广度优先搜索是一种图形遍历算法,可逐级遍历图形或树。在本文中,使用邻接表而不使用队列来实现图的BFS。
例子:
Input: 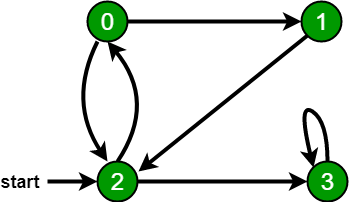
Output: BFS traversal = 2, 0, 3, 1
Explanation:
In the following graph, we start traversal from vertex 2. When we come to vertex 0, we look for all adjacent vertices of it. 2 is also an adjacent vertex of 0. If we don’t mark visited vertices, then 2 will be processed again and it will become a non-terminating process. Therefore, a Breadth-First Traversal of the following graph is 2, 0, 3, 1.
方法:可以使用给定来源的简单的广度优先遍历来解决此问题。该实现使用图的邻接表表示。
这里:
- STL向量容器用于存储BFS遍历所需的相邻节点列表和节点队列。
- DP阵列用于存储节点到源的距离。每次我们从一个节点移动到另一个节点时,距离都会增加1。如果到达节点的距离小于以前的距离,我们将更新DP [node]中存储的值。
下面是上述方法的实现:
// C++ implementation to demonstrate
// the above mentioned approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the distance
// from the source to other nodes
void BFS(int curr, int N, vector& vis,
vector& dp, vector& v,
vector >& adj)
{
while (curr <= N) {
// Current node
int node = v[curr - 1];
cout << node << ", ";
for (int i = 0; i < adj[node].size(); i++) {
// Adjacent node
int next = adj[node][i];
if ((!vis[next])
&& (dp[next] < dp[node] + 1)) {
// Stores the adjacent node
v.push_back(next);
// Increases the distance
dp[next] = dp[node] + 1;
// Mark it as visited
vis[next] = true;
}
}
curr += 1;
}
}
// Function to print the distance
// from source to other nodes
void bfsTraversal(
vector >& adj,
int N, int source)
{
// Initially mark all nodes as false
vector vis(N + 1, false);
// Initialize distance array with 0
vector dp(N + 1, 0), v;
v.push_back(source);
// Initially mark the starting
// source as 0 and visited as true
dp = 0;
vis = true;
// Call the BFS function
BFS(1, N, vis, dp, v, adj);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// No. of nodes in graph
int N = 4;
// Creating adjacency list
// for representing graph
vector > adj(N + 1);
adj[0].push_back(1);
adj[0].push_back(2);
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(0);
adj[2].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(3);
// Following is BFS Traversal
// starting from vertex 2
bfsTraversal(adj, N, 2);
return 0;
}
输出:
2, 0, 3, 1,