根据给定查询在 Matrix 的相邻单元格之间创建边界后计算区域
给定一个大小为 N * M 和 Q 个查询的矩阵,任务是在执行查询后找出有多少不同的区域。在每个查询中:
- 有四个整数 x1, y1, x2, y2 表示矩阵 (x1, y1) 和 (x2, y2) 的两个相邻的单元。
- 沿单元格的公共侧创建边界。
注意:如果不跨越边界就无法从一个区域到另一个区域,则两个区域是不同的
例子:
Input: N = 2, M = 2, Q = 2, queries = { {1, 1, 2, 1}, {2, 2, 1, 2} }
Output: 2
Explanation:
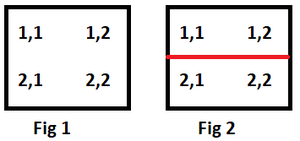
Example 1
See the above image for better understanding. Fig 1 shows matrix without any boundary
Fig 2 shows, matrix after the boundaries are formed between (1, 1), (2, 1) and (2, 2), (1, 2).
Two regions are created.
Input: N = 2, M = 2, Q = 10,
queries = {{2, 1, 2, 2}, {1, 2, 2, 2}, {1, 3, 2, 3}, {1, 4, 2, 4}, {2, 3, 3, 3}, {3, 3, 3, 4}, {3, 3, 4, 3}, {3, 3, 3, 2}, {3, 1, 3, 2}, {4, 1, 4, 2}}
Output: 2
Explanation: See the regions formed in the image provided below
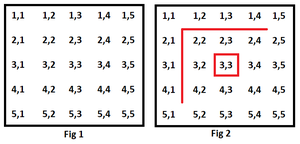
Example 2
方法:这个问题可以通过基于以下思想的哈希和DFS来解决:
Create hash to store if the boundaries are formed vertically or horizontally and which cells have already taken part in the boundary forming operations.
Then visit the cells of the matrix using dfs and check the boundaries between them are forming a different region or not.
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 创建两个哈希表,以存储存在于垂直和水平相邻单元格中的行的状态。
- 创建另一个哈希表来存储是否访问了单元格。
- 开始遍历查询,并在每次迭代中:
- 检查给定的两个单元格是垂直相邻还是水平相邻。
- 根据该标记哈希表,以避免将它们视为同一区域。
- 遍历矩阵,并在每次迭代中:
- 检查当前单元格是否被访问。
- 如果未访问,则增加TotalRegion的计数,然后使用DFS递归访问其相邻单元格(如果它们之间没有边界),并将该区域中的所有单元格标记为已访问。
- 执行后返回矩阵中TotalRegion的计数
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Recursive function to traverse the matrix
void traverse(int i, int j, int N, int M,
vector >& vis,
vector >& row,
vector >& col)
{
if (i <= 0 || i > N || j <= 0 || j > M || vis[i][j])
return;
// Mark Current cell visited.
vis[i][j] = true;
// Traverse adjacent cells in all directions
// (up, down, right, left) that
// do not include lines between
if (row[i][j])
traverse(i, j + 1, N, M,
vis, row, col);
if (col[i][j])
traverse(i + 1, j, N, M,
vis, row, col);
if (row[i][j - 1])
traverse(i, j - 1, N, M,
vis, row, col);
if (col[i - 1][j])
traverse(i - 1, j, N, M,
vis, row, col);
}
// Function to count the total regions
int count(int N, int M, int K,
vector >& q)
{
vector > row(N + 1,
vector(
M + 1, true));
vector > col(N + 1,
vector(
M + 1, true));
vector > vis(N + 1,
vector(
M + 1, false));
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
// Hash array value set to false
// if there is line between
// two adjacent cell in same row
// If query is {0 1 1 1} or
// {1 1 0 1} we make row[0][1]= false,
// that means there is vertical line
// after the cell [0][1]
if (q[i][0] == q[i][2]) {
int mn = min(q[i][1], q[i][3]);
row[q[i][0]][mn] = false;
}
// Hash array value set to false if
// there is line between
// two adjacent cell in same column
// If query is {2 3 2 4} or {2 4 2 3}
// we make col[2][3]= false,
// that means there is horizontal line
// below the cell [2][3]
else {
int mn = min(q[i][0], q[i][2]);
col[mn][q[i][1]] = false;
}
}
// Store count of total regions after
// performing K quires.
