合并两个已排序的链表
编写一个 SortedMerge()函数,该函数接受两个列表,每个列表都按升序排序,然后将这两个列表合并为一个按升序排列的列表。 SortedMerge() 应该返回新列表。应该通过将前两个列表的节点拼接在一起来制作新列表。
例如如果第一个链表 a 是 5->10->15 而另一个链表 b 是 2->3->20,那么 SortedMerge() 应该返回一个指向合并链表 2-> 头节点的指针3->5->10->15->20。
有很多情况需要处理:a或b可能为空,在处理过程中a或b可能先用完,最后出现结果列表开始为空,构建的问题它在经历'a'和'b'时向上。
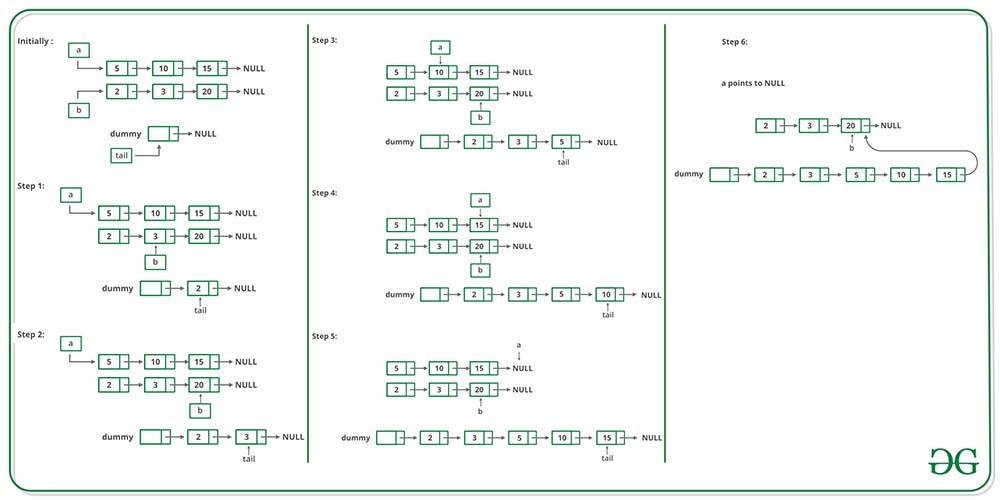
方法一(使用虚拟节点)
这里的策略使用一个临时的虚拟节点作为结果列表的开始。指针 Tail 始终指向结果列表中的最后一个节点,因此添加新节点很容易。
当结果列表为空时,虚拟节点为尾部提供初始指向的对象。这个虚拟节点是有效的,因为它只是临时的,并且在堆栈中分配。循环继续,从“a”或“b”中删除一个节点,并将其添加到尾部。什么时候
我们完成了,结果在 dummy.next 中。
下图是上述方法的试运行:
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
/* C++ program to merge two sorted linked lists */
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
/* pull off the front node of
the source and put it in dest */
void MoveNode(Node** destRef, Node** sourceRef);
/* Takes two lists sorted in increasing
order, and splices their nodes together
to make one big sorted list which
is returned. */
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b)
{
/* a dummy first node to hang the result on */
Node dummy;
/* tail points to the last result node */
Node* tail = &dummy;
/* so tail->next is the place to
add new nodes to the result. */
dummy.next = NULL;
while (1)
{
if (a == NULL)
{
/* if either list runs out, use the
other list */
tail->next = b;
break;
}
else if (b == NULL)
{
tail->next = a;
break;
}
if (a->data <= b->data)
MoveNode(&(tail->next), &a);
else
MoveNode(&(tail->next), &b);
tail = tail->next;
}
return(dummy.next);
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* MoveNode() function takes the
node from the front of the source,
and move it to the front of the dest.
It is an error to call this with the
source list empty.
