图的广度优先搜索或 BFS
图的广度优先遍历(或搜索)类似于树的广度优先遍历(参见本文的方法 2)。这里唯一的问题是,与树不同,图可能包含循环,所以我们可能会再次来到同一个节点。为了避免多次处理一个节点,我们使用布尔访问数组。为简单起见,假设所有顶点都可以从起始顶点到达。
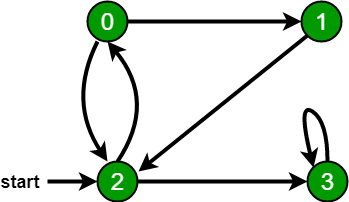
例如,在下图中,我们从顶点 2 开始遍历。当我们到达顶点 0 时,我们寻找它的所有相邻顶点。 2也是0的相邻顶点,如果我们不标记访问过的顶点,那么2会被再次处理,变成一个非终止过程。下图的广度优先遍历是 2, 0, 3, 1。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。
以下是来自给定源的简单广度优先遍历的实现。
该实现使用图的邻接列表表示。 STL 的列表容器用于存储相邻节点的列表和 BFS 遍历所需的节点队列。
C++
// Program to print BFS traversal from a given
// source vertex. BFS(int s) traverses vertices
// reachable from s.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
// Pointer to an array containing adjacency
// lists
list *adj;
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// prints BFS traversal from a given source s
void BFS(int s);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list.
}
void Graph::BFS(int s)
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool *visited = new bool[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Create a queue for BFS
list queue;
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
visited[s] = true;
queue.push_back(s);
// 'i' will be used to get all adjacent
// vertices of a vertex
list::iterator i;
while(!queue.empty())
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
s = queue.front();
cout << s << " ";
queue.pop_front();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued
// vertex s. If a adjacent has not been visited,
// then mark it visited and enqueue it
for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i)
{
if (!visited[*i])
{
visited[*i] = true;
queue.push_back(*i);
}
}
}
}
// Driver program to test methods of graph class
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
cout << "Following is Breadth First Traversal "
<< "(starting from vertex 2) \n";
g.BFS(2);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to print BFS traversal from a given source vertex.
// BFS(int s) traverses vertices reachable from s.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// This class represents a directed graph using adjacency list
// representation
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
private LinkedList adj[]; //Adjacency Lists
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i=0; i queue = new LinkedList();
// Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it
visited[s]=true;
queue.add(s);
while (queue.size() != 0)
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
s = queue.poll();
System.out.print(s+" ");
// Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex s
// If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark it
// visited and enqueue it
Iterator i = adj[s].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n])
{
visited[n] = true;
queue.add(n);
}
}
}
}
// Driver method to
public static void main(String args[])
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
System.out.println("Following is Breadth First Traversal "+
"(starting from vertex 2)");
g.BFS(2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# Python3 Program to print BFS traversal
# from a given source vertex. BFS(int s)
# traverses vertices reachable from s.
from collections import defaultdict
# This class represents a directed graph
# using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
# Constructor
def __init__(self):
# default dictionary to store graph
self.graph = defaultdict(list)
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self,u,v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
# Function to print a BFS of graph
def BFS(self, s):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited
visited = [False] * (max(self.graph) + 1)
# Create a queue for BFS
queue = []
# Mark the source node as
# visited and enqueue it
queue.append(s)
visited[s] = True
while queue:
# Dequeue a vertex from
# queue and print it
s = queue.pop(0)
print (s, end = " ")
# Get all adjacent vertices of the
# dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent
# has not been visited, then mark it
# visited and enqueue it
for i in self.graph[s]:
if visited[i] == False:
queue.append(i)
visited[i] = True
# Driver code
# Create a graph given in
# the above diagram
g = Graph()
g.addEdge(0, 1)
g.addEdge(0, 2)
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 0)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 3)
print ("Following is Breadth First Traversal"
" (starting from vertex 2)")
g.BFS(2)
# This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// C# program to print BFS traversal
// from a given source vertex.
// BFS(int s) traverses vertices
// reachable from s.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
// This class represents a directed
// graph using adjacency list
// representation
class Graph{
// No. of vertices
private int _V;
//Adjacency Lists
LinkedList[] _adj;
public Graph(int V)
{
_adj = new LinkedList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < _adj.Length; i++)
{
_adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
_V = V;
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
public void AddEdge(int v, int w)
{
_adj[v].AddLast(w);
}
// Prints BFS traversal from a given source s
public void BFS(int s)
{
// Mark all the vertices as not
// visited(By default set as false)
bool[] visited = new bool[_V];
for(int i = 0; i < _V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Create a queue for BFS
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
// Mark the current node as
// visited and enqueue it
visited[s] = true;
queue.AddLast(s);
while(queue.Any())
{
// Dequeue a vertex from queue
// and print it
s = queue.First();
Console.Write(s + " " );
queue.RemoveFirst();
// Get all adjacent vertices of the
// dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent
// has not been visited, then mark it
// visited and enqueue it
LinkedList list = _adj[s];
foreach (var val in list)
{
if (!visited[val])
{
visited[val] = true;
queue.AddLast(val);
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.AddEdge(0, 1);
g.AddEdge(0, 2);
g.AddEdge(1, 2);
g.AddEdge(2, 0);
g.AddEdge(2, 3);
g.AddEdge(3, 3);
Console.Write("Following is Breadth First " +
"Traversal(starting from " +
