在此排序算法中,哈希函数f与Order Preserving 函数的属性一起使用,该属性指出![]() 。
。
哈希函数:
f(x) = floor( (x/maximum) * SIZE )
where maximum => maximum value in the array,
SIZE => size of the address table (10 in our case),
floor => floor function
该算法使用地址表来存储值,该值只是链接列表的列表(或数组)。哈希函数应用于数组中的每个值,以在地址表中找到其对应的地址。然后,通过将这些值与该地址中已经存在的值进行比较,以有序的方式将其插入到其对应的地址中。
例子:
Input : arr = [29, 23, 14, 5, 15, 10, 3, 18, 1]
Output:
After inserting all the values in the address table, the address table looks like this:
ADDRESS 0: 1 --> 3
ADDRESS 1: 5
ADDRESS 2:
ADDRESS 3: 10
ADDRESS 4: 14 --> 15
ADDRESS 5: 18
ADDRESS 6:
ADDRESS 7: 23
ADDRESS 8:
ADDRESS 9: 29
下图显示了上面讨论的示例的地址表的表示形式:
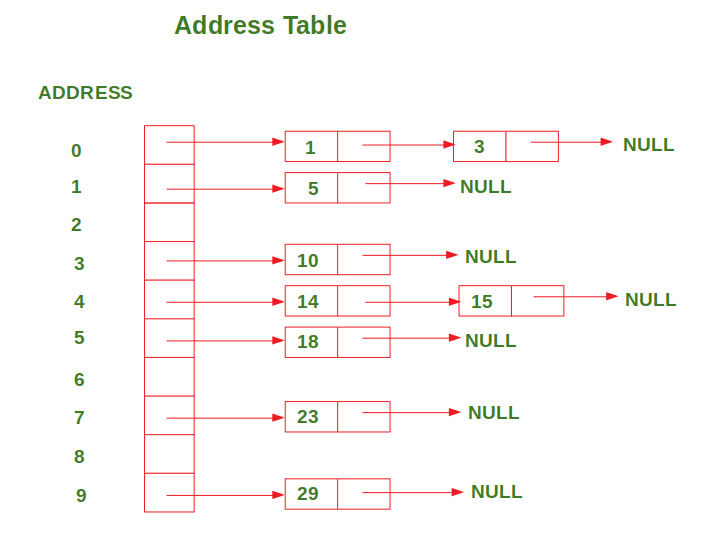
插入后,将对地址表中每个地址的值进行排序。因此,我们一个接一个地遍历每个地址,并将值插入该地址到输入数组中。
下面是上述方法的实现
# Python3 code for implementation of
# Address Calculation Sorting using Hashing
# Size of the address table (In this case 0-9)
SIZE = 10
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data = None):
self.data = data
self.nextNode = None
class LinkedList(object):
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Insert values in such a way that the list remains sorted
def insert(self, data):
newNode = Node(data)
# If there is no node or new Node's value
# is smaller than the first value in the list,
# Insert new Node in the first place
if self.head == None or data < self.head.data:
newNode.nextNode = self.head
self.head = newNode
else:
current = self.head
# If the next node is null or its value
# is greater than the new Node's value,
# Insert new Node in that place
while current.nextNode != None \
and \
current.nextNode.data < data:
current = current.nextNode
newNode.nextNode = current.nextNode
current.nextNode = newNode
# This function sorts the given list
# using Address Calculation Sorting using Hashing
def addressCalculationSort(arr):
# Declare a list of Linked Lists of given SIZE
listOfLinkedLists = []
for i in range(SIZE):
listOfLinkedLists.append(LinkedList())
# Calculate maximum value in the array
maximum = max(arr)
# Find the address of each value
# in the address table
# and insert it in that list
for val in arr:
address = hashFunction(val, maximum)
listOfLinkedLists[address].insert(val)
# Print the address table
# after all the values have been inserted
for i in range(SIZE):
current = listOfLinkedLists[i].head
print("ADDRESS " + str(i), end = ": ")
while current != None:
print(current.data, end = " ")
current = current.nextNode
print()
# Assign the sorted values to the input array
index = 0
for i in range(SIZE):
current = listOfLinkedLists[i].head
while current != None:
arr[index] = current.data
index += 1
current = current.nextNode
# This function returns the corresponding address
# of given value in the address table
def hashFunction(num, maximum):
# Scale the value such that address is between 0 to 9
address = int((num * 1.0 / maximum) * (SIZE-1))
return address
# -------------------------------------------------------
# Driver code
# giving the input address as follows
arr = [29, 23, 14, 5, 15, 10, 3, 18, 1]
# Printing the Input array
print("\nInput array: " + " ".join([str(x) for x in arr]))
# Performing address calculation sort
addressCalculationSort(arr)
# printing the result sorted array
print("\nSorted array: " + " ".join([str(x) for x in arr]))
输出:
Input array: 29 23 14 5 15 10 3 18 1
ADDRESS 0: 1 3
ADDRESS 1: 5
ADDRESS 2:
ADDRESS 3: 10
ADDRESS 4: 14 15
ADDRESS 5: 18
ADDRESS 6:
ADDRESS 7: 23
ADDRESS 8:
ADDRESS 9: 29
Sorted array: 1 3 5 10 14 15 18 23 29
时间复杂度:
该算法的时间复杂度为![]() 在最好的情况下。当数组中的值均匀分布在特定范围内时,会发生这种情况。
在最好的情况下。当数组中的值均匀分布在特定范围内时,会发生这种情况。
而最坏情况下的时间复杂度是![]() 。当大多数值占用1或2个地址时会发生这种情况,因为需要大量工作才能将每个值插入其适当位置。
。当大多数值占用1或2个地址时会发生这种情况,因为需要大量工作才能将每个值插入其适当位置。