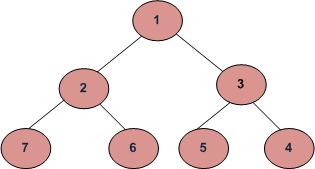
编写函数以打印树的螺旋顺序遍历。对于下面的树,函数应打印1、2、3、4、5、6、7。
方法1(递归)
该问题可以看作是级别订单遍历过帐的扩展。
要以螺旋顺序打印节点,应以交替顺序打印不同级别的节点。另一个布尔变量ltr用于更改级别的打印顺序。如果ltr为1,则printGivenLevel()从左到右打印节点,从右到左打印节点。在每次迭代中翻转ltr的值以更改顺序。
打印树的级别顺序遍历的函数
printSpiral(tree)
bool ltr = 0;
for d = 1 to height(tree)
printGivenLevel(tree, d, ltr);
ltr ~= ltr /*flip ltr*/打印给定级别的所有节点的函数
printGivenLevel(tree, level, ltr)
if tree is NULL then return;
if level is 1, then
print(tree->data);
else if level greater than 1, then
if(ltr)
printGivenLevel(tree->left, level-1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(tree->right, level-1, ltr);
else
printGivenLevel(tree->right, level-1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(tree->left, level-1, ltr);以下是上述算法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for recursive level
// order traversal in spiral form
#include
using namespace std;
// A binary tree node has data,
// pointer to left child and a
// pointer to right child
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
// Function protoypes
void printGivenLevel(struct node* root,
int level, int ltr);
int height(struct node* node);
struct node* newNode(int data);
// Function to print spiral traversal of a tree
void printSpiral(struct node* root)
{
int h = height(root);
int i;
// ltr -> Left to Right. If this variable
// is set,then the given level is traversed
// from left to right.
bool ltr = false;
for(i = 1; i <= h; i++)
{
printGivenLevel(root, i, ltr);
// Revert ltr to traverse next
// level in opposite order
ltr = !ltr;
}
}
// Print nodes at a given level
void printGivenLevel(struct node* root,
int level, int ltr)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (level == 1)
cout << root->data << " ";
else if (level > 1)
{
if (ltr)
{
printGivenLevel(root->left,
level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(root->right,
level - 1, ltr);
}
else
{
printGivenLevel(root->right,
level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(root->left,
level - 1, ltr);
}
}
}
// Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
// nodes along the longest path from the root node
// down to the farthest leaf node.
int height(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
// Compute the height of each subtree
int lheight = height(node->left);
int rheight = height(node->right);
// Use the larger one
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
// Helper function that allocates a new
// node with the given data and NULL left
// and right pointers.
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
node* newnode = new node();
newnode->data = data;
newnode->left = NULL;
newnode->right = NULL;
return (newnode);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->right = newNode(4);
printf("Spiral Order traversal of "
"binary tree is \n");
printSpiral(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by samrat2825 C
// C program for recursive level order traversal in spiral form
#include
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Function protoypes */
void printGivenLevel(struct node* root, int level, int ltr);
int height(struct node* node);
struct node* newNode(int data);
/* Function to print spiral traversal of a tree*/
void printSpiral(struct node* root)
{
int h = height(root);
int i;
/*ltr -> Left to Right. If this variable is set,
then the given level is traversed from left to right. */
bool ltr = false;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) {
printGivenLevel(root, i, ltr);
/*Revert ltr to traverse next level in opposite order*/
ltr = !ltr;
}
}
/* Print nodes at a given level */
void printGivenLevel(struct node* root, int level, int ltr)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (level == 1)
printf("%d ", root->data);
else if (level > 1) {
if (ltr) {
printGivenLevel(root->left, level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(root->right, level - 1, ltr);
}
else {
printGivenLevel(root->right, level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(root->left, level - 1, ltr);
}
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int height(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else {
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node->left);
int rheight = height(node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = (struct node*)
malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->right = newNode(4);
printf("Spiral Order traversal of binary tree is \n");
printSpiral(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for recursive level order traversal in spiral form
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
// Function to print the spiral traversal of tree
void printSpiral(Node node)
{
int h = height(node);
int i;
/* ltr -> left to right. If this variable is set then the
given label is traversed from left to right */
boolean ltr = false;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) {
printGivenLevel(node, i, ltr);
/*Revert ltr to traverse next level in opposite order*/
ltr = !ltr;
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node.*/
int height(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
else {
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node.left);
int rheight = height(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
/* Print nodes at a given level */
void printGivenLevel(Node node, int level, boolean ltr)
{
if (node == null)
return;
if (level == 1)
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
else if (level > 1) {
if (ltr != false) {
printGivenLevel(node.left, level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(node.right, level - 1, ltr);
}
else {
printGivenLevel(node.right, level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(node.left, level - 1, ltr);
}
}
}
/* Driver program to test the above functions */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(4);
System.out.println("Spiral order traversal of Binary Tree is ");
tree.printSpiral(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal(mayank_24)Python3
# Python3 program for recursive level order
# traversal in spiral form
class newNode:
# Construct to create a newNode
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
""" Function to print spiral traversal of a tree"""
def printSpiral(root):
h = height(root)
"""ltr Left to Right. If this variable
is set, then the given level is traversed
from left to right. """
ltr = False
for i in range(1, h + 1):
printGivenLevel(root, i, ltr)
"""Revert ltr to traverse next level
in opposite order"""
ltr = not ltr
""" Print nodes at a given level """
def printGivenLevel(root, level, ltr):
if(root == None):
return
if(level == 1):
print(root.data, end = " ")
elif (level > 1):
if(ltr):
printGivenLevel(root.left, level - 1, ltr)
printGivenLevel(root.right, level - 1, ltr)
else:
printGivenLevel(root.right, level - 1, ltr)
printGivenLevel(root.left, level - 1, ltr)
""" Compute the "height" of a tree -- the number of
nodes along the longest path from the root node
down to the farthest leaf node."""
