给定一个二叉搜索树和一个二进制整数K ,如果K = 0 ,则任务是将二叉搜索树按升序转换为倾斜树,如果K = 1 ,则按降序转换。
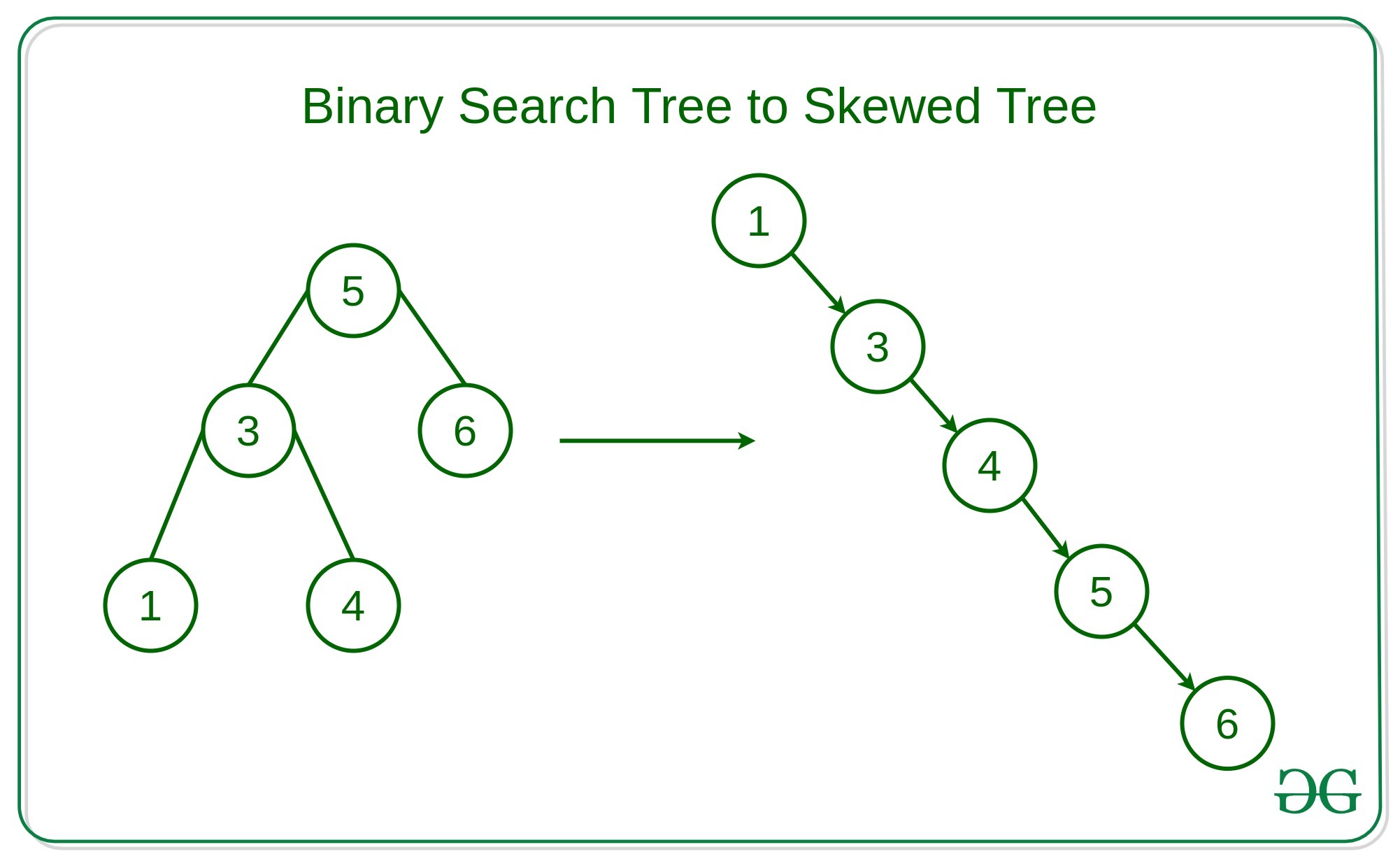
例子:
Input: K = 0,
5
/ \
3 6
Output:
3
\
5
\
6
Input: K = 1,
2
/ \
1 3
Output:
3
\
2
\
1方法:
- 问题中的主要观察结果是,偏斜树的第一个节点将分别是BST的最左节点或最右节点,分别用于递增顺序和递减顺序。
- 对于递增顺序,我们需要进行顺序遍历,因为BST的顺序遍历为我们提供了节点值的递增顺序。因此,在每个节点上的遍历顺序将是:
- 左节点:递归到其左节点(如果存在)以获取较小的值。
- 根节点:完全遍历其左节点/子树后,将偏斜树的前一个节点连接到根节点。
- 右节点:递归到右节点(如果存在),以获取更大的值。
- 对于递减顺序,在每个节点上的遍历顺序将是:
- 右节点:递归到其右节点(如果存在)以获取更大的值。
- 根节点:完全遍历其右节点/子树后,将偏斜树的前一个节点连接到根节点。
- 左侧节点:递归到左侧节点/子树以获取较小的值。
- 同样,通过跟踪先前的节点,我们可以根据所需顺序遍历二叉搜索树并形成倾斜的树。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++14
// C++ implementation to flatten the
// binary search tree into a skewed
// tree in increasing / decreasing order
#include
using namespace std;
// Class of the node
struct Node
{
int val;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int x)
{
val = x;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
Node *prevNode = NULL;
Node *headNode = NULL;
// Function to to flatten the binary
// search tree into a skewed tree in
// increasing / decreasing order
void flattenBTToSkewed(Node *root, int order)
{
// Base Case
if (!root)
return;
// Condition to check the order
// in which the skewed tree to
// maintained
if (order)
flattenBTToSkewed(root->right, order);
else
flattenBTToSkewed(root->left, order);
Node *rightNode = root->right;
Node *leftNode = root->left;
// Condition to check if the root Node
// of the skewed tree is not defined
if (!headNode)
{
headNode = root;
root->left = NULL;
prevNode = root;
}
else
{
prevNode->right = root;
root->left = NULL;
prevNode = root;
}
// Similarly recurse for the left / right
// subtree on the basis of the order required
if (order)
flattenBTToSkewed(leftNode, order);
else
flattenBTToSkewed(rightNode, order);
}
// Function to traverse the right
// skewed tree using recursion
void traverseRightSkewed(Node *root)
{
if (!root)
return;
cout << root->val << " ";
traverseRightSkewed(root->right);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// 5
// / \
// 3 6
Node *root =new Node(5);
root->left = new Node(3);
root->right = new Node(6);
// Order of the Skewed tree can
// be defined as follows -
// For Increasing order - 0
// For Decreasing order - 1
int order = 0;
flattenBTToSkewed(root, order);
traverseRightSkewed(headNode);
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 Java
// Java implementation to flatten the
// binary search tree into a skewed
// tree in increasing / decreasing order
import java.io.*;
// Class of the node
class Node
{
int val;
Node left, right;
// Helper function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL left and right
// pointers.
