给定一个维度为N * M的二进制矩阵,任务是找到矩阵的索引,以便根据以下条件从单元格(0, 0)遍历给定矩阵导致矩阵外部:
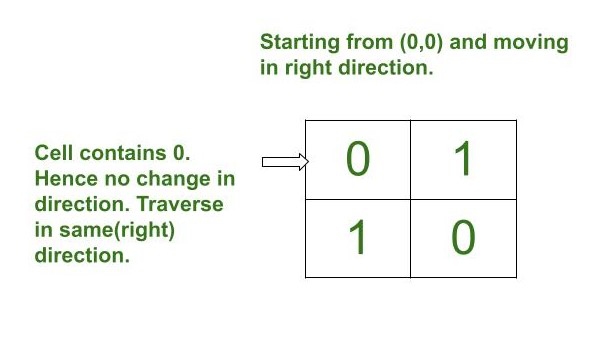
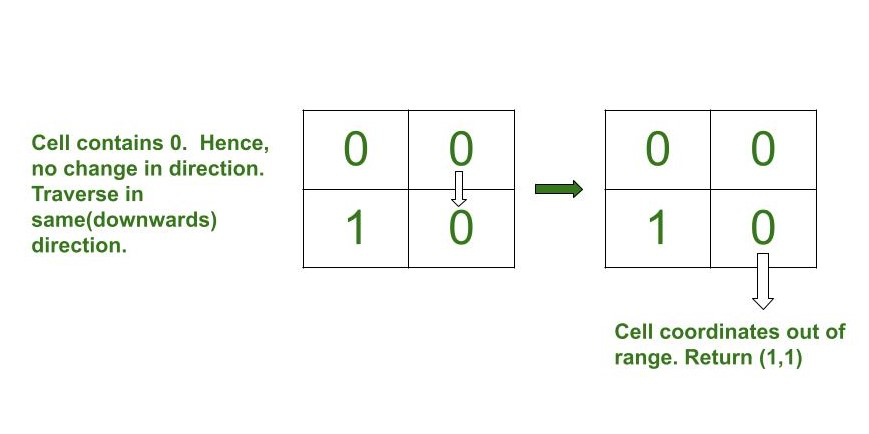
- 如果arr[i][j] 的值为0 ,则沿相同方向遍历并检查下一个值。
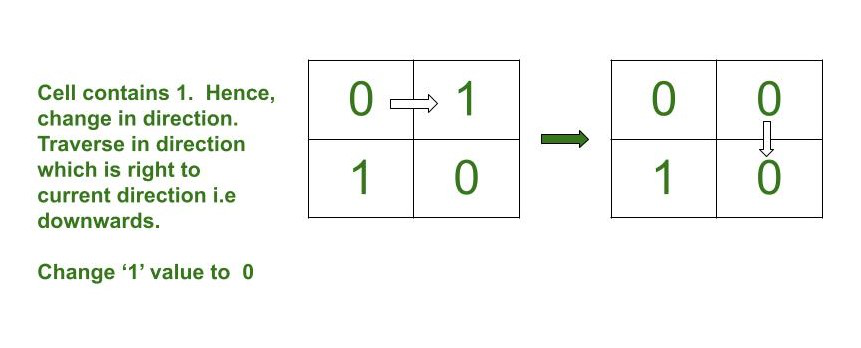
- 如果arr[i][j] 的值为1 ,则将arr[i][j]更新为0并将当前方向从向上、向右、向下或向左更改为向右、向下、向左和向上分别。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}}
Output: (1, 1)
Explanation:
Below is the image to illustrate the simulation:
Input: arr[] = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 1, 0, 0}}
Output: (2, 0)
处理方法:按照以下步骤解决问题:
-
- 初始化两个变量,比如current_i和current_j ,都为0 。
- 从索引(0, 0) 开始遍历矩阵,并将当前方向设置为右为R 。
- 如果current_i或current_j的值分别为N或M ,则执行以下操作:
- 如果arr[i][j] 的值为0 ,则沿相同方向遍历并检查下一个值。
- 否则,将arr[i][j]更新为0并选择一个与当前方向正好的方向。如果当前方向的正确方向是:
- L:将当前行向后移动,即j – 1 。
- R:向前移动当前行,即j + 1 。
- U:向上移动当前列,即i – 1 。
- D:向下移动当前列,即i + 1 。
- 如果新坐标不在范围内,则将当前坐标打印为结果坐标并跳出循环。
C++
// CPP program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to check if the indices (i, j)
// are valid indices in a Matrix or not
bool issafe(int m, int n, int i, int j)
{
// Cases for invalid cells
if (i < 0)
return false;
if (j < 0)
return false;
if (i >= m)
return false;
if (j >= n)
return false;
// Return true if valid
return true;
}
// Function to find indices of cells
// of a matrix from which traversal
// leads to out of the matrix
pair endpoints(vector> arr, int m, int n){
// Starting from cell (0, 0),
// traverse in right direction
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int current_i = 0;
int current_j = 0;
char current_d = 'r';
// Stores direction changes
map rcd = {{'l', 'u'},{'u', 'r'},
{'r', 'd'},
{'d', 'l'}};
// Iterate until the current cell
// exceeds beyond the matrix
while (issafe(m, n, i, j)){
// Current index
current_i = i;
current_j = j;
// If the current cell is 1
if (arr[i][j] == 1){
char move_in = rcd[current_d];
// Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i][j] = 0;
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (move_in == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(move_in == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'r')
j += 1;
current_d = move_in;
}
// Otherwise
else{
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (current_d == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(current_d == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'r')
j += 1;
}
}
// The exit cooridnates
return {current_i, current_j};
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of rows
int M = 3;
// Number of columns
int N = 5;
// Given matrix arr[][]
vector> arr{{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0}};
pair p = endpoints(arr, M, N);
cout << "(" << p.first << ", " << p.second << ")" << endl;
}
// This code is contributed by ipg2016107. Java
// JAVA program for the above approach
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class GFG
{
// Function to check if the indices (i, j)
// are valid indices in a Matrix or not
static boolean issafe(int m, int n, int i, int j)
{
// Cases for invalid cells
if (i < 0)
return false;
if (j < 0)
return false;
if (i >= m)
return false;
if (j >= n)
return false;
// Return true if valid
return true;
}
// Function to find indices of cells
// of a matrix from which traversal
// leads to out of the matrix
static int [] endpoints(int [][]arr, int m, int n){
// Starting from cell (0, 0),
// traverse in right direction
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int current_i = 0;
int current_j = 0;
char current_d = 'r';
// Stores direction changes
Map rcd = new HashMap<>();
rcd.put('l', 'u');
rcd.put('u', 'r');
rcd.put('r', 'd');
rcd.put('d', 'l');
// Iterate until the current cell
// exceeds beyond the matrix
while (issafe(m, n, i, j)){
// Current index
current_i = i;
current_j = j;
// If the current cell is 1
if (arr[i][j] == 1){
char move_in = rcd.get(current_d);
// Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i][j] = 0;
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (move_in == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(move_in == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(move_in == 'r')
j += 1;
current_d = move_in;
}
// Otherwise
else{