def height(node):
if (node == None):
return 0
else:
""" compute the height of each subtree """
lheight = height(node.left)
rheight = height(node.right)
""" use the larger one """
if (lheight > rheight):
return(lheight + 1)
else:
return(rheight + 1)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(7)
root.left.right = newNode(6)
root.right.left = newNode(5)
root.right.right = newNode(4)
print("Spiral Order traversal of binary tree is")
printSpiral(root)
# This code is contributed
# by SHUBHAMSINGH10C#
// C# program for recursive level
// order traversal in spiral form
using System;
/* A binary tree node has data,
pointer to left child and a
pointer to right child */
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
public Node root;
// Function to print the spiral
// traversal of tree
public virtual void printSpiral(Node node)
{
int h = height(node);
int i;
/* ltr -> left to right. If this
variable is set then the given
label is traversed from left to right */
bool ltr = false;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) {
printGivenLevel(node, i, ltr);
/*Revert ltr to traverse next
level in opposite order*/
ltr = !ltr;
}
}
/* Compute the "height" of a tree -- the
number of nodes along the longest path
from the root node down to the farthest
leaf node.*/
public virtual int height(Node node)
{
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
else {
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height(node.left);
int rheight = height(node.right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight) {
return (lheight + 1);
}
else {
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
}
/* Print nodes at a given level */
public virtual void printGivenLevel(Node node,
int level,
bool ltr)
{
if (node == null) {
return;
}
if (level == 1) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
}
else if (level > 1) {
if (ltr != false) {
printGivenLevel(node.left, level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(node.right, level - 1, ltr);
}
else {
printGivenLevel(node.right, level - 1, ltr);
printGivenLevel(node.left, level - 1, ltr);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
GFG tree = new GFG();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(4);
Console.WriteLine("Spiral order traversal "
+ "of Binary Tree is ");
tree.printSpiral(tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13C++
// C++ implementation of a O(n) time method for spiral order traversal
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Binary Tree node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
void printSpiral(struct node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return; // NULL check
// Create two stacks to store alternate levels
stack s1; // For levels to be printed from right to left
stack s2; // For levels to be printed from left to right
// Push first level to first stack 's1'
s1.push(root);
// Keep printing while any of the stacks has some nodes
while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()) {
// Print nodes of current level from s1 and push nodes of
// next level to s2
while (!s1.empty()) {
struct node* temp = s1.top();
s1.pop();
cout << temp->data << " ";
// Note that is right is pushed before left
if (temp->right)
s2.push(temp->right);
if (temp->left)
s2.push(temp->left);
}
// Print nodes of current level from s2 and push nodes of
// next level to s1
while (!s2.empty()) {
struct node* temp = s2.top();
s2.pop();
cout << temp->data << " ";
// Note that is left is pushed before right
if (temp->left)
s1.push(temp->left);
if (temp->right)
s1.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
// A utility function to create a new node
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = new struct node;
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->right = newNode(4);
cout << "Spiral Order traversal of binary tree is \n";
printSpiral(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of an O(n) approach of level order
// traversal in spiral form
import java.util.*;
// A Binary Tree node
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
static Node root;
void printSpiral(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return; // NULL check
// Create two stacks to store alternate levels
// For levels to be printed from right to left
Stack s1 = new Stack();
// For levels to be printed from left to right
Stack s2 = new Stack();
// Push first level to first stack 's1'
s1.push(node);
// Keep printing while any of the stacks has some nodes
while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()) {
// Print nodes of current level from s1 and push nodes of
// next level to s2
while (!s1.empty()) {
Node temp = s1.peek();
s1.pop();
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
// Note that is right is pushed before left
if (temp.right != null)
s2.push(temp.right);
if (temp.left != null)
s2.push(temp.left);
}
// Print nodes of current level from s2 and push nodes of
// next level to s1
while (!s2.empty()) {
Node temp = s2.peek();
s2.pop();
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
