从 Excel 工作表中提取内容的Java程序
电子表格是像数据一样表示表格的更简单方法,并且可以以表格格式提供数据的可视化表示。在本文中,让我们看看如何通过Java提取 Excel 工作表的内容。这里出现了两种情况,在程序中是否考虑了 Maven。讨论它们是更好地理解程序的先决条件。
Apache POI API 基础知识在继续之前至关重要,因此在使用 Apache POI 时需要两个主要前缀如下:
- HSSF:表示该 API 用于处理 Excel 2003 及更早版本。
- XSSF:表示 API 用于 Excel 2007 及更高版本。
以下4个接口很重要,必须经过
- 工作簿:Excel 工作簿的高级表示。 HSSFWorkbook 和 XSSFWorkbook。
- 工作表:Excel 工作表的高级表示。典型的实现类是 HSSFSheet和 XSSFSheet 。
- 行:电子表格中行的高级表示。 HSSFRow 和 XSSFRow 是两个具体的类。
- 单元格:一行中一个单元格的高级表示。 HSSFCell和XSSFCell是典型的实现类。
案例一: Maven Java项目,依赖如下
- 所有 Maven 项目都将 pom.xml 作为主文件。
- 在那里我们需要添加依赖项。
- pom.xml文件内容 Excel 格式确实有所不同,如下所示:
- 建议指定最新版本。 (这里使用的Maven项目示例是3.11)
对于 Excel 2003 格式
org.apache.poi
poi
VERSION
对于 Excel 2007 格式
org.apache.poi
poi-ooxml
VERSION
案例 2:非 Maven Java项目。
为了满足要求,迫切需要在构建路径中添加 jar 文件以提取内容。为此,请下载最新版本的 Apache POI 库。
从中提取内容
Excel 2003 格式
poi-VERSION.jar is enough.Excel 2007 格式:
poi-ooxml-VERSION.jar
poi-ooxml-schemas-VERSION.jar
xmlbeans-VERSION.jar过程:使用带有示例的 Apache POI 从 Excel 文件中读取。目标是从给定的 Excel 文件中读取内容,并在“输出”窗口中显示 Excel 文件的内容。
第 1 步:这里我们使用 POJO 类,它的字段数与附加的 Excel 文件中给出的字段数相同。 Excel 文件有 3 列,因此 POJO 类中有 3 个字段。示例 Excel 文件内容如下所示。为这些类型的操作使用 POJO(Plain old Java object)类总是更好。由于有 3 个列值并且详细信息与员工相关,因此让我们创建一个员工类。
示例输入图像:

Empname、EmpDesignation、Salary 是列
例子:
Java
// Java Program in which a Class is declared and
// its methods are defined
// Class
class Employee {
// Member variable of Employee Class
// Name, Designation and Salary
private String employeeName;
private String employeeDesignation;
private double salary;
// Constructor of Employee class
public Employee() {}
// Method 1
public String toString()
{
return String.format("%s - %s - %f", employeeName,
employeeDesignation, salary);
}
// method 2
// To get name of an employee
public String getEmployeeName()
{
// Return the name of the employee
return employeeName;
}
// Method - 3
// To set employee name
public void setEmployeeName(String employeeName)
{
// This keyword refer to the current
// method or constructor itself
// Hence, same employee name can be set
// through this method
this.employeeName = employeeName;
}
// Method - 4
// To get already assigned designation of
// the employee over which method is invoked
public String getEmployeeDesignation()
{
// Return the designation of the employee
// over which the function is called
return employeeDesignation;
}
// Method - 5
// To assign a designation to an employee
public void
setEmployeeDesignation(String employeeDesignation)
{
// This keyword refer to the current
// method or constructor itself
this.employeeDesignation = employeeDesignation;
}
// Method - 6
// To get salary of an employee
public double getSalary()
{
// Return the salry of the employee for which
// the function is invoked
return salary;
}
// Method - 7
// To set salary of the existing employee with
// assigned name and designation
public void setSalary(double salary)
{
this.salary = salary;
}
}Java
// Java Program to get the cell value
// of the corresponding cells
// Method
// To get the cell value
private Object getCellValue(Cell cell)
{
// Now either do-while or switch can be used
// to display menu/user's choice
// Switch case is used here for illustration
// Switch case to get the users choice
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
// Case 1
// If cell contents are string
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
return cell.getStringCellValue();
// Case 2
// If cell contents are Boolean
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
return cell.getBooleanCellValue();
// Case 3
// If cell contents are Numeric which includes
// int, float , double etc
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
return cell.getNumericCellValue();
}
// Case 4
// Default case
// If cell contents are neither
// string nor Boolean nor Numeric,
// simply nothing is returned
return null;
}Java
// Java Program to get the Excel file name
// as an argument
public List
readDataFromExcelFile(String excelFilePath)
throws IOException
{
// Creating an List object of Employee type
// Note: User defined type
List listEmployees
= new ArrayList();
FileInputStream inputStream
= new FileInputStream(new File(excelFilePath));
// As used 'xlsx' file is used so XSSFWorkbook will be
// used
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
// Read the first sheet and if the contents are in
// different sheets specifying the correct index
Sheet firstSheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// Iterators to traverse over
Iterator iterator = firstSheet.iterator();
// Condition check using hasNext() method which holds
// true till there is single element remaining in List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Get a row in sheet
Row nextRow = iterator.next();
// This is for a Row's cells
Iterator| cellIterator
= nextRow.cellIterator();
// We are taking Employee as reference.