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (current_d == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'd')
i += 1;
else if(current_d == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if(current_d == 'r')
j += 1;
}
}
// The exit cooridnates
return new int[]{current_i, current_j};
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of rows
int M = 3;
// Number of columns
int N = 5;
// Given matrix arr[][]
int [][]arr = {{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 0}};
int []p = endpoints(arr, M, N);
System.out.print("(" + p[0]+ ", " + p[1]+ ")" +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput Python3
# Python program for the above approach
# Function to check if the indices (i, j)
# are valid indices in a Matrix or not
def issafe(m, n, i, j):
# Cases for invalid cells
if i < 0:
return False
if j < 0:
return False
if i >= m:
return False
if j >= n:
return False
# Return true if valid
return True
# Function to find indices of cells
# of a matrix from which traversal
# leads to out of the matrix
def endpoints(arr, m, n):
# Starting from cell (0, 0),
# traverse in right direction
i = 0
j = 0
current_d = 'r'
# Stores direction changes
rcd = {'l': 'u',
'u': 'r',
'r': 'd',
'd': 'l'}
# Iterate until the current cell
# exceeds beyond the matrix
while issafe(m, n, i, j):
# Current index
current_i = i
current_j = j
# If the current cell is 1
if arr[i][j] == 1:
move_in = rcd[current_d]
# Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i][j] = 0
# Update indices according
# to the direction
if move_in == 'u':
i -= 1
elif move_in == 'd':
i += 1
elif move_in == 'l':
j -= 1
elif move_in == 'r':
j += 1
current_d = move_in
# Otherwise
else:
# Update indices according
# to the direction
if current_d == 'u':
i -= 1
elif current_d == 'd':
i += 1
elif current_d == 'l':
j -= 1
elif current_d == 'r':
j += 1
# The exit cooridnates
return (current_i, current_j)
# Driver Code
# Number of rows
M = 3
# Number of columns
N = 5
# Given matrix arr[][]
arr = [[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
]
print(endpoints(arr, M, N))C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Function to check if the indices (i, j)
// are valid indices in a Matrix or not
static bool issafe(int m, int n, int i, int j)
{
// Cases for invalid cells
if (i < 0)
return false;
if (j < 0)
return false;
if (i >= m)
return false;
if (j >= n)
return false;
// Return true if valid
return true;
}
// Function to find indices of cells
// of a matrix from which traversal
// leads to out of the matrix
static int[] endpoints(int[, ] arr, int m, int n)
{
// Starting from cell (0, 0),
// traverse in right direction
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int current_i = 0;
int current_j = 0;
char current_d = 'r';
// Stores direction changes
Dictionary rcd
= new Dictionary();
rcd['l'] = 'u';
rcd['u'] = 'r';
rcd['r'] = 'd';
rcd['d'] = 'l';
// Iterate until the current cell
// exceeds beyond the matrix
while (issafe(m, n, i, j)) {
// Current index
current_i = i;
current_j = j;
// If the current cell is 1
if (arr[i, j] == 1) {
char move_in = rcd[current_d];
// Update arr[i][j] = 0
arr[i, j] = 0;
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (move_in == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if (move_in == 'd')
i += 1;
else if (move_in == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if (move_in == 'r')
j += 1;
current_d = move_in;
}
// Otherwise
else {
// Update indices according
// to the direction
if (current_d == 'u')
i -= 1;
else if (current_d == 'd')
i += 1;
else if (current_d == 'l')
j -= 1;
else if (current_d == 'r')
j += 1;
}
}
// The exit cooridnates
return new int[] { current_i, current_j };
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Number of rows
int M = 3;
// Number of columns
int N = 5;
// Given matrix arr[][]
int[, ] arr = { { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 0, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 } };
int[] p = endpoints(arr, M, N);
Console.WriteLine("(" + p[0] + ", " + p[1] + ")"
+ "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp. 输出
(2, 0)如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live