给定无向加权图G ,任务是使用Prim的算法找到图的最大生成树
Prims algorithm is a Greedy algorithm which can be used to find the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) as well as the Maximum Spanning Tree of a Graph.
例子:
Input: graph[V][V] = {{0, 2, 0, 6, 0}, {2, 0, 3, 8, 5}, {0, 3, 0, 0, 7}, {6, 8, 0, 0, 9}, {0, 5, 7, 9, 0}}
Output:
The total weight of the Maximum Spanning tree is 30.
Edges Weight
3 – 1 8
4 – 2 7
0 – 3 6
3 – 4 9
Explanation:
Choosing other edges won’t result in maximum spanning tree.
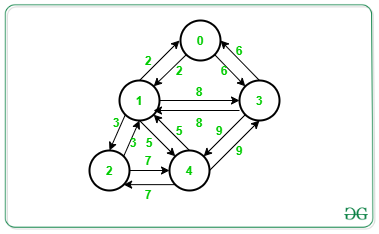
最大生成树:
给定无向加权图,最大生成树是具有最大权重的生成树。使用Prim的算法可以很容易地计算出它。这里的目标是在所有可能的生成树中找到具有最大权重的生成树。
普里姆算法:
Prim的算法是一种贪婪算法,其工作原理是生成树必须连接所有顶点。该算法的工作原理是,从任意起始顶点一次构建一个顶点,并在树与另一个顶点之间添加最昂贵的可能连接,这将为我们提供最大生成树(MST) 。
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化已访问的布尔数据类型的数组,以跟踪到目前为止已访问的顶点。用false初始化所有值。
- 初始化一个数组weights [] ,表示连接该顶点的最大权重。用某个最小值初始化所有值。
- 初始化一个数组parent [] ,以跟踪最大生成树。
- 分配一些较大的值,作为第一个顶点的权重,将父级的权重设置为-1 ,以便首先选择该值且没有父级。
- 从所有未访问的顶点中,选择一个具有最大权重的顶点v并将其标记为已访问。
- 更新v的所有未访问相邻顶点的权重。要更新权重,请遍历v的所有未访问邻居。对于每一个相邻的顶点的x,如果V之间的边缘和重量x大于V的前面的值时,更新的v的与权重的值。
下面是上述算法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
#define V 5
// Function to find index of max-weight
// vertex from set of unvisited vertices
int findMaxVertex(bool visited[], int weights[])
{
// Stores the index of max-weight vertex
// from set of unvisited vertices
int index = -1;
// Stores the maximum weight from
// the set of unvisited vertices
int maxW = INT_MIN;
// Iterate over all possible
// nodes of a graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// If the current node is unvisited
// and weight of current vertex is
// greater than maxW
if (visited[i] == false
&& weights[i] > maxW) {
// Update maxW
maxW = weights[i];
// Update index
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
// Utility function to find the maximum
// spanning tree of graph
void printMaximumSpanningTree(int graph[V][V],
int parent[])
{
// Stores total weight of
// maximum spanning tree
// of a graph
int MST = 0;
// Iterate over all possible nodes
// of a graph
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) {
// Update MST
MST += graph[i][parent[i]];
}
cout << "Weight of the maximum Spanning-tree "
<< MST << '\n'
<< '\n';
cout << "Edges \tWeight\n";
// Print the Edges and weight of
// maximum spanning tree of a graph
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) {
cout << parent[i] << " - " << i << " \t"
<< graph[i][parent[i]] << " \n";
}
}
// Function to find the maximum spanning tree
void maximumSpanningTree(int graph[V][V])
{
// visited[i]:Check if vertex i
// is visited or not
bool visited[V];
// weights[i]: Stores maximum weight of
// graph to connect an edge with i
int weights[V];
// parent[i]: Stores the parent node
// of vertex i
int parent[V];
// Initialize weights as -INFINITE,
// and visited of a node as false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
weights[i] = INT_MIN;
}
// Include 1st vertex in
// maximum spanning tree
weights[0] = INT_MAX;
parent[0] = -1;
// Search for other (V-1) vertices
// and build a tree
for (int i = 0; i < V - 1; i++) {
// Stores index of max-weight vertex
// from a set of unvisited vertex
int maxVertexIndex
= findMaxVertex(visited, weights);
// Mark that vertex as visited
visited[maxVertexIndex] = true;
// Update adjacent vertices of
// the current visited vertex
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
// If there is an edge between j
// and current visited vertex and
// also j is unvisited vertex
if (graph[j][maxVertexIndex] != 0
&& visited[j] == false) {
// If graph[v][x] is
// greater than weight[v]
if (graph[j][maxVertexIndex] > weights[j]) {
// Update weights[j]
weights[j] = graph[j][maxVertexIndex];
// Update parent[j]
parent[j] = maxVertexIndex;
}
}
}
}
// Print maximum spanning tree
printMaximumSpanningTree(graph, parent);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given graph
int graph[V][V] = { { 0, 2, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 3, 8, 5 },
{ 0, 3, 0, 0, 7 },
{ 6, 8, 0, 0, 9 },
{ 0, 5, 7, 9, 0 } };
// Function call
maximumSpanningTree(graph);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above algorithm
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
public static int V = 5;
// Function to find index of max-weight
// vertex from set of unvisited vertices
static int findMaxVertex(boolean visited[],
int weights[])
{
// Stores the index of max-weight vertex
// from set of unvisited vertices
int index = -1;
// Stores the maximum weight from