Before calling MoveNode():
source == {1, 2, 3}
dest == {1, 2, 3}
After calling MoveNode():
source == {2, 3}
dest == {1, 1, 2, 3} */
void MoveNode(Node** destRef, Node** sourceRef)
{
/* the front source node */
Node* newNode = *sourceRef;
assert(newNode != NULL);
/* Advance the source pointer */
*sourceRef = newNode->next;
/* Link the old dest off the new node */
newNode->next = *destRef;
/* Move dest to point to the new node */
*destRef = newNode;
}
/* Function to insert a node at
the beginning of the linked list */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(Node *node)
{
while (node!=NULL)
{
cout<data<<" ";
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* res = NULL;
Node* a = NULL;
Node* b = NULL;
/* Let us create two sorted linked lists
to test the functions
Created lists, a: 5->10->15, b: 2->3->20 */
push(&a, 15);
push(&a, 10);
push(&a, 5);
push(&b, 20);
push(&b, 3);
push(&b, 2);
/* Remove duplicates from linked list */
res = SortedMerge(a, b);
cout << "Merged Linked List is: \n";
printList(res);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
/* C program to merge two sorted linked lists */
#include
#include
#include
/* Link list node */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* pull off the front node of the source and put it in dest */
void MoveNode(struct Node** destRef, struct Node** sourceRef);
/* Takes two lists sorted in increasing order, and splices
their nodes together to make one big sorted list which
is returned. */
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a, struct Node* b)
{
/* a dummy first node to hang the result on */
struct Node dummy;
/* tail points to the last result node */
struct Node* tail = &dummy;
/* so tail->next is the place to add new nodes
to the result. */
dummy.next = NULL;
while (1)
{
if (a == NULL)
{
/* if either list runs out, use the
other list */
tail->next = b;
break;
}
else if (b == NULL)
{
tail->next = a;
break;
}
if (a->data <= b->data)
MoveNode(&(tail->next), &a);
else
MoveNode(&(tail->next), &b);
tail = tail->next;
}
return(dummy.next);
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* MoveNode() function takes the node from the front of the
source, and move it to the front of the dest.
It is an error to call this with the source list empty.
Before calling MoveNode():
source == {1, 2, 3}
dest == {1, 2, 3}
After calling MoveNode():
source == {2, 3}
dest == {1, 1, 2, 3} */
void MoveNode(struct Node** destRef, struct Node** sourceRef)
{
/* the front source node */
struct Node* newNode = *sourceRef;
assert(newNode != NULL);
/* Advance the source pointer */
*sourceRef = newNode->next;
/* Link the old dest off the new node */
newNode->next = *destRef;
/* Move dest to point to the new node */
*destRef = newNode;
}
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the
linked list */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(struct Node *node)
{
while (node!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Drier program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* res = NULL;
struct Node* a = NULL;
struct Node* b = NULL;
/* Let us create two sorted linked lists to test
the functions
Created lists, a: 5->10->15, b: 2->3->20 */
push(&a, 15);
push(&a, 10);
push(&a, 5);
push(&b, 20);
push(&b, 3);
push(&b, 2);
/* Remove duplicates from linked list */
res = SortedMerge(a, b);
printf("Merged Linked List is: \n");
printList(res);
return 0;
} Java
/* Java program to merge two
sorted linked lists */
import java.util.*;
/* Link list node */
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {data = d;
next = null;}
}
class MergeLists
{
Node head;
/* Method to insert a node at
the end of the linked list */
public void addToTheLast(Node node)
{
if (head == null)
{
head = node;
}
else
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = node;
}
}
/* Method to print linked list */
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
/* Let us create two sorted linked
lists to test the methods
Created lists:
llist1: 5->10->15,
llist2: 2->3->20
*/
MergeLists llist1 = new MergeLists();
MergeLists llist2 = new MergeLists();
// Node head1 = new Node(5);
llist1.addToTheLast(new Node(5));
llist1.addToTheLast(new Node(10));
llist1.addToTheLast(new Node(15));
// Node head2 = new Node(2);
llist2.addToTheLast(new Node(2));
llist2.addToTheLast(new Node(3));
llist2.addToTheLast(new Node(20));
llist1.head = new Gfg().sortedMerge(llist1.head,
llist2.head);
llist1.printList();
}
}
class Gfg
{
/* Takes two lists sorted in
