给定一棵树,以及所有节点的权重和整数x ,任务是找到一个节点i ,以使weight [i] xor x最大。
例子:
Input: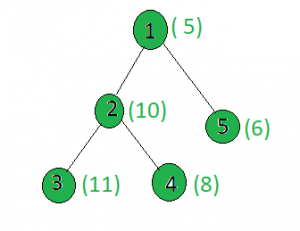
x = 15
Output: 1
Node 1: 5 xor 15 = 10
Node 2: 10 xor 15 = 5
Node 3: 11 xor 15 = 4
Node 4: 8 xor 15 = 7
Node 5: 6 xor 15 = 9
方法:在树上执行dfs并跟踪其加权xor与x给出最大值的节点。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
int maximum = INT_MIN, x, ans;
vector graph[100];
vector weight(100);
// Function to perform dfs to find
// the maximum xored value
void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If current value is less than
// the current maximum
if (maximum < (weight[node] ^ x)) {
maximum = weight[node] ^ x;
ans = node;
}
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
x = 15;
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(4);
graph[1].push_back(5);
dfs(1, 1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int maximum = Integer.MIN_VALUE, x, ans;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector[] graph = new Vector[100];
static int[] weight = new int[100];
// This block is executed even before main() function
// This is necessary otherwise this program will
// throw "NullPointerException"
static
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector<>();
}
// Function to perform dfs to find
// the maximum xored value
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If current value is less than
// the current maximum
if (maximum < (weight[node] ^ x))
{
maximum = weight[node] ^ x;
ans = node;
}
for (int to : graph[node])
{
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
x = 15;
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].add(2);
graph[2].add(3);
graph[2].add(4);
graph[1].add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
import sys
maximum = -sys.maxsize - 1
graph = [[0 for i in range(100)]
for j in range(100)]
weight = [0 for i in range(100)]
ans = []
# Function to perform dfs to find
# the maximum xored value
def dfs(node, parent):
global maximum
# If current value is less than
# the current maximum
if (maximum < (weight[node] ^ x)):
maximum = weight[node] ^ x
ans.append(node)
for to in graph[node]:
if (to == parent):
continue
dfs(to, node)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = 15
# Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5
weight[2] = 10
weight[3] = 11
weight[4] = 8
weight[5] = 6
# Edges of the tree
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(3)
graph[2].append(4)
graph[1].append(5)
dfs(1, 1)
print(ans[0])
# This code is contributed by
# Surendra_GangwarC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int maximum = int.MinValue, x,
ans = int.MaxValue;
static List> graph = new List>();
static List weight = new List();
// Function to perform dfs to find
// the maximum value
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If current value is less than
// the current maximum
if (maximum < (weight[node] ^ x))
{
maximum = weight[node] ^ x;
ans = node;
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph[node].Count; i++)
{
if (graph[node][i] == parent)
continue;
dfs(graph[node][i], node);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
x = 15;
// Weights of the node
weight.Add(0);
weight.Add(5);
weight.Add(10);
weight.Add(11);;
weight.Add(8);
weight.Add(6);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
graph.Add(new List());
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(3);
graph[2].Add(4);
graph[1].Add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
Console.Write( ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10 输出:
1
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(N)。
在dfs中,树的每个节点都处理一次,因此,如果树中总共有N个节点,则由于dfs而导致的复杂度为O(N)。因此,时间复杂度为O(N)。 - 辅助空间: O(1)。
不需要任何额外的空间,因此空间复杂度是恒定的。