部分分数展开
如果 f(x) 是一个需要积分的函数,则 f(x) 称为被积函数,函数没有任何限制或边界的积分称为不定积分。不定积分有自己的公式,可以使积分过程更容易。但是,有时有些功能过于复杂,无法轻松集成,需要更多时间。例如,在函数的分母中有一个长的二次表达式。在这种情况下,可以在部分分数的帮助下进行不定积分,以使该过程变得简单且耗时更少。
无限整合
不定积分也称为反导数,因为它是微分的逆过程。不定是指函数的整合没有任何限制或界限,需要整合整个函数。函数f(x) 是积分,这里的 x 是积分的变量,积分使用的符号是∫。让我们看一下用于不定积分的一些基本公式,
不定积分的一些基本公式:Functions Formulae ∫a dx ax + C, a∈ R ∫xn dx ![]() +C, x∉ -1
+C, x∉ -1∫1/x dx log|x| + C ∫ex dx ex + C ∫1/√x dx 2√x + C ∫ax dx ![]()
∫Sinx dx -Cosx +C ∫Cosx dx Sinx +C ∫Tanx dx log|secx| +C ∫Secx tanx dx Secx + C ∫Cosecx cotx dx -Cosecx + C ∫ Sec2x dx tanx +C ∫ Cosec2x dx – cotx + C
例1:求函数的积分,
f(x) = x 5 + 3/x
解决方案:
∫f(x)dx = ∫x5 dx + ∫3/x dx
∫f(x)dx = ![]()
示例 2:积分,f(x)= 5cosx – 9tanx
解决方案:
∫f(x)dx= ∫[5cosx- 9tanx]dx
∫f(x)dx= ∫5cosxdx- ∫9tanxdx
∫f(x)dx= 5sinx- (log|secx|) +C
除了只需要公式的简单问题外,重要的是要了解复杂的函数不能轻易解决。为了找到复函数的积分,一种方法是使用部分分数,
部分分数积分
有理函数定义为 P(x)/Q(x) 形式的函数,其中 Q(x) ≠ 0。这些函数可以是适当形式,也可以是不适当形式。 Proper ration函数定义为 Q(x) 中的最高程度大于 P(x) 中的最高程度的函数。不当函数是指 P(x) 的最高次数大于 Q(x) 的函数。如果函数中的分母可以分解为线性因子,则有理函数可以很容易地通过偏分数积分。
部分分数分解
被积函数,即给定函数可以分解为更简单的形式,这称为部分分数分解。下面给出了函数的一些广义部分分数, x2+ bx+ c cannot be factorizedFunctions Partial Fractions ![]() , a≠b
, a≠b![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
,![]()
这些广义形式是如何获得的,或者是否有任何步骤可用于部分分数分解?是的。这些步骤可以很容易地帮助达到完美的部分分数形式,
部分分数分解的步骤
- 为了分解,从正确的有理表达式开始。将分母分解为最基本的形式。
- 写下得到的单独的部分分数,为了处理分子,用很快就会发现的变量填充它们。
- 现在,为了找到变量的值,这里是 A、B 和 C,将方程乘以分母。
- 通过相应地替换不同的值来求解变量。
- 得到分子的值后,将它们放在部分分数中。
使用长除法或合成除法积分
当函数没有以有理形式给出时使用这种方法,即分数是假分数并且分子的次数大于或等于分母的次数。在这些情况下,假设分子的度数是 a,分母的度数是 b,在这里做部分分数时,需要记住,(ab)的附加值与分母一起被添加到分母中。部分分数。
让我们考虑下面给出的函数:
f(x) = ![]()
该函数是一个不正确的积分,因此可以使用长除法求解。
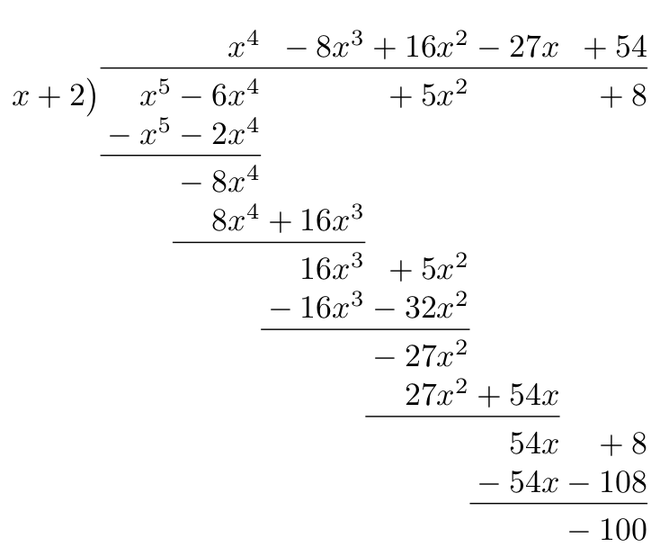
这里,S(x) = x 5 – 6x 4 + 5x 2 + 8 和 R(x) = -100 和 Q(x) = x + 2。
因此,积分可以重写为,
∫(x 5 – 6x 4 + 5x 2 + 8 + ![]() )dx
)dx
⇒ 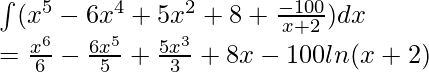
If the numerator P(x) has a degree greater than or equal to the degree of the denominator Q(x), then the rational function ![]() is called improper. In this case, we use long division of polynomials to write the ratio as a polynomial with a remainder.