increasing order, and splices
their nodes together to make
one big sorted list which is
returned. */
Node sortedMerge(Node headA, Node headB)
{
/* a dummy first node to
hang the result on */
Node dummyNode = new Node(0);
/* tail points to the
last result node */
Node tail = dummyNode;
while(true)
{
/* if either list runs out,
use the other list */
if(headA == null)
{
tail.next = headB;
break;
}
if(headB == null)
{
tail.next = headA;
break;
}
/* Compare the data of the two
lists whichever lists' data is
smaller, append it into tail and
advance the head to the next Node
*/
if(headA.data <= headB.data)
{
tail.next = headA;
headA = headA.next;
}
else
{
tail.next = headB;
headB = headB.next;
}
/* Advance the tail */
tail = tail.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Shubhaw KumarPython3
""" Python program to merge two
sorted linked lists """
# Linked List Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Create & Handle List operations
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Method to display the list
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while temp:
print(temp.data, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
# Method to add element to list
def addToList(self, newData):
newNode = Node(newData)
if self.head is None:
self.head = newNode
return
last = self.head
while last.next:
last = last.next
last.next = newNode
# Function to merge the lists
# Takes two lists which are sorted
# joins them to get a single sorted list
def mergeLists(headA, headB):
# A dummy node to store the result
dummyNode = Node(0)
# Tail stores the last node
tail = dummyNode
while True:
# If any of the list gets completely empty
# directly join all the elements of the other list
if headA is None:
tail.next = headB
break
if headB is None:
tail.next = headA
break
# Compare the data of the lists and whichever is smaller is
# appended to the last of the merged list and the head is changed
if headA.data <= headB.data:
tail.next = headA
headA = headA.next
else:
tail.next = headB
headB = headB.next
# Advance the tail
tail = tail.next
# Returns the head of the merged list
return dummyNode.next
# Create 2 lists
listA = LinkedList()
listB = LinkedList()
# Add elements to the list in sorted order
listA.addToList(5)
listA.addToList(10)
listA.addToList(15)
listB.addToList(2)
listB.addToList(3)
listB.addToList(20)
# Call the merge function
listA.head = mergeLists(listA.head, listB.head)
# Display merged list
print("Merged Linked List is:")
listA.printList()
""" This code is contributed
by Debidutta Rath """C#
/* C# program to merge two
sorted linked lists */
using System;
/* Link list node */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
public class MergeLists
{
Node head;
/* Method to insert a node at
the end of the linked list */
public void addToTheLast(Node node)
{
if (head == null)
{
head = node;
}
else
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = node;
}
}
/* Method to print linked list */
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
/* Let us create two sorted linked
lists to test the methods
Created lists:
llist1: 5->10->15,
llist2: 2->3->20
*/
MergeLists llist1 = new MergeLists();
MergeLists llist2 = new MergeLists();
// Node head1 = new Node(5);
llist1.addToTheLast(new Node(5));
llist1.addToTheLast(new Node(10));
llist1.addToTheLast(new Node(15));
// Node head2 = new Node(2);
llist2.addToTheLast(new Node(2));
llist2.addToTheLast(new Node(3));
llist2.addToTheLast(new Node(20));
llist1.head = new Gfg().sortedMerge(llist1.head,
llist2.head);
llist1.printList();
}
}
public class Gfg
{
/* Takes two lists sorted in
increasing order, and splices
their nodes together to make
one big sorted list which is
returned. */
public Node sortedMerge(Node headA, Node headB)
{
/* a dummy first node to
hang the result on */
Node dummyNode = new Node(0);
/* tail points to the
last result node */
Node tail = dummyNode;
while(true)
{
/* if either list runs out,
use the other list */
if(headA == null)
{
tail.next = headB;
break;
}
if(headB == null)
{
tail.next = headA;
break;
}
/* Compare the data of the two
lists whichever lists' data is
smaller, append it into tail and
advance the head to the next Node
*/
if(headA.data <= headB.data)
{
tail.next = headA;
headA = headA.next;
}
else
{
tail.next = headB;
headB = headB.next;
}
/* Advance the tail */
tail = tail.next;
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
// This code is contributed 29AjayKumarJavascript
C++14
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b)
