什么是插值?
插值法是在一组离散的已知数据点范围内查找新数据点的方法(源Wiki)。换句话说,对于独立变量的任何中间值,插值是一种估算数学函数值的技术。
例如,在给定的表中,对于未知函数f(x),我们得到了4组离散数据点:
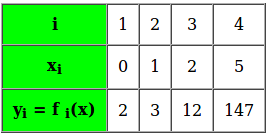
怎么找?
在这里,我们可以应用拉格朗日的插值公式来获取解决方案。
拉格朗日插值公式:
如果y = f(x)取值y0,y1,…,yn对应于x = x0,x1,…,xn,则,
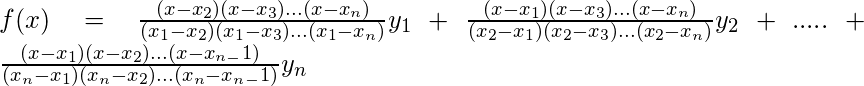
该方法比牛顿方法等同类方法更为可取,因为它甚至适用于x的不等距值。
我们可以使用插值技术来找到中间数据点,例如x = 3。
C++
// C++ program for implementation of Lagrange's Interpolation
#include
using namespace std;
// To represent a data point corresponding to x and y = f(x)
struct Data
{
int x, y;
};
// function to interpolate the given data points using Lagrange's formula
// xi corresponds to the new data point whose value is to be obtained
// n represents the number of known data points
double interpolate(Data f[], int xi, int n)
{
double result = 0; // Initialize result
for (int i=0; i Java
// Java program for implementation
// of Lagrange's Interpolation
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// To represent a data point
// corresponding to x and y = f(x)
static class Data
{
int x, y;
public Data(int x, int y)
{
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
};
// function to interpolate the given
// data points using Lagrange's formula
// xi corresponds to the new data point
// whose value is to be obtained n
// represents the number of known data points
static double interpolate(Data f[], int xi, int n)
{
double result = 0; // Initialize result
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Compute individual terms of above formula
double term = f[i].y;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (j != i)
term = term*(xi - f[j].x) / (f[i].x - f[j].x);
}
// Add current term to result
result += term;
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating an array of 4 known data points
Data f[] = {new Data(0, 2), new Data(1, 3),
new Data(2, 12), new Data(5, 147)};
// Using the interpolate function to obtain
// a data point corresponding to x=3
System.out.print("Value of f(3) is : " +
(int)interpolate(f, 3, 4));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python3 program for implementation
# of Lagrange's Interpolation
# To represent a data point corresponding to x and y = f(x)
class Data:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
# function to interpolate the given data points
# using Lagrange's formula
# xi -> corresponds to the new data point
# whose value is to be obtained
# n -> represents the number of known data points
def interpolate(f: list, xi: int, n: int) -> float:
# Initialize result
result = 0.0
for i in range(n):
# Compute individual terms of above formula
term = f[i].y
for j in range(n):
if j != i:
term = term * (xi - f[j].x) / (f[i].x - f[j].x)
# Add current term to result
result += term
return result
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# creating an array of 4 known data points
f = [Data(0, 2), Data(1, 3), Data(2, 12), Data(5, 147)]
# Using the interpolate function to obtain a data point
# corresponding to x=3
print("Value of f(3) is :", interpolate(f, 3, 4))
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552C#
// C# program for implementation
// of Lagrange's Interpolation
using System;
class GFG
{
// To represent a data point
// corresponding to x and y = f(x)
class Data
{
public int x, y;
public Data(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
};
// function to interpolate the given
// data points using Lagrange's formula
// xi corresponds to the new data point
// whose value is to be obtained n
// represents the number of known data points
static double interpolate(Data []f,
int xi, int n)
{
double result = 0; // Initialize result
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Compute individual terms
// of above formula
double term = f[i].y;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (j != i)
term = term * (xi - f[j].x) /
(f[i].x - f[j].x);
}
// Add current term to result
result += term;
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// creating an array of 4 known data points
Data []f = {new Data(0, 2),
new Data(1, 3),
new Data(2, 12),
new Data(5, 147)};
// Using the interpolate function to obtain
// a data point corresponding to x=3
Console.Write("Value of f(3) is : " +
(int)interpolate(f, 3, 4));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992输出:
Value of f(3) is : 35复杂:
上述解决方案的时间复杂度为O(n 2 ),辅助空间为O(1)。
参考:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lagrange_polynomial
高级工程数学博士BS Grewal
https://mat.iitm.ac.in/home/sryedida/public_html/caimna/interpolation/lagrange.html