Employee emp = new Employee();
// Iterate over the cells
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell nextCell = cellIterator.next();
// Switch case variable to
// get the columnIndex
int columnIndex = nextCell.getColumnIndex();
// Depends upon the cell contents we need to
// typecast
// Switch-case
switch (columnIndex) {
// Case 1
case 0:
// First column is alpha and hence
// it is typecasted to String
emp.setEmployeeName(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell));
// Break keyword to directly terminate
// if this case is hit
break;
// Case 2
case 1:
// Second column is alpha and hence
// it is typecasted to String
emp.setEmployeeDesignation(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell));
// Break keyword to directly terminate
// if this case is hit
break;
// Case 3
case 2:
// Third column is double value and
// hence it is typecasted to Double
emp.setSalary(
(Double)getCellValue(nextCell));
break;
// Note: If additional cells are present
// then
// they should be specified further down,
// and POJO class should accommodate those
// cell values
}
}
// Adding up to the list
listEmployees.add(emp);
}
// Closing the workbook and inputstream
// as it free up the space in memory
workbook.close();
inputStream.close();
// Return all the employees present in List
// object of Employee type
return listEmployees;
} |
Java
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Detecting the file type
GetContentFromExcelSheets getContentFromExcelSheets
= new GetContentFromExcelSheets();
// Creating an List object of Employee type
// in main() method
List extractedEmployeeData
= new ArrayList();
// Try block to check if any exception/s occurs
try {
// excelFileContents.xlsx location need to be
// specified correctly or else IOException will be
// thrown. If file is available in that location, it
// gets the data and stored in a list variable
extractedEmployeeData
= getContentFromExcelSheets
.readDataFromExcelFile(
"excelFileContents.xlsx");
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions if occurred
catch (IOException e) {
// Print the line number and exception
// in the program
e.printStackTrace();
}
// As there are possibility of data in multiple cells,
// it is always a good approach to follow a POJO pattern
// and get a row value in specified POJO As all data is
// collected in a list, we can iterate and display as
// below
for (int i = 0; i < extractedEmployeeData.size(); i++) {
// Print and display the employees data to the
// console using toString() method to the user
System.out.println(
extractedEmployeeData.get(i).toString());
}
} Java
// Java Program to Extract Content from a Excel sheet
// As we are reading the excel file, java.io package is
// compulsorily required
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
// Below imports are required to access Apache POI
// The usermodel package maps HSSF low level structures to
// familiar workbook/sheet model
// org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel
// But we are using higher excel formats hence,
// org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel is used To determine the type
// of cell content
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
// each and every row of excel is taken and stored in this
// row format
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
// excel sheet is read in this sheet format
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
// excel Workbook is read in this Workbook format
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
// XSSFWorkbook denotes the API is for working with Excel
// 2007 and later.