{
Node* result = NULL;
/* point to the last result pointer */
Node** lastPtrRef = &result;
while(1)
{
if (a == NULL)
{
*lastPtrRef = b;
break;
}
else if (b==NULL)
{
*lastPtrRef = a;
break;
}
if(a->data <= b->data)
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, &a);
}
else
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, &b);
}
/* tricky: advance to point to the next ".next" field */
lastPtrRef = &((*lastPtrRef)->next);
}
return(result);
}
//This code is contributed by rathbhupendraC
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a, struct Node* b)
{
struct Node* result = NULL;
/* point to the last result pointer */
struct Node** lastPtrRef = &result;
while(1)
{
if (a == NULL)
{
*lastPtrRef = b;
break;
}
else if (b==NULL)
{
*lastPtrRef = a;
break;
}
if(a->data <= b->data)
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, &a);
}
else
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, &b);
}
/* tricky: advance to point to the next ".next" field */
lastPtrRef = &((*lastPtrRef)->next);
}
return(result);
}Java
Node SortedMerge(Node a, Node b)
{
Node result = null;
/* point to the last result pointer */
Node lastPtrRef = result;
while(1)
{
if (a == null)
{
lastPtrRef = b;
break;
}
else if (b==null)
{
lastPtrRef = a;
break;
}
if(a.data <= b.data)
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, a);
}
else
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, b);
}
/* tricky: advance to point to the next ".next" field */
lastPtrRef = ((lastPtrRef).next);
}
return(result);
}
// This code contributed by umadevi9616C#
Node SortedMerge(Node a, Node b)
{
Node result = null;
// Point to the last result pointer
Node lastPtrRef = result;
while(1)
{
if (a == null)
{
lastPtrRef = b;
break;
}
else if (b == null)
{
lastPtrRef = a;
break;
}
if (a.data <= b.data)
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, a);
}
else
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, b);
}
// tricky: advance to point to
// the next ".next" field
lastPtrRef = ((lastPtrRef).next);
}
return(result);
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1Javascript
C++
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b)
{
Node* result = NULL;
/* Base cases */
if (a == NULL)
return(b);
else if (b == NULL)
return(a);
/* Pick either a or b, and recur */
if (a->data <= b->data)
{
result = a;
result->next = SortedMerge(a->next, b);
}
else
{
result = b;
result->next = SortedMerge(a, b->next);
}
return(result);
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendraC
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a, struct Node* b)
{
struct Node* result = NULL;
/* Base cases */
if (a == NULL)
return(b);
else if (b==NULL)
return(a);
/* Pick either a or b, and recur */
if (a->data <= b->data)
{
result = a;
result->next = SortedMerge(a->next, b);
}
else
{
result = b;
result->next = SortedMerge(a, b->next);
}
return(result);
}Java
class GFG
{
public Node SortedMerge(Node A, Node B)
{
if(A == null) return B;
if(B == null) return A;
if(A.data < B.data)
{
A.next = SortedMerge(A.next, B);
return A;
}
else
{
B.next = SortedMerge(A, B.next);
return B;
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Tuhin DasPython3
# Python3 program merge two sorted linked
# in third linked list using recursive.
# Node class
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Constructor to initialize the node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Method to print linked list
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while temp :
print(temp.data, end="->")
temp = temp.next
# Function to add of node at the end.
def append(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
last = self.head
while last.next:
last = last.next
last.next = new_node
# Function to merge two sorted linked list.
def mergeLists(head1, head2):
# create a temp node NULL
temp = None
# List1 is empty then return List2
if head1 is None:
return head2
# if List2 is empty then return List1
if head2 is None:
return head1
# If List1's data is smaller or
# equal to List2's data
if head1.data <= head2.data:
# assign temp to List1's data
temp = head1
# Again check List1's data is smaller or equal List2's
# data and call mergeLists function.
temp.next = mergeLists(head1.next, head2)
else:
# If List2's data is greater than or equal List1's
# data assign temp to head2
temp = head2
# Again check List2's data is greater or equal List's
# data and call mergeLists function.
temp.next = mergeLists(head1, head2.next)
