited);
}
// Recursive function which process and explore
// all the adjacent vertex of the vertex with which it is called
DFSUtil(vert, visited)
{
visited[vert] = true;
console.log(vert);
var get_neighbours = this.AdjList.get(vert);
for (var i in get_neighbours) {
var get_elem = get_neighbours[i];
if (!visited[get_elem])
this.DFSUtil(get_elem, visited);
}
}JavaScript
// prints
// DFS
// A B C E D F
console.log("DFS");
g.dfs('A');上面的例子展示了一个Graph类的框架。我们定义了两个私有变量,即noOfVertices来存储图中的顶点数和AdjList ,它存储特定顶点的邻接列表。我们使用 ES6 提供的Map Object 来实现邻接列表。地图的键包含一个顶点,值包含一个相邻节点的数组。
现在让我们实现函数来对图执行基本操作:
- addVertex(v) - 它将顶点v作为键添加到adjList并使用数组初始化其值。
JavaScript
// add vertex to the graph
addVertex(v)
{
// initialize the adjacent list with a
// null array
this.AdjList.set(v, []);
}
- addEdge(src, dest) - 它在src和dest之间添加一条边。
JavaScript
// add edge to the graph
addEdge(v, w)
{
// get the list for vertex v and put the
// vertex w denoting edge between v and w
this.AdjList.get(v).push(w);
// Since graph is undirected,
// add an edge from w to v also
this.AdjList.get(w).push(v);
}
- 为了添加边,我们获取对应src顶点的邻接表,并将dest添加到邻接表中。
- printGraph() - 它打印顶点及其邻接列表。
JavaScript
// Prints the vertex and adjacency list
printGraph()
{
// get all the vertices
var get_keys = this.AdjList.keys();
// iterate over the vertices
for (var i of get_keys)
{
// great the corresponding adjacency list
// for the vertex
var get_values = this.AdjList.get(i);
var conc = "";
// iterate over the adjacency list
// concatenate the values into a string
for (var j of get_values)
conc += j + " ";
// print the vertex and its adjacency list
console.log(i + " -> " + conc);
}
}
- 让我们看一个图表的例子
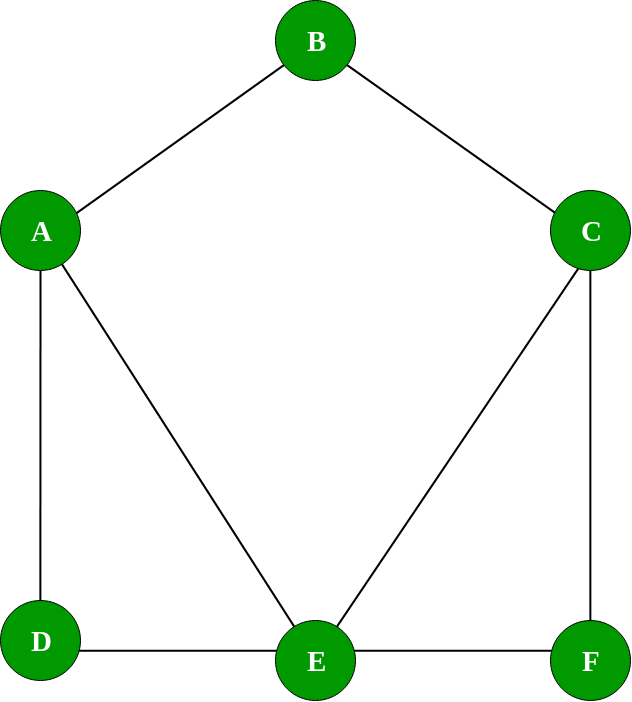
现在我们将使用图形类来实现如上所示的图形:
JavaScript
// Using the above implemented graph class
var g = new Graph(6);
var vertices = [ 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F' ];
// adding vertices
for (var i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) {
g.addVertex(vertices[i]);
}
// adding edges
g.addEdge('A', 'B');
g.addEdge('A', 'D');
g.addEdge('A', 'E');
g.addEdge('B', 'C');
g.addEdge('D', 'E');
g.addEdge('E', 'F');
g.addEdge('E', 'C');
g.addEdge('C', 'F');
// prints all vertex and
// its adjacency list
// A -> B D E
// B -> A C
// C -> B E F
// D -> A E
// E -> A D F C
// F -> E C
g.printGraph();
图遍历
我们将实现最常见的图遍历算法:
- 图的广度优先遍历
- 图的深度优先遍历
BFS和DFS的实现:
- bfs(startingNode) - 它从给定的startingNode执行广度优先搜索
JavaScript
// function to performs BFS
bfs(startingNode)
{
// create a visited object
var visited = {};
// Create an object for queue
var q = new Queue();
// add the starting node to the queue
visited[startingNode] = true;
q.enqueue(startingNode);
// loop until queue is empty
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// get the element from the queue
var getQueueElement = q.dequeue();
// passing the current vertex to callback function
console.log(getQueueElement);
// get the adjacent list for current vertex
var get_List = this.AdjList.get(getQueueElement);
// loop through the list and add the element to the
// queue if it is not processed yet
for (var i in get_List) {
var neigh = get_List[i];
if (!visited[neigh]) {
visited[neigh] = true;
q.enqueue(neigh);
}
}
}
}
- 在上述方法中,我们实现了 BFS 算法。 A Queue 用于保存未访问的节点
让我们使用上面的方法,沿着图遍历
JavaScript
// prints
// BFS
// A B D E C F
console.log("BFS");
g.bfs('A');
- 下图显示了示例图上的 BFS:
- dfs(startingNode) - 它在图上执行深度优先遍历
JavaScript
// Main DFS method
dfs(startingNode)
{
var visited = {};
this.DFSUtil(startingNode, visited);
}
// Recursive function which process and explore
// all the adjacent vertex of the vertex with which it is called
DFSUtil(vert, visited)
{
visited[vert] = true;
console.log(vert);
var get_neighbours = this.AdjList.get(vert);
for (var i in get_neighbours) {
var get_elem = get_neighbours[i];
if (!visited[get_elem])
this.DFSUtil(get_elem, visited);
}
}
- 在上面的例子中, dfs(startingNode)用来初始化一个visited数组, DFSutil(vert,visited)
包含 DFS 算法的实现
让我们用上面的方法随着图一起遍历
JavaScript
// prints
// DFS
// A B C E D F
console.log("DFS");
g.dfs('A');
- 下图显示了示例图上的 DFS