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
// POJO class having 3 fields matching with the given excel
// file
class Employee {
private String employeeName;
private String employeeDesignation;
private double salary;
// All 3 fields getter, setter methods should be there
public Employee() {}
public String toString()
{
return String.format("%s - %s - %f", employeeName,
employeeDesignation, salary);
}
public String getEmployeeName() { return employeeName; }
public void setEmployeeName(String employeeName)
{
this.employeeName = employeeName;
}
public String getEmployeeDesignation()
{
return employeeDesignation;
}
public void
setEmployeeDesignation(String employeeDesignation)
{
this.employeeDesignation = employeeDesignation;
}
public double getSalary() { return salary; }
public void setSalary(double d) { this.salary = d; }
}
// class to assign the cell value once it is getting done to
// read from excel sheet It can be String/Boolean/Numeric
public class GetContentFromExcelSheets {
private Object getCellValue(Cell cell)
{
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
return cell.getStringCellValue();
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
return cell.getBooleanCellValue();
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
return cell.getNumericCellValue();
}
return null;
}
// Read the excel sheet contents and get the contents in
// a list
public List
readBooksFromExcelFile(String excelFilePath)
throws IOException
{
List listEmployees
= new ArrayList();
FileInputStream inputStream
= new FileInputStream(new File(excelFilePath));
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
Sheet firstSheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator iterator = firstSheet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Row nextRow = iterator.next();
Iterator cellIterator
= nextRow.cellIterator();
Employee emp = new Employee();
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell nextCell = cellIterator.next();
int columnIndex = nextCell.getColumnIndex();
switch (columnIndex) {
case 1:
emp.setEmployeeName(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell));
break;
case 2:
emp.setEmployeeDesignation(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell));
break;
case 3:
emp.setSalary(Double.valueOf(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell)));
break;
}
}
listEmployees.add(emp);
}
((FileInputStream)workbook).close();
inputStream.close();
return listEmployees;
}
// Main program
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// detecting the file type
GetContentFromExcelSheets getContentFromExcelSheets
= new GetContentFromExcelSheets();
List extractedEmployeeData
= new ArrayList();
try {
extractedEmployeeData
= getContentFromExcelSheets
.readBooksFromExcelFile(
"excelFileContents.xlsx");
}
catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(extractedEmployeeData);
}
} |
第 2 步:取决于不同的数据类型,如字符串、数字(适用于整数、双精度、浮点数等)、布尔值,我们需要有一种方法来获取 Excel 的单元格值
例子:
Java
// Java Program to get the cell value
// of the corresponding cells
// Method
// To get the cell value
private Object getCellValue(Cell cell)
{
// Now either do-while or switch can be used
// to display menu/user's choice
// Switch case is used here for illustration
// Switch case to get the users choice
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
// Case 1
// If cell contents are string
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
return cell.getStringCellValue();
// Case 2
// If cell contents are Boolean
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
return cell.getBooleanCellValue();
// Case 3
// If cell contents are Numeric which includes
// int, float , double etc
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
return cell.getNumericCellValue();
}
// Case 4
// Default case
// If cell contents are neither
// string nor Boolean nor Numeric,
// simply nothing is returned
return null;
}
步骤3:提取Excel文件内容的方法。我们需要指定位置 正确归档。否则,它将以 IOException 结束
例子:
Java
// Java Program to get the Excel file name
// as an argument
public List
readDataFromExcelFile(String excelFilePath)
throws IOException
{
// Creating an List object of Employee type
// Note: User defined type
List listEmployees
= new ArrayList();
FileInputStream inputStream
= new FileInputStream(new File(excelFilePath));
// As used 'xlsx' file is used so XSSFWorkbook will be
// used
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
// Read the first sheet and if the contents are in
// different sheets specifying the correct index
Sheet firstSheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// Iterators to traverse over
Iterator iterator = firstSheet.iterator();
// Condition check using hasNext() method which holds
// true till there is single element remaining in List
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Get a row in sheet
Row nextRow = iterator.next();
// This is for a Row's cells
Iterator| cellIterator
= nextRow.cellIterator();
// We are taking Employee as reference.