// Note that is left is pushed before right
if (temp.left != null)
s1.push(temp.left);
if (temp.right != null)
s1.push(temp.right);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(4);
System.out.println("Spiral Order traversal of Binary Tree is ");
tree.printSpiral(root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal(mayank_24) Python3
# Python3 implementation of a O(n) time
# method for spiral order traversal
# A class to create a new node
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def printSpiral(root):
if (root == None):
return # None check
# Create two stacks to store
# alternate levels
s1 = [] # For levels to be printed
# from right to left
s2 = [] # For levels to be printed
# from left to right
# append first level to first stack 's1'
s1.append(root)
# Keep printing while any of the
# stacks has some nodes
while not len(s1) == 0 or not len(s2) == 0:
# Print nodes of current level from s1
# and append nodes of next level to s2
while not len(s1) == 0:
temp = s1[-1]
s1.pop()
print(temp.data, end = " ")
# Note that is right is appended
# before left
if (temp.right):
s2.append(temp.right)
if (temp.left):
s2.append(temp.left)
# Print nodes of current level from s2
# and append nodes of next level to s1
while (not len(s2) == 0):
temp = s2[-1]
s2.pop()
print(temp.data, end = " ")
# Note that is left is appended
# before right
if (temp.left):
s1.append(temp.left)
if (temp.right):
s1.append(temp.right)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(7)
root.left.right = newNode(6)
root.right.left = newNode(5)
root.right.right = newNode(4)
print("Spiral Order traversal of",
"binary tree is ")
printSpiral(root)
# This code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// C# implementation of an O(n) approach of
// level order traversal in spiral form
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// A Binary Tree node
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
public static Node root;
public virtual void printSpiral(Node node)
{
if (node == null) {
return; // NULL check
}
// Create two stacks to store alternate levels
Stack s1 = new Stack(); // For levels to be printed
// from right to left
Stack s2 = new Stack(); // For levels to be printed
// from left to right
// Push first level to first stack 's1'
s1.Push(node);
// Keep printing while any of the
// stacks has some nodes
while (s1.Count > 0 || s2.Count > 0) {
// Print nodes of current level from
// s1 and push nodes of next level to s2
while (s1.Count > 0) {
Node temp = s1.Peek();
s1.Pop();
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
// Note that is right is pushed before left
if (temp.right != null) {
s2.Push(temp.right);
}
if (temp.left != null) {
s2.Push(temp.left);
}
}
// Print nodes of current level from s2
// and push nodes of next level to s1
while (s2.Count > 0) {
Node temp = s2.Peek();
s2.Pop();
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
// Note that is left is pushed before right
if (temp.left != null) {
s1.Push(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null) {
s1.Push(temp.right);
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree.root = new Node(1);
BinaryTree.root.left = new Node(2);
BinaryTree.root.right = new Node(3);
BinaryTree.root.left.left = new Node(7);
BinaryTree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
BinaryTree.root.right.left = new Node(5);
BinaryTree.root.right.right = new Node(4);
Console.WriteLine("Spiral Order traversal of Binary Tree is ");
tree.printSpiral(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13 输出:
Spiral Order traversal of binary tree is
1 2 3 4 5 6 7时间复杂度:最坏情况是上述方法的时间复杂度为O(n ^ 2) 。最坏的情况发生在树木倾斜的情况下。
方法2(迭代)
我们可以在O(n)时间和O(n)额外空间中打印螺旋阶遍历。这个想法是使用两个堆栈。我们可以使用一个堆栈从左到右打印,而另一个堆栈从右到左打印。在每次迭代中,我们在堆栈之一中具有一个级别的节点。我们打印节点,并将下一层的节点推入其他堆栈中。
C++
// C++ implementation of a O(n) time method for spiral order traversal
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Binary Tree node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
void printSpiral(struct node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return; // NULL check
// Create two stacks to store alternate levels
stack s1; // For levels to be printed from right to left
stack s2; // For levels to be printed from left to right
// Push first level to first stack 's1'
s1.push(root);
// Keep printing while any of the stacks has some nodes
while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()) {
// Print nodes of current level from s1 and push nodes of
// next level to s2
while (!s1.empty()) {
struct node* temp = s1.top();
s1.pop();
cout << temp->data << " ";
// Note that is right is pushed before left
if (temp->right)
s2.push(temp->right);
if (temp->left)
s2.push(temp->left);
}
// Print nodes of current level from s2 and push nodes of
// next level to s1
while (!s2.empty()) {
struct node* temp = s2.top();
s2.pop();
cout << temp->data << " ";
// Note that is left is pushed before right
if (temp->left)
s1.push(temp->left);
if (temp->right)
s1.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
