毫升 |使用 KNN 和交叉验证进行 Kaggle 威斯康星乳腺癌诊断
数据集:
它由来自 UCI 机器学习存储库的 Kaggle 在其挑战之一中提供。
https://www.kaggle.com/uciml/breast-cancer-wisconsin-data。它是患有恶性肿瘤和良性肿瘤的乳腺癌患者的数据集。
K-最近邻算法用于预测患者是否患有癌症(恶性肿瘤)或没有(良性肿瘤)。
用于分类的 KNN 算法的实现。
代码:导入库
# performing linear algebra
import numpy as np
# data processing
import pandas as pd
# visualisation
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
代码:加载数据集
df = pd.read_csv("..\\breast-cancer-wisconsin-data\\data.csv")
print (data.head)
输出 : 
代码:数据信息
df.info()
输出 :
RangeIndex: 569 entries, 0 to 568
Data columns (total 33 columns):
id 569 non-null int64
diagnosis 569 non-null object
radius_mean 569 non-null float64
texture_mean 569 non-null float64
perimeter_mean 569 non-null float64
area_mean 569 non-null float64
smoothness_mean 569 non-null float64
compactness_mean 569 non-null float64
concavity_mean 569 non-null float64
concave points_mean 569 non-null float64
symmetry_mean 569 non-null float64
fractal_dimension_mean 569 non-null float64
radius_se 569 non-null float64
texture_se 569 non-null float64
perimeter_se 569 non-null float64
area_se 569 non-null float64
smoothness_se 569 non-null float64
compactness_se 569 non-null float64
concavity_se 569 non-null float64
concave points_se 569 non-null float64
symmetry_se 569 non-null float64
fractal_dimension_se 569 non-null float64
radius_worst 569 non-null float64
texture_worst 569 non-null float64
perimeter_worst 569 non-null float64
area_worst 569 non-null float64
smoothness_worst 569 non-null float64
compactness_worst 569 non-null float64
concavity_worst 569 non-null float64
concave points_worst 569 non-null float64
symmetry_worst 569 non-null float64
fractal_dimension_worst 569 non-null float64
Unnamed: 32 0 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(31), int64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 146.8+ KB
代码:我们正在删除列 - 'id' 和 'Unnamed: 32' 因为它们在预测中没有作用
df.drop(['Unnamed: 32', 'id'], axis = 1)
print(df.shape)
输出:
(569, 31)代码:将 M 和 B 的诊断值转换为 M(恶性)= 1 和 B(良性)= 0 的数值
def diagnosis_value(diagnosis):
if diagnosis == 'M':
return 1
else:
return 0
df['diagnosis'] = df['diagnosis'].apply(diagnosis_value)
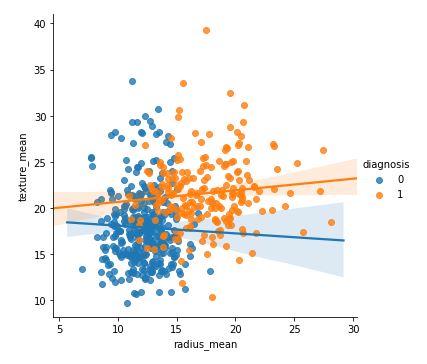
代码 :
sns.lmplot(x = 'radius_mean', y = 'texture_mean', hue = 'diagnosis', data = df)
输出:
代码 :
sns.lmplot(x ='smoothness_mean', y = 'compactness_mean',
data = df, hue = 'diagnosis')
输出: 
代码:输入和输出数据
X = np.array(df.iloc[:, 1:])
y = np.array(df['diagnosis'])
代码:将数据拆分为训练和测试
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size = 0.33, random_state = 42)
代码:使用 Sklearn
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = 13)
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
输出:
KNeighborsClassifier(algorithm='auto', leaf_size=30,
metric='minkowski', metric_params=None,
n_jobs=None, n_neighbors=13, p=2,
weights='uniform')
代码:预测分数
knn.score(X_test, y_test)
输出:
0.9627659574468085
代码:执行交叉验证
neighbors = []
cv_scores = []
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
# perform 10 fold cross validation
for k in range(1, 51, 2):
neighbors.append(k)
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors = k)
scores = cross_val_score(
knn, X_train, y_train, cv = 10, scoring = 'accuracy')
cv_scores.append(scores.mean())
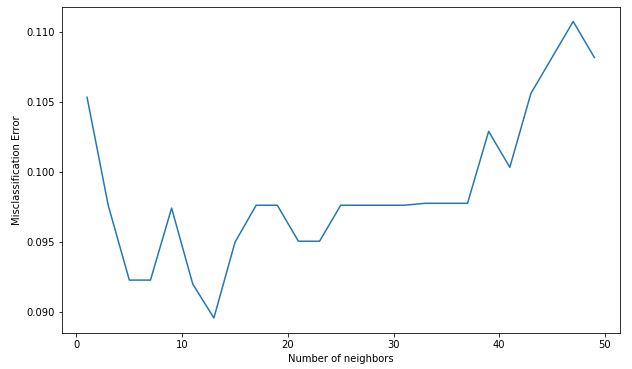
代码:误分类误差与 k
MSE = [1-x for x in cv_scores]
# determining the best k
optimal_k = neighbors[MSE.index(min(MSE))]
print('The optimal number of neighbors is % d ' % optimal_k)
# plot misclassification error versus k
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 6))
plt.plot(neighbors, MSE)
plt.xlabel('Number of neighbors')
plt.ylabel('Misclassification Error')
plt.show()
输出:
The optimal number of neighbors is 13