Node(int item)
{
val = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG
{
public static Node node;
static Node prevNode = null;
static Node headNode = null;
// Function to to flatten the binary
// search tree into a skewed tree in
// increasing / decreasing order
static void flattenBTToSkewed(Node root,
int order)
{
// Base Case
if(root == null)
{
return;
}
// Condition to check the order
// in which the skewed tree to
// maintained
if(order > 0)
{
flattenBTToSkewed(root.right, order);
}
else
{
flattenBTToSkewed(root.left, order);
}
Node rightNode = root.right;
Node leftNode = root.left;
// Condition to check if the root Node
// of the skewed tree is not defined
if(headNode == null)
{
headNode = root;
root.left = null;
prevNode = root;
}
else
{
prevNode.right = root;
root.left = null;
prevNode = root;
}
// Similarly recurse for the left / right
// subtree on the basis of the order required
if (order > 0)
{
flattenBTToSkewed(leftNode, order);
}
else
{
flattenBTToSkewed(rightNode, order);
}
}
// Function to traverse the right
// skewed tree using recursion
static void traverseRightSkewed(Node root)
{
if(root == null)
{
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
traverseRightSkewed(root.right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// 5
// / \
// 3 6
GFG tree = new GFG();
tree.node = new Node(5);
tree.node.left = new Node(3);
tree.node.right = new Node(6);
// Order of the Skewed tree can
// be defined as follows -
// For Increasing order - 0
// For Decreasing order - 1
int order = 0;
flattenBTToSkewed(node, order);
traverseRightSkewed(headNode);
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155Python3
# Python3 implementation to flatten
# the binary search tree into a skewed
# tree in increasing / decreasing order
# Class of the node
class Node:
# Constructor of node
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
prevNode = None
headNode = None
# Function to to flatten
# the binary search tree into a skewed
# tree in increasing / decreasing order
def flattenBTToSkewed(root, order):
# Base Case
if not root:
return
# Condition to check the order
# in which the skewed tree to maintained
if order:
flattenBTToSkewed(root.right, order)
else:
flattenBTToSkewed(root.left, order)
global headNode; global prevNode
rightNode = root.right
leftNode = root.left
# Condition to check if the root Node
# of the skewed tree is not defined
if not headNode:
headNode = root
root.left = None
prevNode = root
else:
prevNode.right = root
root.left = None
prevNode = root
# Similarly recurse for the left / right
# subtree on the basis of the order required
if order:
flattenBTToSkewed(leftNode, order)
else:
flattenBTToSkewed(rightNode, order)
# Function to traverse the right
# skewed tree using recursion
def traverseRightSkewed(root):
if not root:
return
print(root.val, end = " ")
traverseRightSkewed(root.right)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 5
# / \
# 3 6
root = Node(5)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(6)
prevNode = None
headNode = None
# Order of the Skewed tree can
# be defined as follows -
# For Increasing order - 0
# For Decreasing order - 1
order = 0
flattenBTToSkewed(root, order)
traverseRightSkewed(headNode)C#
// C# implementation to flatten the
// binary search tree into a skewed
// tree in increasing / decreasing order
using System;
// Class of the node
class Node
{
public int val;
public Node left, right;
// Helper function that allocates a new
// node with the given data and NULL
// left and right pointers.
public Node(int item)
{
val = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG{
public static Node node;
static Node prevNode = null;
static Node headNode = null;
// Function to to flatten the binary
// search tree into a skewed tree in
// increasing / decreasing order
static void flattenBTToSkewed(Node root, int order)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
// Condition to check the order
// in which the skewed tree to
// maintained
if (order > 0)
{
flattenBTToSkewed(root.right, order);
}
else
{
flattenBTToSkewed(root.left, order);
}
Node rightNode = root.right;
Node leftNode = root.left;
// Condition to check if the root Node
// of the skewed tree is not defined
if (headNode == null)
{
headNode = root;
root.left = null;
prevNode = root;
}
else
{
prevNode.right = root;
root.left = null;
prevNode = root;
}
// Similarly recurse for the left / right
// subtree on the basis of the order required
if (order > 0)
{
flattenBTToSkewed(leftNode, order);
}
else
{
flattenBTToSkewed(rightNode, order);
}
}
// Function to traverse the right
// skewed tree using recursion
static void traverseRightSkewed(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
Console.Write(root.val + " ");
traverseRightSkewed(root.right);
}
// Driver Code
static public void Main()
{
// 5
// / \
// 3 6
GFG.node = new Node(5);
GFG.node.left = new Node(3);
GFG.node.right = new Node(6);
// Order of the Skewed tree can
// be defined as follows -
// For Increasing order - 0
// For Decreasing order - 1
int order = 0;
flattenBTToSkewed(node, order);
traverseRightSkewed(headNode);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127输出:
3 5 6