# return the temp list.
return temp
# Driver Function
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create linked list :
# 10->20->30->40->50
list1 = LinkedList()
list1.append(10)
list1.append(20)
list1.append(30)
list1.append(40)
list1.append(50)
# Create linked list 2 :
# 5->15->18->35->60
list2 = LinkedList()
list2.append(5)
list2.append(15)
list2.append(18)
list2.append(35)
list2.append(60)
# Create linked list 3
list3 = LinkedList()
# Merging linked list 1 and linked list 2
# in linked list 3
list3.head = mergeLists(list1.head, list2.head)
print(" Merged Linked List is : ", end="")
list3.printList()
# This code is contributed by 'Shriaknt13'.C#
using System;
class GFG{
public Node sortedMerge(Node A, Node B)
{
// Base cases
if (A == null)
return B;
if (B == null)
return A;
// Pick either a or b, and recur
if (A.data < B.data)
{
A.next = sortedMerge(A.next, B);
return A;
}
else
{
B.next = sortedMerge(A, B.next);
return B;
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by hunter2000Javascript
C++
/*Given two sorted linked lists consisting of N and M nodes
respectively. The task is to merge both of the list
(in-place) and return head of the merged list.*/
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list Node */
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to reverse a given Linked List using Recursion
Node* reverseList(Node* head)
{
if (head->next == NULL)
return head;
Node* rest = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return rest;
}
// Given two non-empty linked lists 'a' and 'b'
Node* sortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b)
{
// Reverse Linked List 'a'
a = reverseList(a);
// Reverse Linked List 'b'
b = reverseList(b);
// Initialize head of resultant list
Node* head = NULL;
Node* temp;
// Traverse both lists while both of them
// have nodes.
while (a != NULL && b != NULL) {
// If a's current value is greater than or equal to
// b's current value.
if (a->key >= b->key) {
// Store next of current Node in first list
temp = a->next;
// Add 'a' at the front of resultant list
a->next = head;
// Make 'a' - head of the result list
head = a;
// Move ahead in first list
a = temp;
}
// If b's value is greater. Below steps are similar
// to above (Only 'a' is replaced with 'b')
else {
temp = b->next;
b->next = head;
head = b;
b = temp;
}
}
// If second list reached end, but first list has
// nodes. Add remaining nodes of first list at the
// beginning of result list
while (a != NULL) {
temp = a->next;
a->next = head;
head = a;
a = temp;
}
// If first list reached end, but second list has
// nodes. Add remaining nodes of second list at the
// beginning of result list
while (b != NULL) {
temp = b->next;
b->next = head;
head = b;
b = temp;
}
// Return the head of the result list
return head;
}
/* Function to print Nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(struct Node* Node)
{
while (Node != NULL) {
cout << Node->key << " ";
Node = Node->next;
}
}
/* Utility function to create a new node with
given key */
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* res = NULL;
/* Let us create two sorted linked lists to test
the above functions. Created lists shall be
a: 5->10->15->40
b: 2->3->20 */
Node* a = newNode(5);
a->next = newNode(10);
a->next->next = newNode(15);
a->next->next->next = newNode(40);
Node* b = newNode(2);
b->next = newNode(3);
b->next->next = newNode(20);
cout << "List A before merge: \n";
printList(a);
cout << "\nList B before merge: \n";
printList(b);
/* merge 2 sorted Linked Lists */
res = sortedMerge(a, b);
cout << "\nMerged Linked List is: \n";
printList(res);
return 0;
} 输出 :
Merged Linked List is:
2 3 5 10 15 20方法 2(使用本地引用)
该解决方案在结构上与上述非常相似,但它避免了使用虚拟节点。相反,它维护一个 struct node** 指针 lastPtrRef,该指针始终指向结果列表的最后一个指针。这解决了与虚拟节点相同的情况——在结果列表为空时处理它。如果您试图在其尾部构建一个列表,则可以使用虚拟节点或结构节点**“引用”策略(有关详细信息,请参阅第 1 节)。
C++14
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b)
{
Node* result = NULL;
/* point to the last result pointer */
Node** lastPtrRef = &result;
while(1)
{
if (a == NULL)
{
*lastPtrRef = b;
break;
}
else if (b==NULL)
{
*lastPtrRef = a;
break;
}
if(a->data <= b->data)
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, &a);
}
else
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, &b);
}
/* tricky: advance to point to the next ".next" field */
lastPtrRef = &((*lastPtrRef)->next);
}
return(result);
}
//This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a, struct Node* b)
{
struct Node* result = NULL;