// the set of unvisited vertices
int maxW = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Iterate over all possible
// nodes of a graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If the current node is unvisited
// and weight of current vertex is
// greater than maxW
if (visited[i] == false && weights[i] > maxW)
{
// Update maxW
maxW = weights[i];
// Update index
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
// Utility function to find the maximum
// spanning tree of graph
static void printMaximumSpanningTree(int graph[][],
int parent[])
{
// Stores total weight of
// maximum spanning tree
// of a graph
int MST = 0;
// Iterate over all possible nodes
// of a graph
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++)
{
// Update MST
MST += graph[i][parent[i]];
}
System.out.println("Weight of the maximum Spanning-tree "
+ MST);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Edges \tWeight");
// Print the Edges and weight of
// maximum spanning tree of a graph
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++)
{
System.out.println(parent[i] + " - " + i + " \t"
+ graph[i][parent[i]]);
}
}
// Function to find the maximum spanning tree
static void maximumSpanningTree(int[][] graph)
{
// visited[i]:Check if vertex i
// is visited or not
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
// weights[i]: Stores maximum weight of
// graph to connect an edge with i
int[] weights = new int[V];
// parent[i]: Stores the parent node
// of vertex i
int[] parent = new int[V];
// Initialize weights as -INFINITE,
// and visited of a node as false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
weights[i] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
// Include 1st vertex in
// maximum spanning tree
weights[0] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
parent[0] = -1;
// Search for other (V-1) vertices
// and build a tree
for (int i = 0; i < V - 1; i++) {
// Stores index of max-weight vertex
// from a set of unvisited vertex
int maxVertexIndex
= findMaxVertex(visited, weights);
// Mark that vertex as visited
visited[maxVertexIndex] = true;
// Update adjacent vertices of
// the current visited vertex
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
// If there is an edge between j
// and current visited vertex and
// also j is unvisited vertex
if (graph[j][maxVertexIndex] != 0
&& visited[j] == false) {
// If graph[v][x] is
// greater than weight[v]
if (graph[j][maxVertexIndex]
> weights[j]) {
// Update weights[j]
weights[j]
= graph[j][maxVertexIndex];
// Update parent[j]
parent[j] = maxVertexIndex;
}
}
}
}
// Print maximum spanning tree
printMaximumSpanningTree(graph, parent);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given graph
int[][] graph = { { 0, 2, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 3, 8, 5 },
{ 0, 3, 0, 0, 7 },
{ 6, 8, 0, 0, 9 },
{ 0, 5, 7, 9, 0 } };
// Function call
maximumSpanningTree(graph);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L VPython3
# Python program for the above algorithm
import sys
V = 5;
# Function to find index of max-weight
# vertex from set of unvisited vertices
def findMaxVertex(visited, weights):
# Stores the index of max-weight vertex
# from set of unvisited vertices
index = -1;
# Stores the maximum weight from
# the set of unvisited vertices
maxW = -sys.maxsize;
# Iterate over all possible
# Nodes of a graph
for i in range(V):
# If the current Node is unvisited
# and weight of current vertex is
# greater than maxW
if (visited[i] == False and weights[i] > maxW):
# Update maxW
maxW = weights[i];
# Update index
index = i;
return index;
# Utility function to find the maximum
# spanning tree of graph
def printMaximumSpanningTree(graph, parent):
# Stores total weight of
# maximum spanning tree
# of a graph
MST = 0;
# Iterate over all possible Nodes
# of a graph
for i in range(1, V):
# Update MST
MST += graph[i][parent[i]];
print("Weight of the maximum Spanning-tree ", MST);
print();
print("Edges \tWeight");
# Prthe Edges and weight of
# maximum spanning tree of a graph
for i in range(1, V):
print(parent[i] , " - " , i , " \t" , graph[i][parent[i]]);
# Function to find the maximum spanning tree
def maximumSpanningTree(graph):
# visited[i]:Check if vertex i
# is visited or not
visited = [True]*V;
# weights[i]: Stores maximum weight of
# graph to connect an edge with i
weights = [0]*V;
# parent[i]: Stores the parent Node
# of vertex i
parent = [0]*V;
# Initialize weights as -INFINITE,
# and visited of a Node as False
for i in range(V):
