给定一个字符矩阵。从给定字符找出最长路径的长度,以使路径中的所有字符彼此连续,即,路径中的每个字符都按字母顺序位于前一个字符之后。允许从一个单元沿所有8个方向移动。
例子
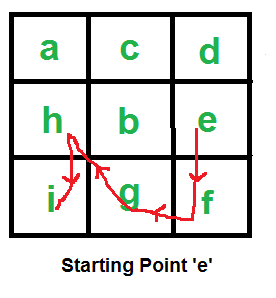
Input: mat[][] = { {a, c, d},
{h, b, e},
{i, g, f}}
Starting Point = 'e'
Output: 5
If starting point is 'e', then longest path with consecutive
characters is "e f g h i".
Input: mat[R][C] = { {b, e, f},
{h, d, a},
{i, c, a}};
Starting Point = 'b'
Output: 1
'c' is not present in all adjacent cells of 'b'
这个想法是首先在给定的矩阵中搜索给定的起始字符。对所有事件进行深度优先搜索(DFS),以查找所有连续路径。在执行DFS时,我们可能会一次又一次地遇到许多子问题。因此,我们使用动态编程来存储子问题的结果。
以下是上述想法的实现。
C++
// C++ program to find the longest consecutive path
#include
#define R 3
#define C 3
using namespace std;
// tool matrices to recur for adjacent cells.
int x[] = {0, 1, 1, -1, 1, 0, -1, -1};
int y[] = {1, 0, 1, 1, -1, -1, 0, -1};
// dp[i][j] Stores length of longest consecutive path
// starting at arr[i][j].
int dp[R][C];
// check whether mat[i][j] is a valid cell or not.
bool isvalid(int i, int j)
{
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= R || j >= C)
return false;
return true;
}
// Check whether current character is adjacent to previous
// character (character processed in parent call) or not.
bool isadjacent(char prev, char curr)
{
return ((curr - prev) == 1);
}
// i, j are the indices of the current cell and prev is the
// character processed in the parent call.. also mat[i][j]
// is our current character.
int getLenUtil(char mat[R][C], int i, int j, char prev)
{
// If this cell is not valid or current character is not
// adjacent to previous one (e.g. d is not adjacent to b )
// or if this cell is already included in the path than return 0.
if (!isvalid(i, j) || !isadjacent(prev, mat[i][j]))
return 0;
// If this subproblem is already solved , return the answer
if (dp[i][j] != -1)
return dp[i][j];
int ans = 0; // Initialize answer
// recur for paths with different adjacent cells and store
// the length of longest path.
for (int k=0; k<8; k++)
ans = max(ans, 1 + getLenUtil(mat, i + x[k],
j + y[k], mat[i][j]));
// save the answer and return
return dp[i][j] = ans;
}
// Returns length of the longest path with all characters consecutive
// to each other. This function first initializes dp array that
// is used to store results of subproblems, then it calls
// recursive DFS based function getLenUtil() to find max length path
int getLen(char mat[R][C], char s)
{
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp);
int ans = 0;
for (int i=0; i Java
// Java program to find the longest consecutive path
class path
{
// tool matrices to recur for adjacent cells.
static int x[] = {0, 1, 1, -1, 1, 0, -1, -1};
static int y[] = {1, 0, 1, 1, -1, -1, 0, -1};
static int R = 3;
static int C = 3;
// dp[i][j] Stores length of longest consecutive path
// starting at arr[i][j].
static int dp[][] = new int[R][C];
// check whether mat[i][j] is a valid cell or not.
static boolean isvalid(int i, int j)
{
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= R || j >= C)
return false;
return true;
}
// Check whether current character is adjacent to previous
// character (character processed in parent call) or not.
static boolean isadjacent(char prev, char curr)
{
return ((curr - prev) == 1);
}
// i, j are the indices of the current cell and prev is the
// character processed in the parent call.. also mat[i][j]
// is our current character.
