给定一棵树,该树具有最初没有颜色的N个节点和大小为N的数组color [] ,它们表示在着色过程之后每个节点的颜色。任务是使用尽可能少的步骤将树着色为给定的颜色。在每个步骤中,可以选择一个顶点v和一个颜色x ,然后用颜色x为v的子树中的所有顶点(包括v本身)着色。请注意,根是顶点编号1。
例子:
Input: color[] = { 1, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1}
Output: 4
Color the sub-tree rooted at node 1 with color 1.
Then all the vertices have colors 1.
Now, color the sub-tree rooted at 3 with color 2.
Finally, color the sub-trees rooted at 5 and 6 with colors 3 and 1 respectively.
Input: color[] = { 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 3}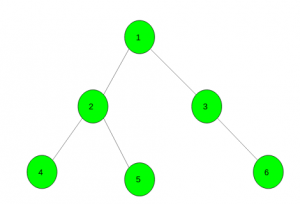
Output: 3
方法:在顶点1调用DFS函数,并最初将答案保持为零。只要子节点和父节点的颜色不同,就增加答案。
请参阅下面的代码以获得更好的理解。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// To store the required answer
int ans = 0;
// To store the graph
vector gr[100005];
// Function to add edges
void Add_Edge(int u, int v)
{
gr[u].push_back(v);
gr[v].push_back(u);
}
// Dfs function
void dfs(int child, int par, int color[])
{
// When there is difference in colors
if (color[child] != color[par])
ans++;
// For all it's child nodes
for (auto it : gr[child]) {
if (it == par)
continue;
dfs(it, child, color);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Here zero is for parent of node 1
int color[] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 3 };
// Adding edges in the graph
Add_Edge(1, 2);
Add_Edge(1, 3);
Add_Edge(2, 4);
Add_Edge(2, 5);
Add_Edge(3, 6);
// Dfs call
dfs(1, 0, color);
// Required answer
cout << ans;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// To store the required answer
static int ans = 0;
// To store the graph
static Vector> gr = new Vector>();
// Function to add edges
static void Add_Edge(int u, int v)
{
gr.get(u).add(v);
gr.get(v).add(u);
}
// Dfs function
static void dfs(int child, int par, int color[])
{
// When there is difference in colors
if (color[child] != color[par])
ans++;
// For all it's child nodes
for (int i = 0; i < gr.get(child).size(); i++)
{
if (gr.get(child).get(i) == par)
continue;
dfs(gr.get(child).get(i), child, color);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
for(int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
gr.add(new Vector());
// Here zero is for parent of node 1
int color[] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 3 };
// Adding edges in the graph
Add_Edge(1, 2);
Add_Edge(1, 3);
Add_Edge(2, 4);
Add_Edge(2, 5);
Add_Edge(3, 6);
// Dfs call
dfs(1, 0, color);
// Required answer
System.out.println( ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# To store the required answer
ans = 0
# To store the graph
gr = [[] for i in range(100005)]
# Function to add edges
def Add_Edge(u, v):
gr[u].append(v)
gr[v].append(u)
# Dfs function
def dfs(child, par, color):
global ans
# When there is difference in colors
if (color[child] != color[par]):
ans += 1
# For all it's child nodes
for it in gr[child]:
if (it == par):
continue
dfs(it, child, color)
# Driver code
# Here zero is for parent of node 1
color = [0, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 3]
# Adding edges in the graph
Add_Edge(1, 2)
Add_Edge(1, 3)
Add_Edge(2, 4)
Add_Edge(2, 5)
Add_Edge(3, 6)
# Dfs call
dfs(1, 0, color)
# Required answer
print(ans)
# This code is contributed
# by mohit kumarC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// To store the required answer
static int ans = 0;
// To store the graph
static List> gr = new List>();
// Function to add edges
static void Add_Edge(int u, int v)
{
gr[u].Add(v);
gr[v].Add(u);
}
// Dfs function
static void dfs(int child, int par, int []color)
{
// When there is difference in colors
if (color[child] != color[par])
ans++;
// For all it's child nodes
for (int i = 0; i < gr[child].Count; i++)
{
if (gr[child][i] == par)
continue;
dfs(gr[child][i], child, color);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
for(int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
gr.Add(new List());
// Here zero is for parent of node 1
int []color = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 3 };
// Adding edges in the graph
Add_Edge(1, 2);
Add_Edge(1, 3);
Add_Edge(2, 4);
Add_Edge(2, 5);
Add_Edge(3, 6);
// Dfs call
dfs(1, 0, color);
// Required answer
Console.WriteLine( ans);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar 输出:
3