int TotalRegion = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++) {
// If current Cell
// is not visited
// then increment the TotalRegion
// count and traverse
// all the cell in that region
if (!vis[i][j]) {
TotalRegion++;
traverse(i, j, N, M,
vis, row, col);
}
}
}
return TotalRegion;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
vector > q;
int N = 5, M = 5;
int K = 10;
q.push_back({ 2, 1, 2, 2 });
q.push_back({ 1, 2, 2, 2 });
q.push_back({ 1, 3, 2, 3 });
q.push_back({ 1, 4, 2, 4 });
q.push_back({ 2, 3, 3, 3 });
q.push_back({ 3, 3, 3, 4 });
q.push_back({ 3, 3, 4, 3 });
q.push_back({ 3, 3, 3, 2 });
q.push_back({ 3, 1, 3, 2 });
q.push_back({ 4, 1, 4, 2 });
cout << count(N, M, K, q);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python code to implement the approach
# Recursive function to traverse the matrix
def traverse(i, j, N, M, vis, row, col):
if (i <= 0 or i > N or j <= 0 or j > M or vis[i][j]):
return
# Mark Current cell visited.
vis[i][j] = True
# Traverse adjacent cells in all directions
# (up, down, right, left) that
# do not include lines between
if (row[i][j]):
traverse(i, j + 1, N, M,vis, row, col)
if (col[i][j]):
traverse(i + 1, j, N, M,vis, row, col)
if (row[i][j - 1]):
traverse(i, j - 1, N, M,vis, row, col)
if (col[i - 1][j]):
traverse(i - 1, j, N, M,vis, row, col)
# Function to count the total regions
def count(N, M, K, q):
row = [[True for col in range(M+1)]for row in range(N+1)]
col = [[True for col in range(M+1)]for row in range(N+1)]
vis = [[False for col in range(M+1)]for row in range(N+1)]
for i in range(K):
# Hash array value set to false
# if there is line between
# two adjacent cell in same row
# If query is {0 1 1 1} or
# {1 1 0 1} we make row[0][1]= false,
# that means there is vertical line
# after the cell [0][1]
if (q[i][0] == q[i][2]):
mn = min(q[i][1], q[i][3])
row[q[i][0]][mn] = False
# Hash array value set to false if
# there is line between
# two adjacent cell in same column
# If query is {2 3 2 4} or {2 4 2 3}
# we make col[2][3]= false,
# that means there is horizontal line
# below the cell [2][3]
else:
mn = min(q[i][0], q[i][2])
col[mn][q[i][1]] = False
# Store count of total regions after
# performing K quires.
TotalRegion = 0
for i in range(1,N+1):
for j in range(1,M+1):
# If current Cell
# is not visited
# then increment the TotalRegion
# count and traverse
# all the cell in that region
if (vis[i][j] == False):
TotalRegion += 1
traverse(i, j, N, M,vis, row, col)
return TotalRegion
# Driver code
q = []
N = 5
M = 5
K = 10
q.append([2, 1, 2, 2])
q.append([1, 2, 2, 2])
q.append([1, 3, 2, 3])
q.append([1, 4, 2, 4])
q.append([2, 3, 3, 3])
q.append([3, 3, 3, 4])
q.append([3, 3, 4, 3])
q.append([3, 3, 3, 2])
q.append([3, 1, 3, 2])
q.append([4, 1, 4, 2])
print(count(N, M, K, q))
# This code is contributed by ShinjanPatraJavascript
2时间复杂度: O( N*M + Q )
辅助空间: O(N*M)