static int getLenUtil(char mat[][], int i, int j, char prev)
{
// If this cell is not valid or current character is not
// adjacent to previous one (e.g. d is not adjacent to b )
// or if this cell is already included in the path than return 0.
if (!isvalid(i, j) || !isadjacent(prev, mat[i][j]))
return 0;
// If this subproblem is already solved , return the answer
if (dp[i][j] != -1)
return dp[i][j];
int ans = 0; // Initialize answer
// recur for paths with different adjacent cells and store
// the length of longest path.
for (int k=0; k<8; k++)
ans = Math.max(ans, 1 + getLenUtil(mat, i + x[k],
j + y[k], mat[i][j]));
// save the answer and return
return dp[i][j] = ans;
}
// Returns length of the longest path with all characters consecutive
// to each other. This function first initializes dp array that
// is used to store results of subproblems, then it calls
// recursive DFS based function getLenUtil() to find max length path
static int getLen(char mat[][], char s)
{
//assigning all dp values to -1
for(int i = 0;iPython3
# Python3 program to find the longest consecutive path
R=3
C=3
# tool matrices to recur for adjacent cells.
x = [0, 1, 1, -1, 1, 0, -1, -1]
y = [1, 0, 1, 1, -1, -1, 0, -1]
# dp[i][j] Stores length of longest consecutive path
# starting at arr[i][j].
dp=[[0 for i in range(C)]for i in range(R)]
# check whether mat[i][j] is a valid cell or not.
def isvalid( i, j):
if (i < 0 or j < 0 or i >= R or j >= C):
return False
return True
# Check whether current character is adjacent to previous
# character (character processed in parent call) or not.
def isadjacent( prev, curr):
if (ord(curr) -ord(prev)) == 1:
return True
return False
# i, j are the indices of the current cell and prev is the
# character processed in the parent call.. also mat[i][j]
# is our current character.
def getLenUtil(mat,i,j, prev):
# If this cell is not valid or current character is not
# adjacent to previous one (e.g. d is not adjacent to b )
# or if this cell is already included in the path than return 0.
if (isvalid(i, j)==False or isadjacent(prev, mat[i][j])==False):
return 0
# If this subproblem is already solved , return the answer
if (dp[i][j] != -1):
return dp[i][j]
ans = 0 # Initialize answer
# recur for paths with different adjacent cells and store
# the length of longest path.
for k in range(8):
ans = max(ans, 1 + getLenUtil(mat, i + x[k],j + y[k], mat[i][j]))
# save the answer and return
dp[i][j] = ans
return dp[i][j]
# Returns length of the longest path with all characters consecutive
# to each other. This function first initializes dp array that
# is used to store results of subproblems, then it calls
# recursive DFS based function getLenUtil() to find max length path
def getLen(mat, s):
for i in range(R):
for j in range(C):
dp[i][j]=-1
ans = 0
for i in range(R):
for j in range(C):
# check for each possible starting po
if (mat[i][j] == s):
# recur for all eight adjacent cells
for k in range(8):
ans = max(ans, 1 + getLenUtil(mat,i + x[k], j + y[k], s));
return ans
# Driver program
mat = [['a','c','d'],
[ 'h','b','a'],
[ 'i','g','f']]
print (getLen(mat, 'a'))
print (getLen(mat, 'e'))
print (getLen(mat, 'b'))
print (getLen(mat, 'f'))
#code is contributed by sahilshelangiaC#
// C# program to find the longest consecutive path
using System;
class GFG {
// tool matrices to recur for adjacent cells.
static int []x = {0, 1, 1, -1, 1, 0, -1, -1};
static int []y = {1, 0, 1, 1, -1, -1, 0, -1};
static int R = 3;
static int C = 3;
// dp[i][j] Stores length of longest
// consecutive path starting at arr[i][j].