is called improper. In this case, we use long division of polynomials to write the ratio as a polynomial with a remainder.
Let’s say dividing P(x) by Q(x) gives S(x) with the remainder R(x), then the degree of R(x) is less than the degree of Q(x) as a result of the long division.
![]()
After doing this, the function can be integrated.
示例问题
问题一:积分,f(x)= sin(x) + 3tanx
解决方案 :
∫f(x)dx= ∫[sin(x) + 3tanx]dx
∫f(x)dx= ∫sin(x)dx + ∫3tanxdx
∫f(x)dx= -cos(x) + 3(log|secx|) +C
问题2:求下列函数的积分。
f(x) = ![]()
解决方案:
The given function can be decomposed into partial fractions.
f(x) = ![]()
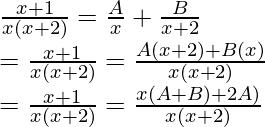
Comparing both sides of the equation,
A + B = 1
2A = 1
From both these equations, it can be concluded that.
A = 1/2, B = 1/2
Thus, the function becomes,
f(x) = ![]()
Now,
F(x) = ∫f(x)
⇒ F(x) = ![]()
⇒ F(x) = ![]()
问题 3:求下列函数的积分。
f(x) = ![]()
解决方案:
The given function can be decomposed into partial fractions.
f(x) = ![]()
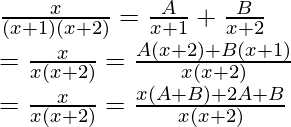
Comparing both sides of the equation,
A + B = 1
2A + B = 0
From both these equations, it can be concluded that.
A = -1, B = 2
Thus, the function becomes,
f(x) = ![]()
Now,
F(x) = ∫f(x)
⇒ F(x) = ![]()
⇒ F(x) = ![]()
问题 4:求下列函数的积分。
f(x) = ![]()
解决方案:
The given function can be decomposed into partial fractions. First let’s simplify the function.
f(x) = ![]()
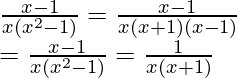
Decomposing the function,
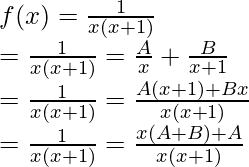
Comparing both sides of the equation,
A + B = 0
A = 1
From both these equations, it can be concluded that.
A = 1, B = -1
Thus, the function becomes,
f(x) = ![]()
Now,
F(x) = ∫f(x)
⇒ F(x) = ![]()
⇒ F(x) = ln(x) – ln(x+1)
问题 5:求下列函数的积分。
f(x) = ![]()
解决方案:
The given function can be decomposed into partial fractions. First let’s simplify the function.
f(x) = ![]()
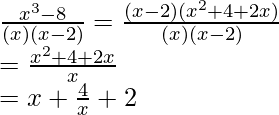
Integrating the function,
F(x) = ∫f(x)dx
⇒ F(x) = ∫(![]() )dx
)dx
⇒ F(x) = ![]()