/* point to the last result pointer */
struct Node** lastPtrRef = &result;
while(1)
{
if (a == NULL)
{
*lastPtrRef = b;
break;
}
else if (b==NULL)
{
*lastPtrRef = a;
break;
}
if(a->data <= b->data)
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, &a);
}
else
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, &b);
}
/* tricky: advance to point to the next ".next" field */
lastPtrRef = &((*lastPtrRef)->next);
}
return(result);
}
Java
Node SortedMerge(Node a, Node b)
{
Node result = null;
/* point to the last result pointer */
Node lastPtrRef = result;
while(1)
{
if (a == null)
{
lastPtrRef = b;
break;
}
else if (b==null)
{
lastPtrRef = a;
break;
}
if(a.data <= b.data)
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, a);
}
else
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, b);
}
/* tricky: advance to point to the next ".next" field */
lastPtrRef = ((lastPtrRef).next);
}
return(result);
}
// This code contributed by umadevi9616
C#
Node SortedMerge(Node a, Node b)
{
Node result = null;
// Point to the last result pointer
Node lastPtrRef = result;
while(1)
{
if (a == null)
{
lastPtrRef = b;
break;
}
else if (b == null)
{
lastPtrRef = a;
break;
}
if (a.data <= b.data)
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, a);
}
else
{
MoveNode(lastPtrRef, b);
}
// tricky: advance to point to
// the next ".next" field
lastPtrRef = ((lastPtrRef).next);
}
return(result);
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
方法三(使用递归)
合并是那些很好的递归问题之一,其中递归解决方案代码比迭代代码更清晰。但是,您可能不想将递归版本用于生产代码,因为它将使用与列表长度成正比的堆栈空间。
C++
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b)
{
Node* result = NULL;
/* Base cases */
if (a == NULL)
return(b);
else if (b == NULL)
return(a);
/* Pick either a or b, and recur */
if (a->data <= b->data)
{
result = a;
result->next = SortedMerge(a->next, b);
}
else
{
result = b;
result->next = SortedMerge(a, b->next);
}
return(result);
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a, struct Node* b)
{
struct Node* result = NULL;
/* Base cases */
if (a == NULL)
return(b);
else if (b==NULL)
return(a);
/* Pick either a or b, and recur */
if (a->data <= b->data)
{
result = a;
result->next = SortedMerge(a->next, b);
}
else
{
result = b;
result->next = SortedMerge(a, b->next);
}
return(result);
}
Java
class GFG
{
public Node SortedMerge(Node A, Node B)
{
if(A == null) return B;
if(B == null) return A;
if(A.data < B.data)
{
A.next = SortedMerge(A.next, B);
return A;
}
else
{
B.next = SortedMerge(A, B.next);
return B;
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Tuhin Das
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program merge two sorted linked
# in third linked list using recursive.
# Node class
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Constructor to initialize the node object
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Method to print linked list
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while temp :
print(temp.data, end="->")
temp = temp.next
# Function to add of node at the end.
def append(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
last = self.head
while last.next:
last = last.next
last.next = new_node
# Function to merge two sorted linked list.
def mergeLists(head1, head2):
# create a temp node NULL
temp = None
# List1 is empty then return List2
if head1 is None:
return head2
# if List2 is empty then return List1
if head2 is None:
return head1
# If List1's data is smaller or
# equal to List2's data
if head1.data <= head2.data:
# assign temp to List1's data
temp = head1
# Again check List1's data is smaller or equal List2's
# data and call mergeLists function.
temp.next = mergeLists(head1.next, head2)
else:
# If List2's data is greater than or equal List1's
# data assign temp to head2
temp = head2
# Again check List2's data is greater or equal List's
# data and call mergeLists function.
temp.next = mergeLists(head1, head2.next)
# return the temp list.
return temp
# Driver Function
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create linked list :
# 10->20->30->40->50
list1 = LinkedList()
list1.append(10)
list1.append(20)
list1.append(30)
list1.append(40)
list1.append(50)
# Create linked list 2 :
# 5->15->18->35->60
list2 = LinkedList()
list2.append(5)
list2.append(15)
list2.append(18)
list2.append(35)
list2.append(60)
# Create linked list 3
list3 = LinkedList()
# Merging linked list 1 and linked list 2
# in linked list 3
list3.head = mergeLists(list1.head, list2.head)
print(" Merged Linked List is : ", end="")
list3.printList()
