使用 BFS 查找从一个顶点到静止的路径
给定有向图的邻接表表示,任务是使用 BFS 找到从源到图中每个其他节点的路径。
例子:
Input:
Output:
0 <- 2
1 <- 0 <- 2
2
3 <- 1 <- 0 <- 2
4 <- 5 <- 2
5 <- 2
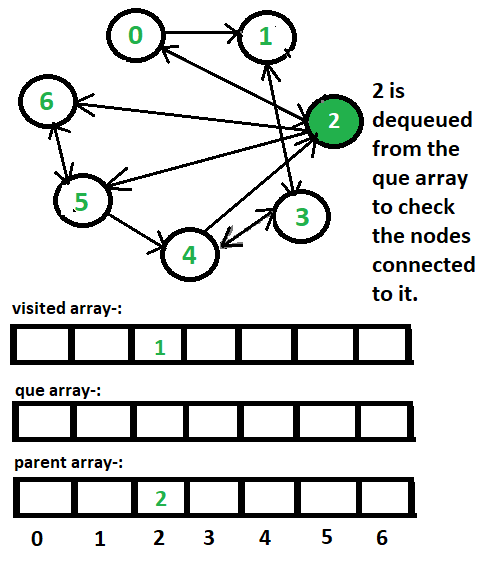
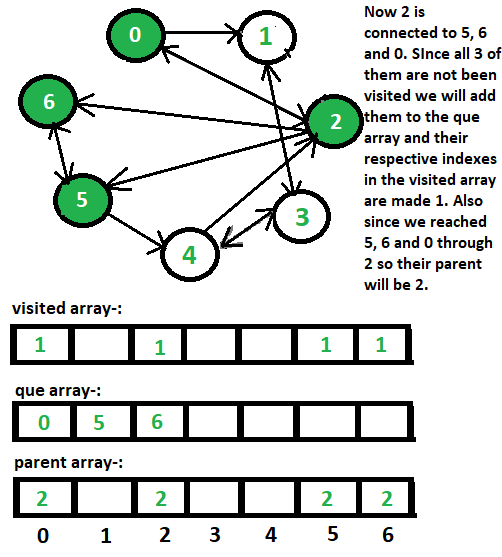
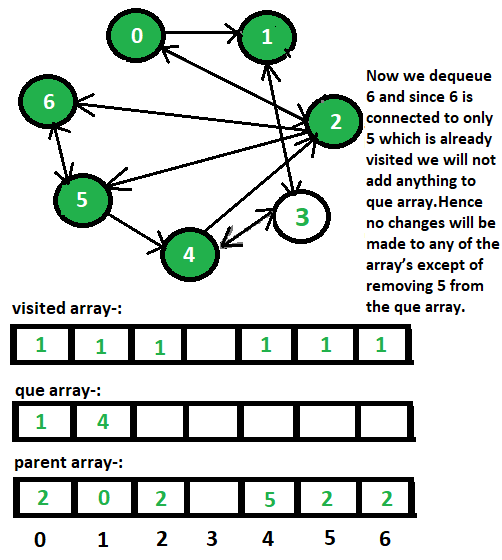
6 <- 2方法:如下图所示:
- que[]数组存储到达的顶点,只有当它没有被访问时,我们才会将一个顶点排入队列,并在考虑了它的所有子节点后将其出列。
- 为了区分节点是否已被访问,我们将在各个索引处的visited[]数组中放入1以表示它已被访问,如果在给定的索引处存在0 ,则表示它尚未被访问。
- 父数组是存储每个顶点的父节点。例如。如果 0 连接到 2,则 2 将是 0 的父节点,我们将 2 放在父数组中的索引 0 处。





下面是上述方法的实现:
C++14
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to print the path from
// source (s) to destination (d)
void print(vector parent, int s, int d)
{
// The while loop will stop only when the
// destination and the source node become equal
while (s != d)
{
// Print the destination and store the parent
// of the node in the destination since parent
// stores the node through which
// the current node has been reached
cout << d << " <- ";
d = parent[d];
}
cout << d << endl;
}
// Finding Path using BFS ALgorithm
void bfs(vector > adjList, int source, int n)
{
vector parent(n, 0);
vector que(n, 0);
int front = -1, rear = -1;
vector visited(n, 0);
//Arrays.fill(visited, 0);
visited = 1;
parent = source;
// To add any non visited node we will increment the rear
// and add that vertex to the end of the array (enqueuing)
que[++rear] = source;
int k;
// The loop will continue till the rear and front are equal
while (front != rear)
{
// Here Dequeuing is nothing but to increment the front int
k = que[++front];
//L list = adjList.get(k);
for (int j:adjList[k])
{
if (visited[j] == 0)
{
que[++rear] = j;
visited[j] = 1;
parent[j] = k;
}
}
}
// Print the path from source to every other node
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
print(parent, source, k);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Adjacency list representation of the graph
vector > adjList;
// Vertices 1 and 2 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 0
adjList.push_back({1, 2});
// Vertex 3 has an incoming edge
// from vertex 1
adjList.push_back({3});
// Vertices 0, 5 and 6 have an incoming
// edge from vertex 2
adjList.push_back({0, 5, 6});
// Vertices 1 and 4 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 3
adjList.push_back({1, 4});
// Vertices 2 and 3 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 4
adjList.push_back({2, 3});
// Vertices 4 and 6 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 5
adjList.push_back({4, 6});
// Vertex 5 has an incoming edge
// from vertex 6
adjList.push_back({5});
int n = adjList.size();
int source = 2;
bfs(adjList, source, n);
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29. Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class GFG
{
// Function to print the path from
// source (s) to destination (d)
static void print(int parent[], int s, int d)
{
// The while loop will stop only when the
// destination and the source node become equal
while (s != d) {
// Print the destination and store the parent
// of the node in the destination since parent
// stores the node through which
// the current node has been reached
System.out.print(d + " <- ");
d = parent[d];
}
System.out.println(d);
}
// Finding Path using BFS ALgorithm
static void bfs(List > adjList, int source, int n)
{
int parent[] = new int[n];
int que[] = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(parent, 0);
Arrays.fill(que, 0);
int front = -1, rear = -1;
int visited[] = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(visited, 0);
visited = 1;
parent = source;
// To add any non visited node we will increment the rear
// and add that vertex to the end of the array (enqueuing)
que[++rear] = source;
int k;
// The loop will continue till the rear and front are equal
while (front != rear) {
