遍历是指访问图的所有节点。广度优先遍历或广度优先搜索是一种递归算法,用于搜索图形或树数据结构的所有顶点。
BFS算法
一个标准的BFS实现将图的每个顶点分为以下两类之一:
- 来过
- 未造访
该算法的目的是将每个顶点标记为已访问,同时避免循环。
该算法的工作原理如下:
- 首先将图形的任意一个顶点放在队列的后面。
- 将队列的最前面的项目添加到访问列表中。
- 创建该顶点的相邻节点的列表。将不在访问列表中的访问者添加到队列的后面。
- 继续重复步骤2和3,直到队列为空。
该图可能具有两个不同的断开部分,因此要确保我们覆盖每个顶点,我们还可以在每个节点上运行BFS算法
BFS示例
让我们来看一个广度优先搜索算法的示例。我们使用具有5个顶点的无向图。

我们从顶点0开始,BFS算法首先将其放入“已访问”列表中,然后将其所有相邻顶点放入堆栈中。
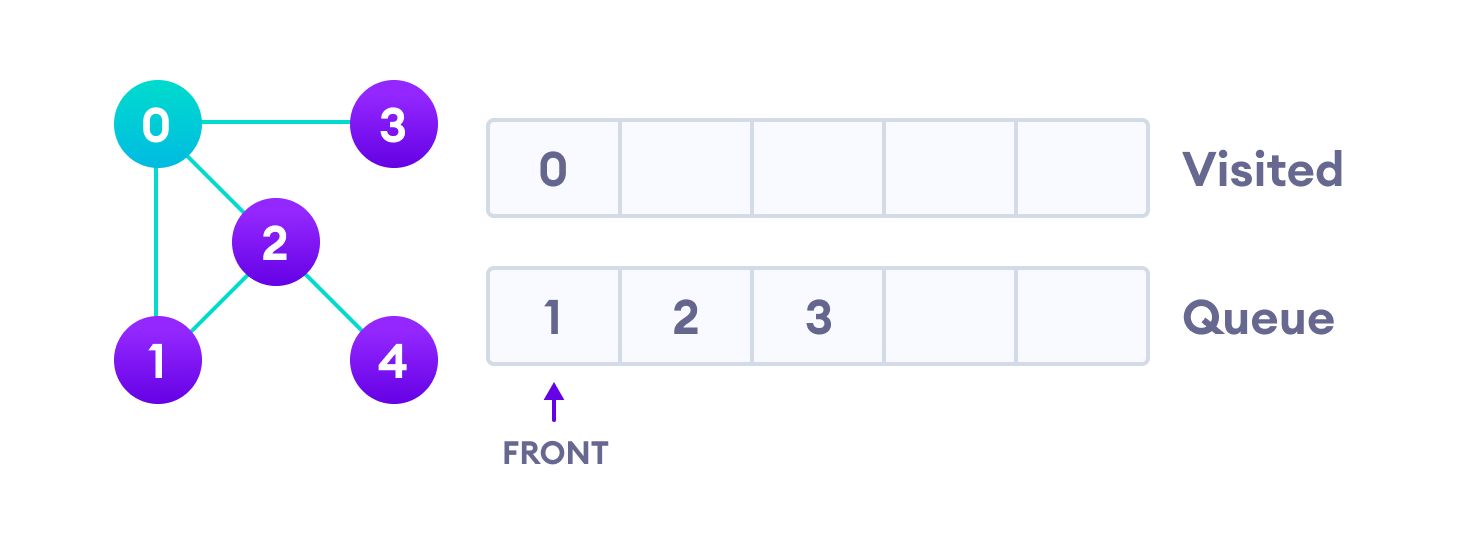
接下来,我们访问队列最前面的元素(即1)并转到其相邻节点。由于已经访问过0,因此我们访问2。
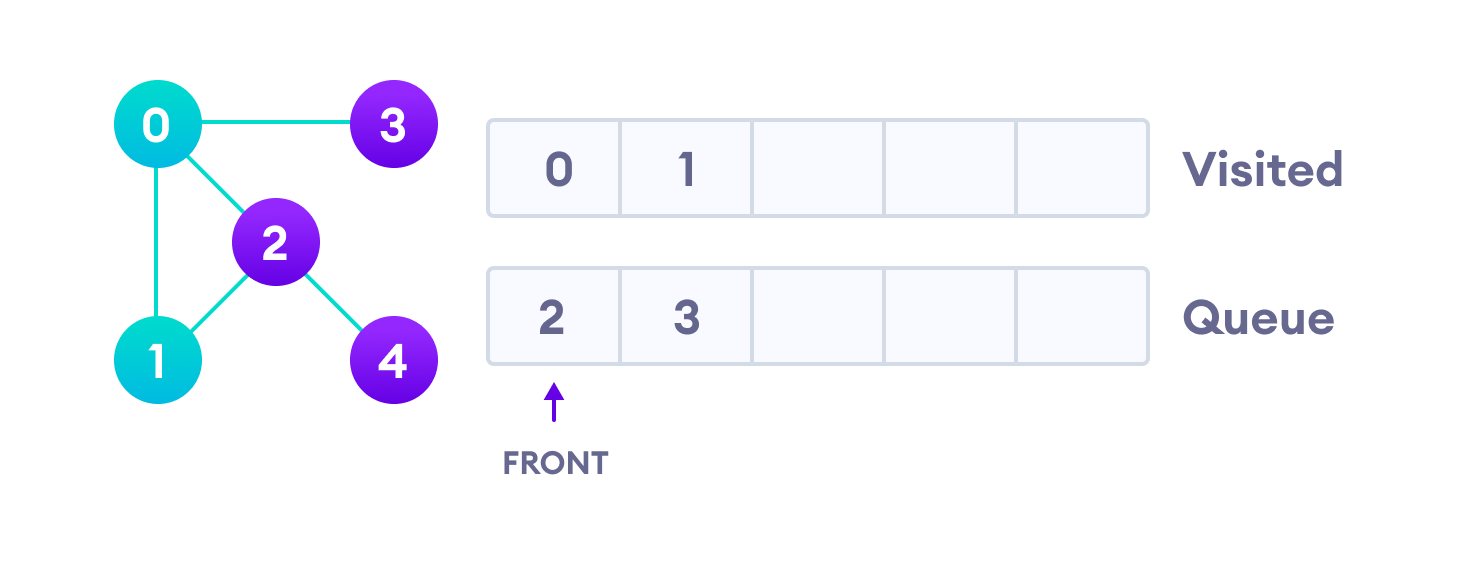
顶点2在4中有一个未访问的相邻顶点,因此我们将其添加到队列的后面,并访问3,它位于队列的前面。
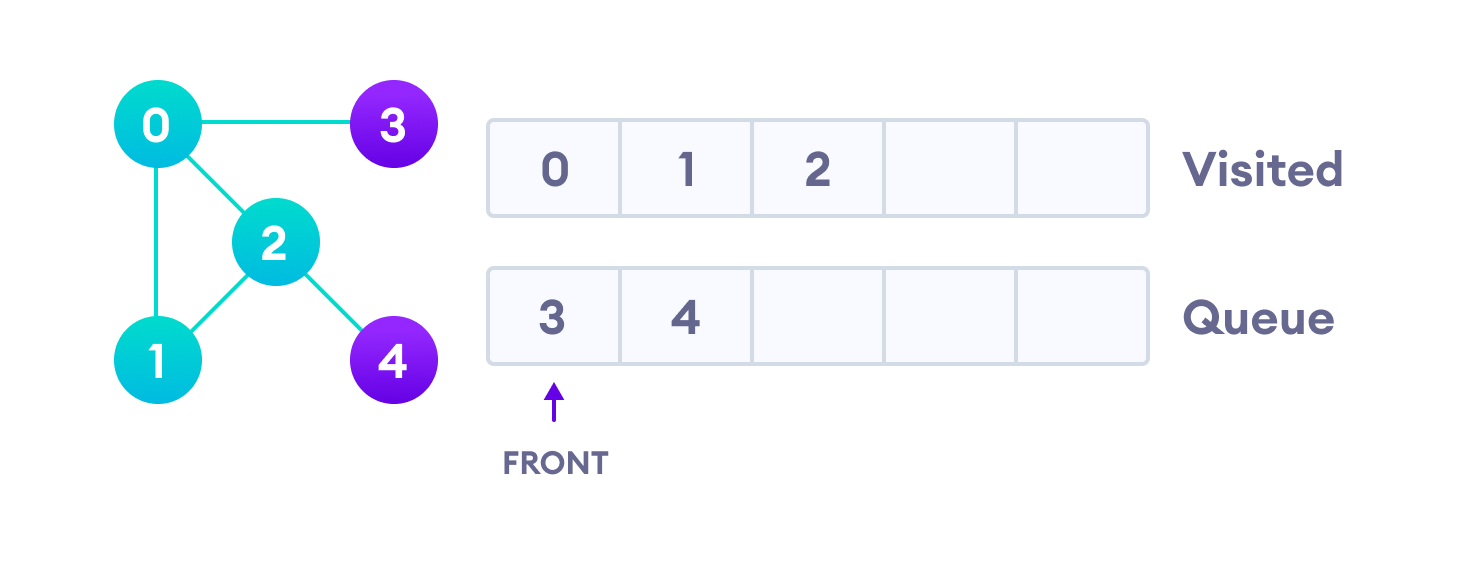
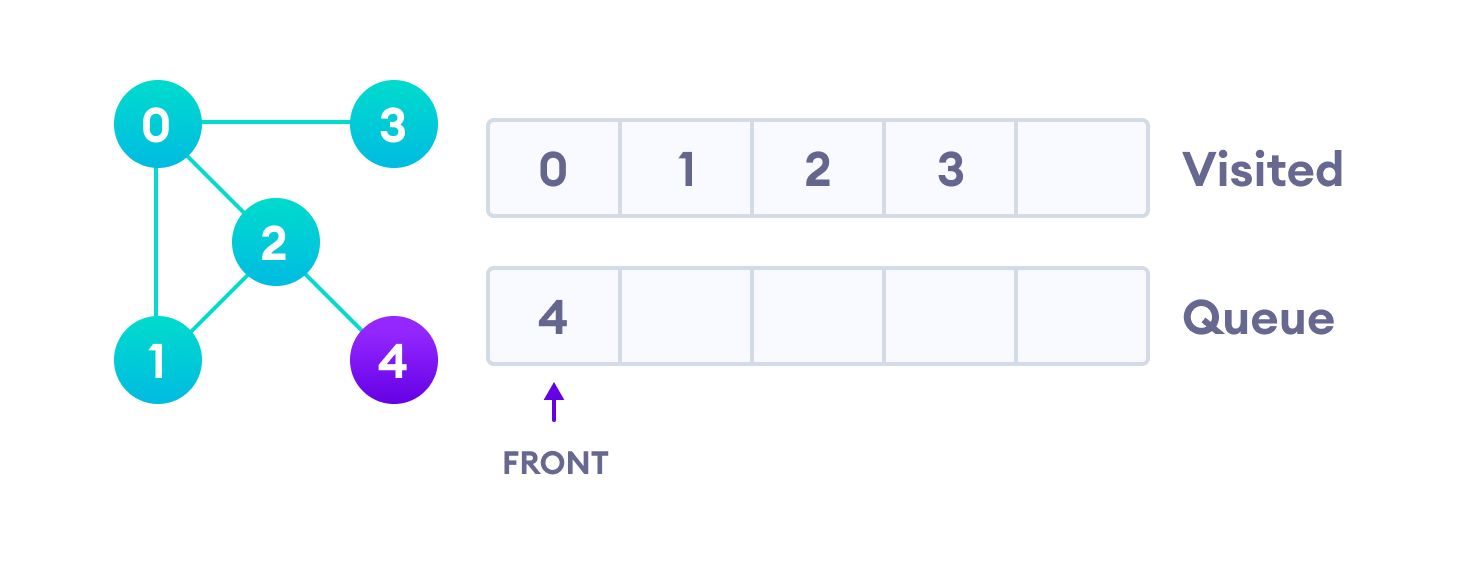
由于只有3个相邻节点(即0)已被访问,因此队列中仅剩下4个。我们参观它。
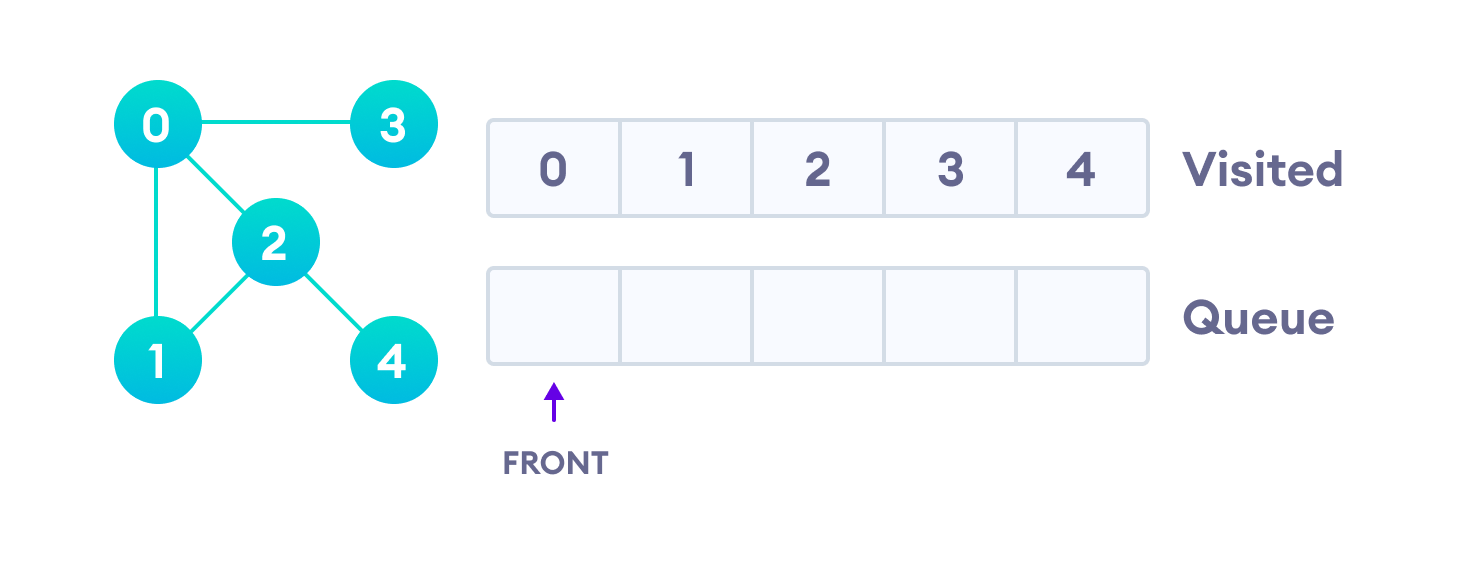
由于队列为空,因此我们已经完成了图的广度优先遍历。
BFS伪代码
create a queue Q
mark v as visited and put v into Q
while Q is non-empty
remove the head u of Q
mark and enqueue all (unvisited) neighbours of uPython,Java和C / C++示例
广度优先搜索算法的代码示例如下。代码已经简化,因此我们可以专注于算法而不是其他细节。
Python
爪哇
C
C +
# BFS algorithm in Python
import collections
# BFS algorithm
def bfs(graph, root):
visited, queue = set(), collections.deque([root])
visited.add(root)
while queue:
# Dequeue a vertex from queue
vertex = queue.popleft()
print(str(vertex) + " ", end="")
# If not visited, mark it as visited, and
# enqueue it
for neighbour in graph[vertex]:
if neighbour not in visited:
visited.add(neighbour)
queue.append(neighbour)