visited[i] = False;
weights[i] = -sys.maxsize;
# Include 1st vertex in
# maximum spanning tree
weights[0] = sys.maxsize;
parent[0] = -1;
# Search for other (V-1) vertices
# and build a tree
for i in range(V - 1):
# Stores index of max-weight vertex
# from a set of unvisited vertex
maxVertexIndex = findMaxVertex(visited, weights);
# Mark that vertex as visited
visited[maxVertexIndex] = True;
# Update adjacent vertices of
# the current visited vertex
for j in range(V):
# If there is an edge between j
# and current visited vertex and
# also j is unvisited vertex
if (graph[j][maxVertexIndex] != 0 and visited[j] == False):
# If graph[v][x] is
# greater than weight[v]
if (graph[j][maxVertexIndex] > weights[j]):
# Update weights[j]
weights[j] = graph[j][maxVertexIndex];
# Update parent[j]
parent[j] = maxVertexIndex;
# Prmaximum spanning tree
printMaximumSpanningTree(graph, parent);
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Given graph
graph = [[0, 2, 0, 6, 0], [2, 0, 3, 8, 5], [0, 3, 0, 0, 7], [6, 8, 0, 0, 9],
[0, 5, 7, 9, 0]];
# Function call
maximumSpanningTree(graph);
# This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarC#
// C# program for the above algorithm
using System;
class GFG
{
public static int V = 5;
// Function to find index of max-weight
// vertex from set of unvisited vertices
static int findMaxVertex(bool[] visited,
int[] weights)
{
// Stores the index of max-weight vertex
// from set of unvisited vertices
int index = -1;
// Stores the maximum weight from
// the set of unvisited vertices
int maxW = int.MinValue;
// Iterate over all possible
// nodes of a graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If the current node is unvisited
// and weight of current vertex is
// greater than maxW
if (visited[i] == false && weights[i] > maxW)
{
// Update maxW
maxW = weights[i];
// Update index
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
// Utility function to find the maximum
// spanning tree of graph
static void printMaximumSpanningTree(int[, ] graph,
int[] parent)
{
// Stores total weight of
// maximum spanning tree
// of a graph
int MST = 0;
// Iterate over all possible nodes
// of a graph
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++)
{
// Update MST
MST += graph[i, parent[i]];
}
Console.WriteLine(
"Weight of the maximum Spanning-tree " + MST);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Edges \tWeight");
// Print the Edges and weight of
// maximum spanning tree of a graph
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) {
Console.WriteLine(parent[i] + " - " + i + " \t"
+ graph[i, parent[i]]);
}
}
// Function to find the maximum spanning tree
static void maximumSpanningTree(int[, ] graph)
{
// visited[i]:Check if vertex i
// is visited or not
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
// weights[i]: Stores maximum weight of
// graph to connect an edge with i
int[] weights = new int[V];
// parent[i]: Stores the parent node
// of vertex i
int[] parent = new int[V];
// Initialize weights as -INFINITE,
// and visited of a node as false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
weights[i] = int.MinValue;
}
// Include 1st vertex in
// maximum spanning tree
weights[0] = int.MaxValue;
parent[0] = -1;
// Search for other (V-1) vertices
// and build a tree
for (int i = 0; i < V - 1; i++) {
// Stores index of max-weight vertex
// from a set of unvisited vertex
int maxVertexIndex
= findMaxVertex(visited, weights);
// Mark that vertex as visited
visited[maxVertexIndex] = true;
// Update adjacent vertices of
// the current visited vertex
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
// If there is an edge between j
// and current visited vertex and
// also j is unvisited vertex
if (graph[j, maxVertexIndex] != 0
&& visited[j] == false) {
// If graph[v][x] is
// greater than weight[v]
if (graph[j, maxVertexIndex]
> weights[j]) {
// Update weights[j]
weights[j]
= graph[j, maxVertexIndex];
// Update parent[j]
parent[j] = maxVertexIndex;
}
}
}
}
// Print maximum spanning tree
printMaximumSpanningTree(graph, parent);
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main()
{
// Given graph
int[, ] graph = { { 0, 2, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 3, 8, 5 },
{ 0, 3, 0, 0, 7 },
{ 6, 8, 0, 0, 9 },
{ 0, 5, 7, 9, 0 } };
// Function call
maximumSpanningTree(graph);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L VWeight of the maximum Spanning-tree 30
Edges Weight
3 - 1 8
4 - 2 7
0 - 3 6
3 - 4 9时间复杂度: O(V 2 ),其中V是图中的节点数。
辅助空间: O(V 2 )