给定一个二叉树,其中N个节点的取值范围为0到N – 1,并且N-1个边缘,并且数组arr []由边缘的值组成,任务是找到将树分成两半的最大代价。
The cost of splitting a tree is equal to the product of sum of node values of the splitted subtrees.
例子:
Input: N = 6, arr[] = {13, 8, 7, 4, 5, 9}, Edges[][] = {{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {1, 4}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}}
Output: 504
Explanation:
Below is the given tree and resultant tree after removing the edge:

Remove the edge between 1st and 4th, then
t1 = valueat[0] + valueat[1] + valueat[2] = 13 + 8 + 7
t1 = valueat[3] + valueat[4] + valueat[5] = 4 + 5 + 9
t1*t2 = (13 + 8 + 7) * (4 + 5 + 9) = 504
Input: N = 7, arr[]= {13, 8, 7, 4, 5, 9, 100}, Edges[][] = { {0, 1}, {1, 2}, {1, 4}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}, {2, 6}}
Output: 4600
Explanation:
Below is the given tree and resultant tree after removing the edge:
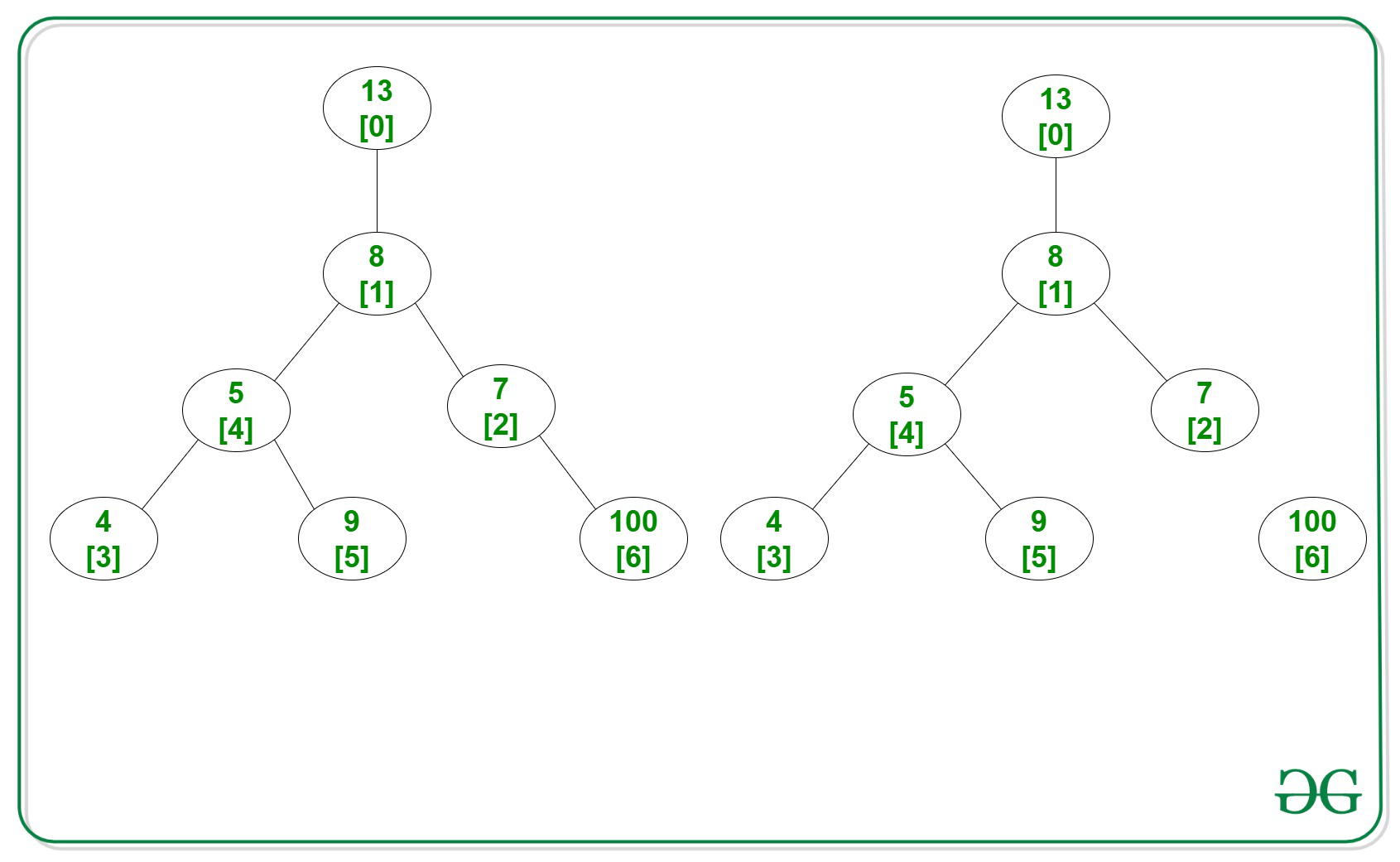
Remove the edge between 2nd and 6th, then
t1 = valueat[0] + valueat[1] + valueat[2] + valueat[3] + valueat[4] + valueat[5]= 13 + 8 + 7 + 4 + 5 + 9
t2 = valueat[6] = 100
t1*t2 = (13 + 8 + 7 + 5 + 4 + 9) * (100) = 4600
方法:想法是遍历给定的树,并尝试在每个可能的边缘断开树,然后找到在该边缘分裂的最大成本。完成上述所有步骤后,请在所有拆分中打印最大成本。步骤如下:
- 使用邻接列表边存储所有边,并且每个节点处的值存储在给定数组arr []中。
- 对于当前节点,找到其后代(包括自身)中的值之和。
- 假设如果删除当前节点与其父节点之间的边缘,则可以形成两棵树。
- 现在,计算t1,t2的值,并检查t1和t2的乘积是否最大。
- 对当前节点的所有子节点递归地重复此过程。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// To store the results and sum of
// all nodes in the array
int ans = 0, allsum = 0;
// To create adjacency list
vector edges[100001];
// Function to add edges into the
// adjacency list
void addedge(int a, int b)
{
edges[a].push_back(b);
edges[b].push_back(a);
}
// Recursive function that calculate
// the value of the cost of splitting
// the tree recursively
void findCost(int r, int p, int arr[])
{
int i, cur;
for (i = 0; i < edges[r].size();
i++) {
// Fetch the child of node-r
cur = edges[r].at(i);
// Neglect if cur node is parent
if (cur == p)
continue;
findCost(cur, r, arr);
// Add all values of nodes
// which are decendents of r
arr[r] += arr[cur];
}
// The two trees formed are rooted
// at 'r' with its decendents
int t1 = arr[r];
int t2 = allsum - t1;
// Check and replace if current
// product t1*t2 is large
if (t1 * t2 > ans) {
ans = t1 * t2;
}
}
// Function to find the maximum cost
// after splitting the tree in 2 halves
void maximumCost(int r, int p,
int N, int M,
int arr[],
int Edges[][2])
{
// Find sum of values in all nodes
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
allsum += arr[i];
}
// Traverse edges to create
// adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
addedge(Edges[i][0],
Edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call