if __name__ == '__main__':
graph = {0: [1, 2], 1: [2], 2: [3], 3: [1, 2]}
print("Following is Breadth First Traversal: ")
bfs(graph, 0)
// BFS algorithm in Java
import java.util.*;
public class Graph {
private int V;
private LinkedList adj[];
// Create a graph
Graph(int v) {
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
// Add edges to the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w) {
adj[v].add(w);
}
// BFS algorithm
void BFS(int s) {
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
LinkedList queue = new LinkedList();
visited[s] = true;
queue.add(s);
while (queue.size() != 0) {
s = queue.poll();
System.out.print(s + " ");
Iterator i = adj[s].listIterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
int n = i.next();
if (!visited[n]) {
visited[n] = true;
queue.add(n);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Graph g = new Graph(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
System.out.println("Following is Breadth First Traversal " + "(starting from vertex 2)");
g.BFS(2);
}
} // BFS algorithm in C
#include
#include
#define SIZE 40
struct queue {
int items[SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
};
struct queue* createQueue();
void enqueue(struct queue* q, int);
int dequeue(struct queue* q);
void display(struct queue* q);
int isEmpty(struct queue* q);
void printQueue(struct queue* q);
struct node {
int vertex;
struct node* next;
};
struct node* createNode(int);
struct Graph {
int numVertices;
struct node** adjLists;
int* visited;
};
// BFS algorithm
void bfs(struct Graph* graph, int startVertex) {
struct queue* q = createQueue();
graph->visited[startVertex] = 1;
enqueue(q, startVertex);
while (!isEmpty(q)) {
printQueue(q);
int currentVertex = dequeue(q);
printf("Visited %d\n", currentVertex);
struct node* temp = graph->adjLists[currentVertex];
while (temp) {
int adjVertex = temp->vertex;
if (graph->visited[adjVertex] == 0) {
graph->visited[adjVertex] = 1;
enqueue(q, adjVertex);
}
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
// Creating a node
struct node* createNode(int v) {
struct node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->vertex = v;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Creating a graph
struct Graph* createGraph(int vertices) {
struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
graph->numVertices = vertices;
graph->adjLists = malloc(vertices * sizeof(struct node*));
graph->visited = malloc(vertices * sizeof(int));
int i;
for (i = 0; i < vertices; i++) {
graph->adjLists[i] = NULL;
graph->visited[i] = 0;
}
return graph;
}
// Add edge
void addEdge(struct Graph* graph, int src, int dest) {
// Add edge from src to dest
struct node* newNode = createNode(dest);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[src];