static int [,]dp = new int[R,C];
// check whether mat[i][j] is a valid
// cell or not.
static bool isvalid(int i, int j)
{
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= R || j >= C)
return false;
return true;
}
// Check whether current character is
// adjacent to previous character
// (character processed in parent call)
// or not.
static bool isadjacent(char prev, char curr)
{
return ((curr - prev) == 1);
}
// i, j are the indices of the current
// cell and prev is the character processed
// in the parent call.. also mat[i][j]
// is our current character.
static int getLenUtil(char [,]mat, int i,
int j, char prev)
{
// If this cell is not valid or current
// character is not adjacent to previous
// one (e.g. d is not adjacent to b )
// or if this cell is already included
// in the path than return 0.
if (!isvalid(i, j) || !isadjacent(prev,
mat[i,j]))
return 0;
// If this subproblem is already solved,
// return the answer
if (dp[i,j] != -1)
return dp[i,j];
int ans = 0; // Initialize answer
// recur for paths with different adjacent
// cells and store the length of
// longest path.
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
ans = Math.Max(ans, 1 + getLenUtil(mat,
i + x[k], j + y[k], mat[i,j]));
// save the answer and return
return dp[i,j] = ans;
}
// Returns length of the longest path
// with all characters consecutive to
// each other. This function first
// initializes dp array that is used
// to store results of subproblems,
// then it calls recursive DFS based
// function getLenUtil() to find max
// length path
static int getLen(char [,]mat, char s)
{
//assigning all dp values to -1
for(int i = 0; i < R; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < C; ++j)
dp[i,j] = -1;
int ans = 0;
for (int i=0; iPHP
= $R || $j >= $C)
return false;
return true;
}
// Check whether current character is adjacent to previous
// character (character processed in parent call) or not.
function isadjacent($prev, $curr)
{
return ((ord($curr) - ord($prev)) == 1);
}
// i, j are the indices of the current cell and prev is the
// character processed in the parent call.. also mat[i][j]
// is our current character.
function getLenUtil($mat, $i, $j,$prev)
{
global $x, $y, $dp;
// If this cell is not valid or current character is not
// adjacent to previous one (e.g. d is not adjacent to b )
// or if this cell is already included in the path than return 0.
if (!isvalid($i, $j) || !isadjacent($prev, $mat[$i][$j]))
return 0;
// If this subproblem is already solved , return the answer
if ($dp[$i][$j] != -1)
return $dp[$i][$j];
$ans = 0; // Initialize answer
// recur for paths with different adjacent cells and store
// the length of longest path.
for ($k=0; $k<8; $k++)
$ans = max($ans, 1 + getLenUtil($mat, $i + $x[$k],
$j + $y[$k], $mat[$i][$j]));
// save the answer and return
$dp[$i][$j] = $ans;
return $ans;
}
// Returns length of the longest path
// with all characters consecutive to
// each other. This function first
// initializes dp array that is used
// to store results of subproblems,
// then it calls recursive DFS based
// function getLenUtil() to find max length path
function getLen($mat, $s)
{
global $R, $C, $x, $y;
$ans = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $R; $i++)
{
for ($j = 0; $j < $C; $j++)
{
// check for each possible starting point
if ($mat[$i][$j] == $s)
{
// recur for all eight adjacent cells
for ($k = 0; $k < 8; $k++)
$ans = max($ans, 1 + getLenUtil($mat,
$i + $x[$k], $j + $y[$k], $s));
}
}
}
return $ans;
}
// Driver code
$mat = array(array('a','c','d'),
array( 'h','b','a'),
array( 'i','g','f'));
print(getLen($mat, 'a')."\n");
print(getLen($mat, 'e')."\n" );
print(getLen($mat, 'b') ."\n");
print(getLen($mat, 'f') ."\n");
// This code is contributed by chandan_jnu
?>输出:
4
0
3
4感谢Gaurav Ahirwar提供上述解决方案。