在Python使用 Qiskit 的带有量子电路的经典非逻辑门
在本文中,我们将看到如何使用量子门在给定的输入(0 或 1)上应用非门,我们必须将 0 转换为 1,将 1 转换为 0。这可以在经典计算机中轻松完成,但是如何我们可以在量子计算机中做到这一点吗?我们必须以量子位表示输入,然后在该量子位中应用 X(量子计算机中非门的表示)操作,然后返回结果量子位
QISKIT是位于一侧量子算法和另一侧物理量子设备之间的包。它将Python等常见的编程语言翻译成量子机器语言。这意味着 IBM Q 实验室之外的任何人都可以对量子计算机进行编程。
要安装此模块,请在终端中运行这些命令:
pip3 install qiskit方法:
- 使用内置函数QuantumCircuit 创建一个具有单个经典量子位和位的量子电路qc ,该函数采用第一个参数“no。整数中的量子位”和第二个参数“no。整数位数”并返回量子电路。 ( QuantumCircuit(1, 1) 返回一个量子位 q[0] 和一位 c[0] 的量子电路)
- 以量子位表示输入('0' 表示量子位状态 |0>,'1' 表示 |1>):
- 使用 qiskit函数reset() 重置 qc 量子位。
- 由于量子位最初是|0⟩,所以对于'0'的输入,我们不需要做任何事情。
- 对于 '1' 的输入,我们做一个 X 将 |0⟩ 旋转到 |1⟩。 x()函数用于对给定参数应用非门。
- 使用barrier() 在输入状态和门操作之间设置屏障。
- 在量子位 0 上应用 NOT,我们可以使用 x 在它上面做一个 NOT
- 在门操作和测量之间设置障碍
- 最后,我们提取量子位 q[0] 的 |0⟩/|1⟩ 输出,并使用 qiskit measure()函数其编码到位 c[0] 中。
- 要可视化并查看电路图,请使用 qiskit draw()函数。
下面是实现:
Python3
# importing qiskit
from qiskit import *
# importing plot_histogram to visualize Output
from qiskit.visualization import plot_histogram
import numpy as np
def NOT(inp):
# Creating a quantum circuit with a
# single qubit and a single classical bit using
qc = QuantumCircuit(1, 1)
qc.reset(0)
# We encode '0' as the qubit state |0⟩, and '1' as |1⟩
# Since the qubit is initially |0⟩, so for
# an input of 0, we don't need to do anything.
# For an input of '1', we do an x to rotate the |0⟩ to |1⟩
# The x() function is to apply NOT gate on given parameter.
if inp == '1':
# applying NOT on qubit 0.
qc.x(0)
# barrier between input state and gate operation
qc.barrier()
# Now we've encoded the input,
# we can do a NOT on it using x
# NOT on |0> converted to |1> and wise verse.
qc.x(0)
# barrier between gate operation and measurement
qc.barrier()
# Finally, we extract the |0⟩/|1⟩ output of
# the qubit q[0] and encode it in the bit c[0]
qc.measure(0, 0)
# to visualize
qc.draw('mpl')
# To run the program on a simulator
backend = Aer.get_backend('qasm_simulator')
# Since the output will be deterministic,
# so we can use just a single shot to get it
job = execute(qc, backend, shots=1, memory=True)
output = job.result().get_memory()[0]
return qc, output
# Sending input to NOT function
for inp in ['0', '1']:
qc, out = NOT(inp)
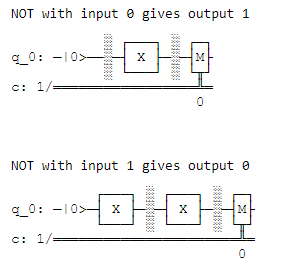
print('NOT with input', inp, 'gives output', out)
display(qc.draw())
print('\n')输出: