通过将字符串S 的子串恰好 K 次反转形成的字典上最小的字符串
给定一个字符串S和一个整数K ,任务是在将任意长度的任何子字符串恰好反转K次后找到字典上可能的最小字符串。
例子:
Input: S = “fgazcbdfge”, K = 3
Output: abcdgfzfge
Explanation: After 1st operation: S = “agfzcbdfge”, in S select S[0 – 2] = “fga” and reverse it
After 2nd operation: S = “abczfgdfge”, in S select S[2 – 4] = “fzc” and reverse it
After 3rd operation: S = “abcdgfzfge”, in S select S[3 – 6] = “zfgd” and reverse it.
Input: S = “abcdefg”, K = 5
Output: abcdefg
Explanation: The string is already lexicographically minimum possible.
Hence pick any 5 substrings having length 1. So the string will remain unchanged.
方法:要在K步中形成按字典顺序最小的字符串,在每一步中选择一个整数L ,其中S[L]是所有字符按排序顺序之前的字符,以及一个整数R ,字符S[R]是必须放置在S[L+1]处,以便S [L+1] 之前的所有字符都按排序顺序排列。在每一步中反转子串S[L..R] ,最终得到所需的字符串。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 让给定的字符串为S ,创建另一个等于S的字符串S1然后按升序对S1进行排序。
- 该算法需要三个嵌套循环,外层循环会从0运行到K (操作次数)
- 在每个操作中,搜索两个整数L和R ,找到它们后,我们反转子字符串S[L ... R]并继续进行后续操作。
- 使用两个嵌套循环根据操作数在S中搜索S1的字符。
- 由于需要在一次操作中只反转一个子字符串,因此只需在S中找到S1的一个字符,即S[R] (在之前的操作中必须放在S的已排序字符之后的字符)并找到S [L] (子字符串S[0…L-1]已排序,因此我们不必对它做任何事情, S[R]将放置在S[L+1] )。
- 在K次操作之后,得到字典序上可能最小的字符串。
插图:
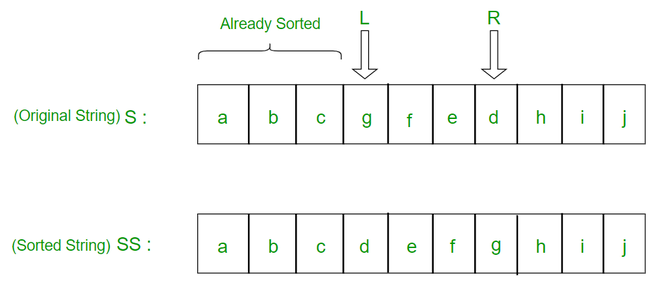
In the above illustration, since the first three characters of the origial string were in sorted order we dont have to involve them in any operation Search that character which will appear after them in the sorted order, assume it appears at index R (the character will be S[R]) we select the index of character after the first three character as R (the character will be S[R]) Now we reverse the substring S[L…R] which will result in the character S[R] to appear at S[L+1] and now the first 4 characters ofthe string S are in sorted order
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the lexicographically
// minimum string after k operations
string findStr(string s, int k)
{
// Sorted string
string ss = s;
sort(ss.begin(), ss.end());
// String after each operation
string ans = "";
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
ans = "";
int r = 0;
int l = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < ss.length(); j++) {
if (s[j] == ss[i] && i == j) {
l = i;
break;
}
else if (s[j] == ss[i]) {
r = j;
break;
}
}
if (r > 0)
// to avoid unnecessary cheking
break;
}
// There is no group of sorted characters
// in the beginning of the string S
if (l == -1) {
for (int i = r; i >= 0; i--)
ans.push_back(s[i]);
for (int i = r + 1; i < s.length(); i++)
ans.push_back(s[i]);
}
// string S is already sorted or S = SS
else if (l == s.length() - 1) {
ans = s;
}
// Some part of string S in the beginning
// is sorted
else {
for (int i = 0; i <= l; i++)
ans.push_back(s[i]);
for (int i = r; i > l; i--)
ans.push_back(s[i]);
for (int i = r + 1; i < s.length(); i++)
ans.push_back(s[i]);
}
// cout << "after " << i+1 << " operations
// : " << ans << '\n'; use the above line of
// code to see how S changes after every
// operation
s = ans;
}
return s;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of operations
int K = 3;
// Given string
string S = "fgazcbdfge";
// Final answer string
string ans = findStr(S, K);
cout << ans;
return 0;
} Python3
# python3 code to implement the approach
# Function to return the lexicographically
# minimum string after k operations
def findStr(s, k):
# Sorted string
ss = list(s)
ss.sort()
# String after each operation
ans = ""
for i in range(0, k):
ans = ""
r = 0
l = -1
for i in range(0, len(s)):
for j in range(0, len(ss)):
if (s[j] == ss[i] and i == j):
l = i
break
elif (s[j] == ss[i]):
r = j
break
if (r > 0):
# to avoid unnecessary cheking
break
# There is no group of sorted characters
# in the beginning of the string S
if (l == -1):
for i in range(r, -1, -1):
ans += s[i]
for i in range(r+1, len(s)):
ans += s[i]
# string S is already sorted or S = SS
elif (l == len(s) - 1):
ans = s
# Some part of string S in the beginning
# is sorted
else:
for i in range(0, l+1):
ans += s[i]
for i in range(r, l, -1):
ans += s[i]
for i in range(r + 1, len(s)):
ans += s[i]
# print(f"after {i+1} operations: {ans}")
# use the above line of
# code to see how S changes after every
# operation
s = ans
return s
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Number of operations
K = 3
# Given string
S = "fgazcbdfge"
# Final answer string
ans = findStr(S, K)
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by rakeshsahniC#
// C# code to implement the approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Function to return the lexicographically
// minimum string after k operations
static string findStr(string s, int k)
{
// Sorted string
string ss = s;
char[] arr = ss.ToCharArray();
Array.Sort(arr);
ss = new string(arr);
// String after each operation
string ans = "";
for (int a = 0; a < k; a++) {
ans = "";
int r = 0;
int l = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < ss.Length; j++) {
if (s[j] == ss[i] && i == j) {
l = i;
break;
}
else if (s[j] == ss[i]) {
r = j;
break;
}
}
if (r > 0)
// to avoid unnecessary cheking
break;
}
// There is no group of sorted characters
// in the beginning of the string S
if (l == -1) {
for (int i = r; i >= 0; i--)
ans += s[i];
for (int i = r + 1; i < s.Length; i++)
ans += s[i];
}
// string S is already sorted or S = SS
else if (l == s.Length - 1) {
ans = s;
}
// Some part of string S in the beginning
// is sorted
else {
for (int i = 0; i <= l; i++)
ans += s[i];
for (int i = r; i > l; i--)
ans += s[i];
for (int i = r + 1; i < s.Length; i++)
ans += s[i];
}
// cout << "after " << i+1 << " operations
// : " << ans << '\n'; use the above line of
// code to see how S changes after every
// operation
s = ans;
}
return s;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Number of operations
int K = 3;
// Given string
string S = "fgazcbdfge";
// Final answer string
string ans = findStr(S, K);
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.Javascript
abcdgfzfge时间复杂度: O(K * N 2 )其中 N 是字符串的长度
辅助空间: O(1)