"vertex 2)\n");
g.BFS(2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by anv89 输出:
Following is Breadth First Traversal (starting from vertex 2)
2 0 3 1插图 :
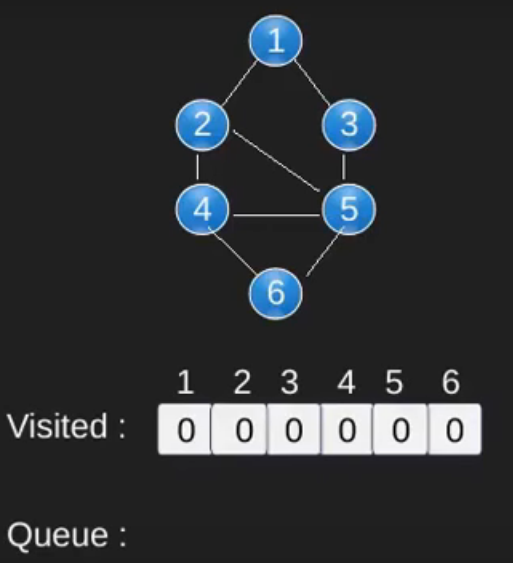
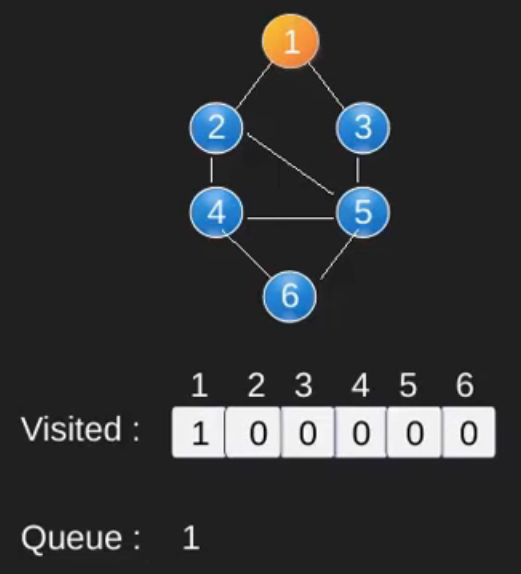
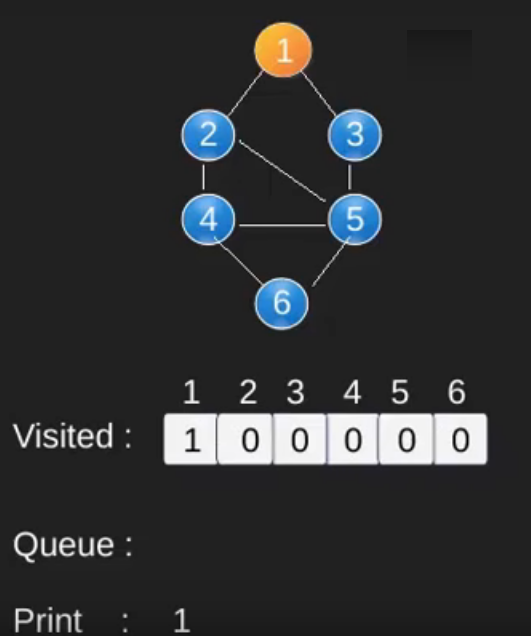
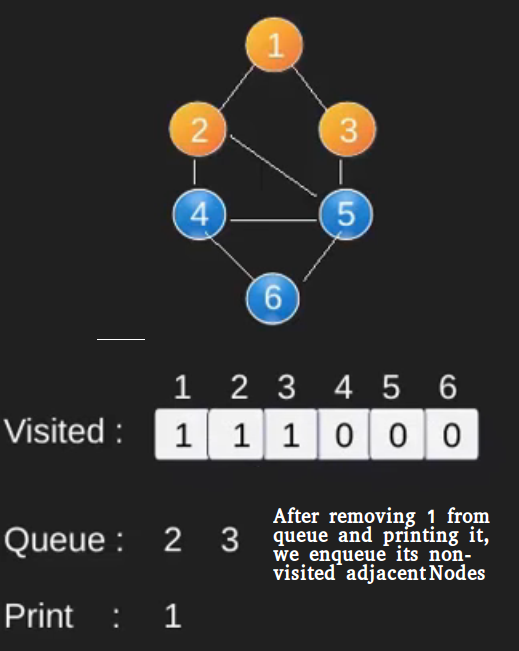
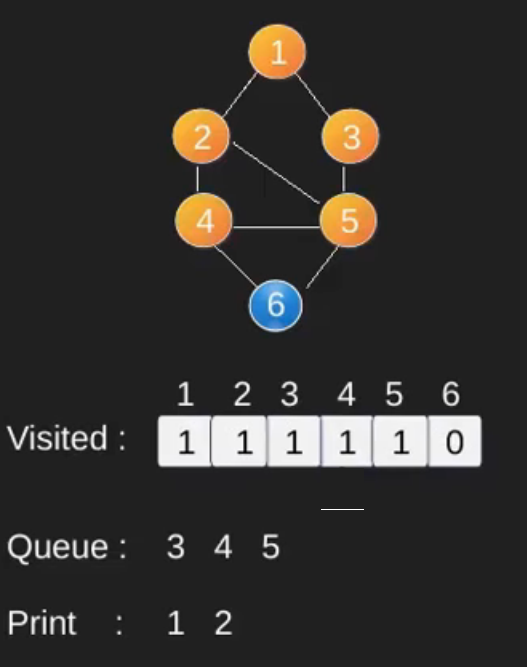
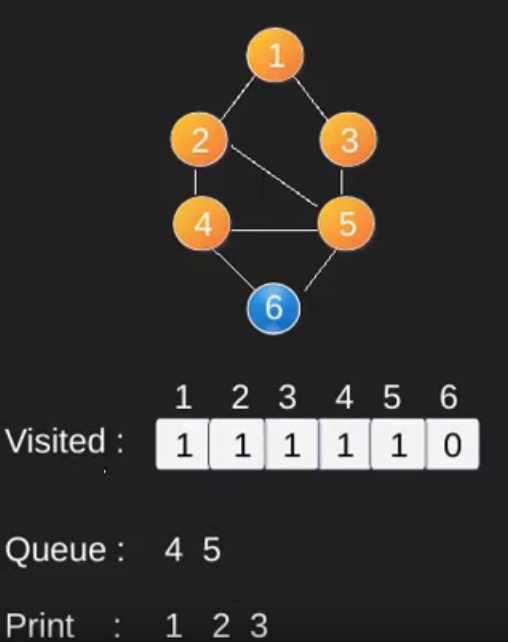
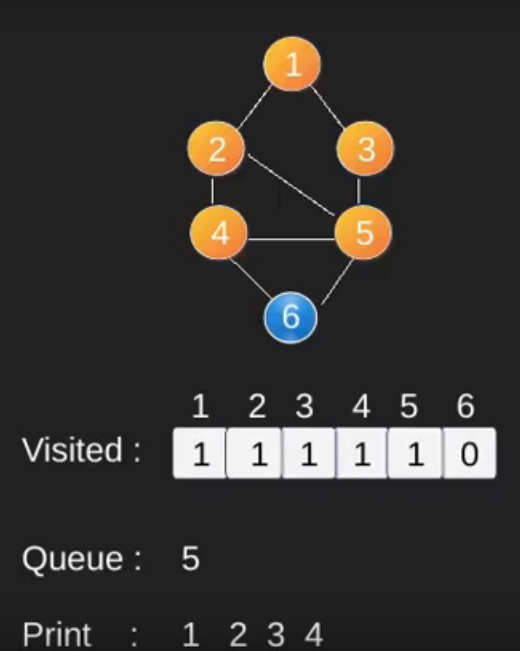
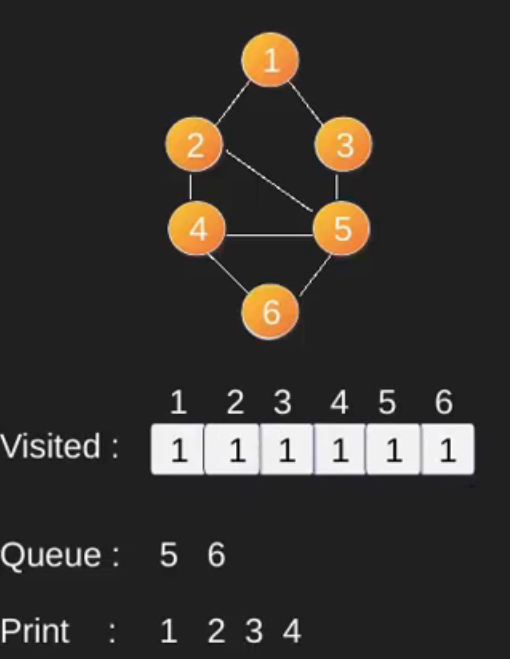
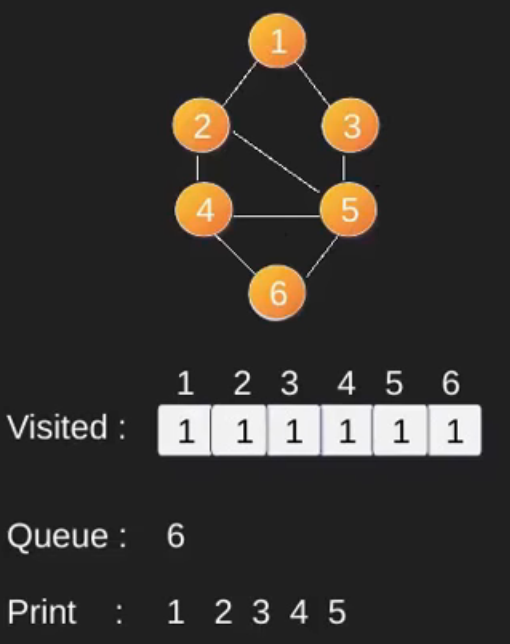
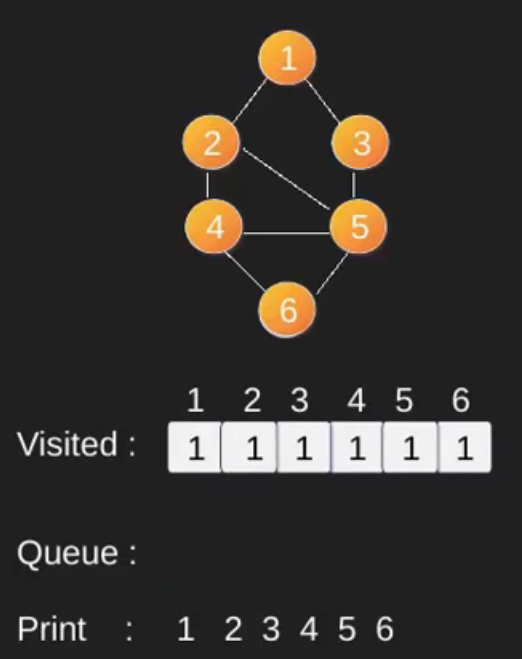
请注意,上述代码仅遍历从给定源顶点可到达的顶点。可能无法从给定顶点(例如断开连接的图)到达所有顶点。为了打印所有的顶点,我们可以修改 BFS函数,从所有节点开始一个一个地遍历(就像 DFS 修改版一样)。
时间复杂度:O(V+E),其中 V 是图中的顶点数,E 是图中的边数。
https://youtu.be/0u78hx-66Xk
您可能还想在下面看到:
- 最近关于 BFS 的文章
- 深度优先遍历
- 广度优先遍历的应用
- 深度优先搜索的应用