findCost(r, p, arr);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int a, b, N = 6;
// Values in each node
int arr[] = { 13, 8, 7, 4, 5, 9 };
int M = 5;
// Given Edges
int Edges[][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 2 },
{ 1, 4 }, { 3, 4 },
{ 4, 5 } };
maximumCost(1, -1, N, M, arr, Edges);
cout << ans;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// To store the results and sum of
// all nodes in the array
static int ans = 0, allsum = 0;
// To create adjacency list
static Vector []edges = new Vector[100001];
// Function to add edges into the
// adjacency list
static void addedge(int a, int b)
{
edges[a].add(b);
edges[b].add(a);
}
// Recursive function that calculate
// the value of the cost of splitting
// the tree recursively
static void findCost(int r, int p, int arr[])
{
int i, cur;
for (i = 0; i < edges[r].size(); i++)
{
// Fetch the child of node-r
cur = edges[r].get(i);
// Neglect if cur node is parent
if (cur == p)
continue;
findCost(cur, r, arr);
// Add all values of nodes
// which are decendents of r
arr[r] += arr[cur];
}
// The two trees formed are rooted
// at 'r' with its decendents
int t1 = arr[r];
int t2 = allsum - t1;
// Check and replace if current
// product t1*t2 is large
if (t1 * t2 > ans)
{
ans = t1 * t2;
}
}
// Function to find the maximum cost
// after splitting the tree in 2 halves
static void maximumCost(int r, int p,
int N, int M,
int arr[],
int Edges[][])
{
// Find sum of values in all nodes
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
allsum += arr[i];
}
// Traverse edges to create
// adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
addedge(Edges[i][0],
Edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call
findCost(r, p, arr);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, b, N = 6;
// Values in each node
int arr[] = {13, 8, 7, 4, 5, 9};
int M = 5;
// Given Edges
int Edges[][] = {{0, 1}, {1, 2},
{1, 4}, {3, 4},
{4, 5}};
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++)
edges[i] = new Vector();
maximumCost(1, -1, N, M, arr, Edges);
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# To store the results and sum of
# all nodes in the array
ans = 0
allsum = 0
# To create adjacency list
edges = [[] for i in range(100001)]
# Function to add edges into the
# adjacency list
def addedge(a, b):
global edges
edges[a].append(b)
edges[b].append(a)
# Recursive function that calculate
# the value of the cost of splitting
# the tree recursively
def findCost(r, p, arr):
global edges
global ans
global allsum
i = 0
for i in range(len(edges[r])):
# Fetch the child of node-r
cur = edges[r][i]
# Neglect if cur node is parent
if (cur == p):