# This code is contributed by 'Shriaknt13'.
C#
using System;
class GFG{
public Node sortedMerge(Node A, Node B)
{
// Base cases
if (A == null)
return B;
if (B == null)
return A;
// Pick either a or b, and recur
if (A.data < B.data)
{
A.next = sortedMerge(A.next, B);
return A;
}
else
{
B.next = sortedMerge(A, B.next);
return B;
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by hunter2000
Javascript
时间复杂度:因为我们完全遍历了两个列表。因此,时间复杂度为O(m+n) ,其中 m 和 n 是要合并的两个列表的长度。
方法 4(反转列表)
这个想法包括首先反转给定的列表,反转后,遍历两个列表直到最后,然后比较两个列表的节点,并在结果列表的开头插入具有较大值的节点。通过这种方式,我们将按递增顺序获得结果列表。
1) Initialize result list as empty: head = NULL.
2) Let 'a' and 'b' be the heads of first and second list respectively.
3) Reverse both the lists.
4) While (a != NULL and b != NULL)
a) Find the larger of two (Current 'a' and 'b')
b) Insert the larger value of node at the front of result list.
c) Move ahead in the list of larger node.
5) If 'b' becomes NULL before 'a', insert all nodes of 'a'
into result list at the beginning.
6) If 'a' becomes NULL before 'b', insert all nodes of 'b'
into result list at the beginning. 下面是上述解决方案的实现。
C++
/*Given two sorted linked lists consisting of N and M nodes
respectively. The task is to merge both of the list
(in-place) and return head of the merged list.*/
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list Node */
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to reverse a given Linked List using Recursion
Node* reverseList(Node* head)
{
if (head->next == NULL)
return head;
Node* rest = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return rest;
}
// Given two non-empty linked lists 'a' and 'b'
Node* sortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b)
{
// Reverse Linked List 'a'
a = reverseList(a);
// Reverse Linked List 'b'
b = reverseList(b);
// Initialize head of resultant list
Node* head = NULL;
Node* temp;
// Traverse both lists while both of them
// have nodes.
while (a != NULL && b != NULL) {
// If a's current value is greater than or equal to
// b's current value.
if (a->key >= b->key) {
// Store next of current Node in first list
temp = a->next;
// Add 'a' at the front of resultant list
a->next = head;
// Make 'a' - head of the result list
head = a;
// Move ahead in first list
a = temp;
}
// If b's value is greater. Below steps are similar
// to above (Only 'a' is replaced with 'b')
else {
temp = b->next;
b->next = head;
head = b;
b = temp;
}
}
// If second list reached end, but first list has
// nodes. Add remaining nodes of first list at the
// beginning of result list
while (a != NULL) {
temp = a->next;
a->next = head;
head = a;
a = temp;
}
// If first list reached end, but second list has
// nodes. Add remaining nodes of second list at the
// beginning of result list
while (b != NULL) {
temp = b->next;
b->next = head;
head = b;
b = temp;
}
// Return the head of the result list
return head;
}
/* Function to print Nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(struct Node* Node)
{
while (Node != NULL) {
cout << Node->key << " ";
Node = Node->next;
}
}
/* Utility function to create a new node with
given key */
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* res = NULL;
/* Let us create two sorted linked lists to test
the above functions. Created lists shall be
a: 5->10->15->40
b: 2->3->20 */
Node* a = newNode(5);
a->next = newNode(10);
a->next->next = newNode(15);
a->next->next->next = newNode(40);
Node* b = newNode(2);
b->next = newNode(3);
b->next->next = newNode(20);
cout << "List A before merge: \n";
printList(a);
cout << "\nList B before merge: \n";
printList(b);
/* merge 2 sorted Linked Lists */
res = sortedMerge(a, b);
cout << "\nMerged Linked List is: \n";
printList(res);
return 0;
}
输出:
List A before merge:
5 10 15 40
List B before merge:
2 3 20
Merged Linked List is:
2 3 5 10 15 20 40 时间复杂度:因为我们完全遍历了两个列表。因此,时间复杂度为 O(m+n),其中 m 和 n 是要合并的两个列表的长度。
该方法由Mehul Mathur(mathurmehul01)贡献。
这个想法类似于这篇文章。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。