// A utility function to create a new node
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* node = new struct node;
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->right = newNode(4);
cout << "Spiral Order traversal of binary tree is \n";
printSpiral(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of an O(n) approach of level order
// traversal in spiral form
import java.util.*;
// A Binary Tree node
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
static Node root;
void printSpiral(Node node)
{
if (node == null)
return; // NULL check
// Create two stacks to store alternate levels
// For levels to be printed from right to left
Stack s1 = new Stack();
// For levels to be printed from left to right
Stack s2 = new Stack();
// Push first level to first stack 's1'
s1.push(node);
// Keep printing while any of the stacks has some nodes
while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()) {
// Print nodes of current level from s1 and push nodes of
// next level to s2
while (!s1.empty()) {
Node temp = s1.peek();
s1.pop();
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
// Note that is right is pushed before left
if (temp.right != null)
s2.push(temp.right);
if (temp.left != null)
s2.push(temp.left);
}
// Print nodes of current level from s2 and push nodes of
// next level to s1
while (!s2.empty()) {
Node temp = s2.peek();
s2.pop();
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
// Note that is left is pushed before right
if (temp.left != null)
s1.push(temp.left);
if (temp.right != null)
s1.push(temp.right);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(4);
System.out.println("Spiral Order traversal of Binary Tree is ");
tree.printSpiral(root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal(mayank_24)
Python3
# Python3 implementation of a O(n) time
# method for spiral order traversal
# A class to create a new node
class newNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def printSpiral(root):
if (root == None):
return # None check
# Create two stacks to store
# alternate levels
s1 = [] # For levels to be printed
# from right to left
s2 = [] # For levels to be printed
# from left to right
# append first level to first stack 's1'
s1.append(root)
# Keep printing while any of the
# stacks has some nodes
while not len(s1) == 0 or not len(s2) == 0:
# Print nodes of current level from s1
# and append nodes of next level to s2
while not len(s1) == 0:
temp = s1[-1]
s1.pop()
print(temp.data, end = " ")
# Note that is right is appended
# before left
if (temp.right):
s2.append(temp.right)
if (temp.left):
s2.append(temp.left)
# Print nodes of current level from s2
# and append nodes of next level to s1
while (not len(s2) == 0):
temp = s2[-1]
s2.pop()
print(temp.data, end = " ")
# Note that is left is appended
# before right
if (temp.left):
s1.append(temp.left)
if (temp.right):
s1.append(temp.right)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(7)
root.left.right = newNode(6)
root.right.left = newNode(5)
root.right.right = newNode(4)
print("Spiral Order traversal of",
"binary tree is ")
printSpiral(root)
# This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# implementation of an O(n) approach of
// level order traversal in spiral form
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// A Binary Tree node
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
public static Node root;
public virtual void printSpiral(Node node)
{
if (node == null) {
return; // NULL check
}
// Create two stacks to store alternate levels
Stack s1 = new Stack(); // For levels to be printed
// from right to left
Stack s2 = new Stack(); // For levels to be printed
// from left to right
// Push first level to first stack 's1'
s1.Push(node);
// Keep printing while any of the
// stacks has some nodes
while (s1.Count > 0 || s2.Count > 0) {
// Print nodes of current level from
// s1 and push nodes of next level to s2
while (s1.Count > 0) {
Node temp = s1.Peek();
s1.Pop();
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
// Note that is right is pushed before left
if (temp.right != null) {
s2.Push(temp.right);
}
if (temp.left != null) {
s2.Push(temp.left);
}
}
// Print nodes of current level from s2
// and push nodes of next level to s1
while (s2.Count > 0) {
Node temp = s2.Peek();
s2.Pop();
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
// Note that is left is pushed before right
if (temp.left != null) {
s1.Push(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right != null) {
s1.Push(temp.right);
}
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
BinaryTree.root = new Node(1);
BinaryTree.root.left = new Node(2);
BinaryTree.root.right = new Node(3);
BinaryTree.root.left.left = new Node(7);
BinaryTree.root.left.right = new Node(6);
BinaryTree.root.right.left = new Node(5);
BinaryTree.root.right.right = new Node(4);
Console.WriteLine("Spiral Order traversal of Binary Tree is ");
tree.printSpiral(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
输出:
Spiral Order traversal of binary tree is
1 2 3 4 5 6 7