continue
findCost(cur, r, arr)
# Add all values of nodes
# which are decendents of r
arr[r] += arr[cur]
# The two trees formed are rooted
# at 'r' with its decendents
t1 = arr[r]
t2 = allsum - t1
# Check and replace if current
# product t1*t2 is large
if (t1 * t2 > ans):
ans = t1 * t2
# Function to find the maximum cost
# after splitting the tree in 2 halves
def maximumCost(r, p, N, M, arr, Edges):
global allsum
# Find sum of values in all nodes
for i in range(N):
allsum += arr[i]
# Traverse edges to create
# adjacency list
for i in range(M):
addedge(Edges[i][0], Edges[i][1])
# Function Call
findCost(r, p, arr)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 6
# Values in each node
arr = [ 13, 8, 7, 4, 5, 9 ]
M = 5
# Given Edges
Edges = [ [ 0, 1 ], [ 1, 2 ],
[ 1, 4 ], [ 3, 4 ],
[ 4, 5 ] ]
maximumCost(1, -1, N, M, arr, Edges)
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by ipg2016107C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// To store the results and sum of
// all nodes in the array
static int ans = 0, allsum = 0;
// To create adjacency list
static List []edges = new List[100001];
// Function to add edges into the
// adjacency list
static void addedge(int a, int b)
{
edges[a].Add(b);
edges[b].Add(a);
}
// Recursive function that calculate
// the value of the cost of splitting
// the tree recursively
static void findCost(int r, int p, int []arr)
{
int i, cur;
for (i = 0; i < edges[r].Count; i++)
{
// Fetch the child of node-r
cur = edges[r][i];
// Neglect if cur node is parent
if (cur == p)
continue;
findCost(cur, r, arr);
// Add all values of nodes
// which are decendents of r
arr[r] += arr[cur];
}
// The two trees formed are rooted
// at 'r' with its decendents
int t1 = arr[r];
int t2 = allsum - t1;
// Check and replace if current
// product t1*t2 is large
if (t1 * t2 > ans)
{
ans = t1 * t2;
}
}
// Function to find the maximum cost
// after splitting the tree in 2 halves
static void maximumCost(int r, int p,
int N, int M,
int []arr, int [, ]Edges)
{
// Find sum of values in all nodes
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
allsum += arr[i];
}
// Traverse edges to create
// adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
addedge(Edges[i, 0],
Edges[i, 1]);
}
// Function Call
findCost(r, p, arr);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 6;
// Values in each node
int []arr = {13, 8, 7, 4, 5, 9};
int M = 5;
// Given Edges
int [,]Edges = {{0, 1},
{1, 2}, {1, 4},
{3, 4}, {4, 5}};
for (int i = 0; i < edges.Length; i++)
edges[i] = new List();
maximumCost(1, -1, N, M, arr, Edges);
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji 504
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)