// Here Dequeuing is nothing but to increment the front int
k = que[++front];
List list = adjList.get(k);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
int j = list.get(i);
if (visited[j] == 0) {
que[++rear] = j;
visited[j] = 1;
parent[j] = k;
}
}
}
// Print the path from source to every other node
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
print(parent, source, k);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Adjacency list representation of the graph
List > adjList = new ArrayList<>();
// Vertices 1 and 2 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 0
List tmp = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertex 3 has an incoming edge from vertex 1
tmp = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(3));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertices 0, 5 and 6 have an incoming
// edge from vertex 2
tmp = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(0, 5, 6));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertices 1 and 4 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 3
tmp = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 4));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertices 2 and 3 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 4
tmp = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(2, 3));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertices 4 and 6 have an incoming edge
// from vertex 5
tmp = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(4, 6));
adjList.add(tmp);
// Vertex 5 has an incoming edge from vertex 6
tmp = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(5));
adjList.add(tmp);
int n = adjList.size();
int source = 2;
bfs(adjList, source, n);
}
} Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to print the path from
# src (s) to destination (d)
def printfunc(parent, s, d):
# The while loop will stop only when
# the destination and the src node
# become equal
while s != d:
# Print the destination and store
# the parent of the node in the
# destination since parent stores
# the node through which the current
# node has been reached
print(str(d) + " <-", end = " ")
d = parent[d]
print(d)
# Finding Path using BFS ALgorithm
def bfs(adjList, src, n):
parent = [0] * (n)
que = [0] * (n)
front, rear = -1, -1
visited = [0] * (n)
visited[src] = 1
parent[src] = src
# To add any non visited node we will
# increment the rear and add that vertex
# to the end of the array (enqueuing)
rear += 1
que[rear] = src
# The loop will continue till the rear
# and front are equal
while front != rear:
# Here Dequeuing is nothing but to
# increment the front int
front += 1
k = que[front]
List = adjList[k]
for i in range(0, len(List)):
j = List[i]
if visited[j] == 0:
rear += 1
que[rear] = j
visited[j] = 1
parent[j] = k
# Print the path from src to every
# other node
for k in range(0, n):
printfunc(parent, src, k)
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Adjacency list representation
# of the graph
adjList = []
# Vertices 1 and 2 have an incoming edge
# from vertex 0
adjList.append([1, 2])
# Vertex 3 has an incoming edge
# from vertex 1
adjList.append([3])
# Vertices 0, 5 and 6 have an incoming
# edge from vertex 2
adjList.append([0, 5, 6])
# Vertices 1 and 4 have an incoming edge
# from vertex 3
adjList.append([1, 4])
# Vertices 2 and 3 have an incoming edge
# from vertex 4
adjList.append([2, 3])
# Vertices 4 and 6 have an incoming edge
# from vertex 5
adjList.append([4, 6])
# Vertex 5 has an incoming edge
# from vertex 6
adjList.append([5])
n = len(adjList)
src = 2
bfs(adjList, src, n)
# This code is contributed by Rituraj JainJavascript
输出:
0 <- 2
1 <- 0 <- 2
2
3 <- 1 <- 0 <- 2
4 <- 5 <- 2
5 <- 2
6 <- 2时间复杂度:O(V + E),其中 V 和 E 分别是图中的顶点数和边数。
辅助空间:O(V + E)。