graph->adjLists[src] = newNode;
// Add edge from dest to src
newNode = createNode(src);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[dest];
graph->adjLists[dest] = newNode;
}
// Create a queue
struct queue* createQueue() {
struct queue* q = malloc(sizeof(struct queue));
q->front = -1;
q->rear = -1;
return q;
}
// Check if the queue is empty
int isEmpty(struct queue* q) {
if (q->rear == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
// Adding elements into queue
void enqueue(struct queue* q, int value) {
if (q->rear == SIZE - 1)
printf("\nQueue is Full!!");
else {
if (q->front == -1)
q->front = 0;
q->rear++;
q->items[q->rear] = value;
}
}
// Removing elements from queue
int dequeue(struct queue* q) {
int item;
if (isEmpty(q)) {
printf("Queue is empty");
item = -1;
} else {
item = q->items[q->front];
q->front++;
if (q->front > q->rear) {
printf("Resetting queue ");
q->front = q->rear = -1;
}
}
return item;
}
// Print the queue
void printQueue(struct queue* q) {
int i = q->front;
if (isEmpty(q)) {
printf("Queue is empty");
} else {
printf("\nQueue contains \n");
for (i = q->front; i < q->rear + 1; i++) {
printf("%d ", q->items[i]);
}
}
}
int main() {
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(6);
addEdge(graph, 0, 1);
addEdge(graph, 0, 2);
addEdge(graph, 1, 2);
addEdge(graph, 1, 4);
addEdge(graph, 1, 3);
addEdge(graph, 2, 4);