Employee emp = new Employee();
// Iterate over the cells
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell nextCell = cellIterator.next();
// Switch case variable to
// get the columnIndex
int columnIndex = nextCell.getColumnIndex();
// Depends upon the cell contents we need to
// typecast
// Switch-case
switch (columnIndex) {
// Case 1
case 0:
// First column is alpha and hence
// it is typecasted to String
emp.setEmployeeName(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell));
// Break keyword to directly terminate
// if this case is hit
break;
// Case 2
case 1:
// Second column is alpha and hence
// it is typecasted to String
emp.setEmployeeDesignation(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell));
// Break keyword to directly terminate
// if this case is hit
break;
// Case 3
case 2:
// Third column is double value and
// hence it is typecasted to Double
emp.setSalary(
(Double)getCellValue(nextCell));
break;
// Note: If additional cells are present
// then
// they should be specified further down,
// and POJO class should accommodate those
// cell values
}
}
// Adding up to the list
listEmployees.add(emp);
}
// Closing the workbook and inputstream
// as it free up the space in memory
workbook.close();
inputStream.close();
// Return all the employees present in List
// object of Employee type
return listEmployees;
}
|
第 4 步:在主程序中集成第 1 步到第 3 步的概念
Java
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Detecting the file type
GetContentFromExcelSheets getContentFromExcelSheets
= new GetContentFromExcelSheets();
// Creating an List object of Employee type
// in main() method
List extractedEmployeeData
= new ArrayList();
// Try block to check if any exception/s occurs
try {
// excelFileContents.xlsx location need to be
// specified correctly or else IOException will be
// thrown. If file is available in that location, it
// gets the data and stored in a list variable
extractedEmployeeData
= getContentFromExcelSheets
.readDataFromExcelFile(
"excelFileContents.xlsx");
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions if occurred
catch (IOException e) {
// Print the line number and exception
// in the program
e.printStackTrace();
}
// As there are possibility of data in multiple cells,
// it is always a good approach to follow a POJO pattern
// and get a row value in specified POJO As all data is
// collected in a list, we can iterate and display as
// below
for (int i = 0; i < extractedEmployeeData.size(); i++) {
// Print and display the employees data to the
// console using toString() method to the user
System.out.println(
extractedEmployeeData.get(i).toString());
}
}
输出:对于我们的示例,我们只有 3 行数据
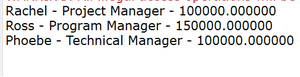
执行:
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Extract Content from a Excel sheet
// As we are reading the excel file, java.io package is
// compulsorily required
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
// Below imports are required to access Apache POI
// The usermodel package maps HSSF low level structures to
// familiar workbook/sheet model
// org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel
// But we are using higher excel formats hence,
// org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel is used To determine the type
// of cell content
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
// each and every row of excel is taken and stored in this
// row format
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
// excel sheet is read in this sheet format
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
// excel Workbook is read in this Workbook format
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
// XSSFWorkbook denotes the API is for working with Excel
// 2007 and later.
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
// POJO class having 3 fields matching with the given excel
// file
class Employee {
private String employeeName;
private String employeeDesignation;
private double salary;
// All 3 fields getter, setter methods should be there
public Employee() {}
public String toString()
{
return String.format("%s - %s - %f", employeeName,
employeeDesignation, salary);
}
public String getEmployeeName() { return employeeName; }
public void setEmployeeName(String employeeName)
{
this.employeeName = employeeName;
}
public String getEmployeeDesignation()
{
return employeeDesignation;
}
public void
setEmployeeDesignation(String employeeDesignation)
{
this.employeeDesignation = employeeDesignation;
}
public double getSalary() { return salary; }
public void setSalary(double d) { this.salary = d; }
}
// class to assign the cell value once it is getting done to
// read from excel sheet It can be String/Boolean/Numeric
public class GetContentFromExcelSheets {
private Object getCellValue(Cell cell)
{
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
return cell.getStringCellValue();
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
return cell.getBooleanCellValue();
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
return cell.getNumericCellValue();
}
return null;
}
// Read the excel sheet contents and get the contents in
// a list
public List
readBooksFromExcelFile(String excelFilePath)
throws IOException
{
List listEmployees
= new ArrayList();
FileInputStream inputStream
= new FileInputStream(new File(excelFilePath));
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
Sheet firstSheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator iterator = firstSheet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Row nextRow = iterator.next();
Iterator cellIterator
= nextRow.cellIterator();
Employee emp = new Employee();
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell nextCell = cellIterator.next();
int columnIndex = nextCell.getColumnIndex();
switch (columnIndex) {
case 1:
emp.setEmployeeName(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell));
break;
case 2:
emp.setEmployeeDesignation(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell));
break;
case 3:
emp.setSalary(Double.valueOf(
(String)getCellValue(nextCell)));
break;
}
}
listEmployees.add(emp);
}
((FileInputStream)workbook).close();
inputStream.close();
return listEmployees;
}
// Main program
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// detecting the file type
GetContentFromExcelSheets getContentFromExcelSheets
= new GetContentFromExcelSheets();
List extractedEmployeeData
= new ArrayList();
try {
extractedEmployeeData
= getContentFromExcelSheets
.readBooksFromExcelFile(
"excelFileContents.xlsx");
}
catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(extractedEmployeeData);
}
}
|
Conclusion : Apache POI provides a nicer implementation to extract Excel file contents. In coding, according to the availability of data in the number of cells, we need to have POJO class attributes and also we need to specify coll data in the “readDataFromExcelFile” method. We can format Double data as per our requirement also.