在 R 脚本中导入数据
在本文中,我们将了解如何在 R 编程语言中导入数据。
在 R 中导入数据
首先,让我们考虑一个可用于演示的数据集。对于此演示,我们将使用单个数据集的两个示例,一个为 .csv 格式,另一个为 .txt

读取逗号分隔值 (CSV) 文件
方法一:使用 read.csv()函数将 CSV 文件读入 R
该函数有两个参数:
- file.choose():它打开一个菜单来从桌面选择一个 csv 文件。
- header:表示数据集的第一行是否为变量名。如果变量名存在,则应用 T/True,否则应用 F/False。
例子:
R
# import and store the dataset in data1
data1 <- read.csv(file.choose(), header=T)
# display the data
data1R
# import and store the dataset in data2
data2 <- read.table(file.choose(), header=T, sep=", ")
# display data
data2R
# import and store the dataset in data3
data3 <- read.delim(file.choose(), header=T)
# display the data
data3R
# import and store the dataset in data4
data4 <- read.table(file.choose(), header=T, sep="\t")
# display the data
data4R
# display the dataset
datasetR
# To load the data for use
attach(dataset)R
# Read a JSON file
# Load the package required to read JSON files.
library("rjson")
# Give the input file name to the function.
result <- fromJSON(file = "E:\\example.json")
# Print the result.
print(result)输出:

方法二:使用 read.table()函数
该函数指定数据集的分离方式,在这种情况下,我们将sep=”, “作为参数。
例子:
R
# import and store the dataset in data2
data2 <- read.table(file.choose(), header=T, sep=", ")
# display data
data2
输出:

在 R 编程语言中读取制表符分隔 (txt) 文件
方法一:使用 read.delim()函数
该函数有两个参数:
- file.choose():它打开一个菜单来从桌面选择一个 csv 文件。
- header:表示数据集的第一行是否为变量名。如果变量名存在,则应用 T/True,否则应用 F/False。
例子:
R
# import and store the dataset in data3
data3 <- read.delim(file.choose(), header=T)
# display the data
data3
输出:

方法二:使用 read.table()函数
该函数指定数据集的分离方式,在这种情况下,我们将sep=”\t”作为参数。
例子:
R
# import and store the dataset in data4
data4 <- read.table(file.choose(), header=T, sep="\t")
# display the data
data4
输出:

使用 R-Studio
在这里,我们将通过以下步骤通过 R studio 导入数据。
脚步:
- 从环境选项卡单击导入数据集菜单
- 从选项中选择文件扩展名
- 第三步,会出现一个弹框,可以输入文件名,也可以浏览桌面。
- 所选文件将显示在新窗口及其尺寸。
- 为了在控制台上查看输出,输入文件名。
例子:
R
# display the dataset
dataset
输出:
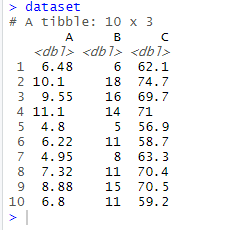
- 为了将数据加载到控制台上使用,我们使用了attach命令。
例子:
R
# To load the data for use
attach(dataset)
将 JSON 文件读入 R
为了在 R 中使用 JSON 文件,需要安装“rjson”包。使用 rjson 包下的 JSON 文件完成的最常见任务如下:
- 在 R 控制台中安装和加载 rjson 包
- 创建 JSON 文件
- 从 JSON 文件中读取数据
- 写入 JSON 文件
- 将 JSON 数据转换为 Dataframe
- 使用 URL
用于演示的 JSON 文件:
{
"ID":["1","2","3","4","5"],
"Name":["Mithuna","Tanushree","Parnasha","Arjun","Pankaj"],
"Salary":["722.5","815.2","1611","2829","843.25"],
"StartDate":["6/17/2014","1/1/2012","11/15/2014","9/23/2013","5/21/2013"],
"Dept":["IT","IT","HR","Operations","Finance"]
}代码:
R
# Read a JSON file
# Load the package required to read JSON files.
library("rjson")
# Give the input file name to the function.
result <- fromJSON(file = "E:\\example.json")
# Print the result.
print(result)
输出:
$ID
[1] "1" "2" "3" "4" "5"
$Name
[1] "Mithuna" "Tanushree" "Parnasha" "Arjun" "Pankaj"
$Salary
[1] "722.5" "815.2" "1611" "2829" "843.25"
$StartDate
[1] "6/17/2014" "1/1/2012" "11/15/2014" "9/23/2013" "5/21/2013"
$Dept
[1] "IT" "IT" "HR" "Operations" "Finance"