addEdge(graph, 3, 4);
bfs(graph, 0);
return 0;
} // BFS algorithm in C++
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int numVertices;
list* adjLists;
bool* visited;
public:
Graph(int vertices);
void addEdge(int src, int dest);
void BFS(int startVertex);
};
// Create a graph with given vertices,
// and maintain an adjacency list
Graph::Graph(int vertices) {
numVertices = vertices;
adjLists = new list[vertices];
}
// Add edges to the graph
void Graph::addEdge(int src, int dest) {
adjLists[src].push_back(dest);
adjLists[dest].push_back(src);
}
// BFS algorithm
void Graph::BFS(int startVertex) {
visited = new bool[numVertices];
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
visited[i] = false;
list queue;
visited[startVertex] = true;
queue.push_back(startVertex);
list::iterator i;
while (!queue.empty()) {
int currVertex = queue.front();
cout << "Visited " << currVertex << " ";
queue.pop_front();
for (i = adjLists[currVertex].begin(); i != adjLists[currVertex].end(); ++i) {
int adjVertex = *i;
if (!visited[adjVertex]) {
visited[adjVertex] = true;
queue.push_back(adjVertex);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
Graph g(4);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 0);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 3);
g.BFS(2);
return 0;
}
BFS算法复杂度
BFS算法的时间复杂度以O(V + E)的形式表示,其中V是节点数,E是边数。
该算法的空间复杂度为O(V) 。
BFS算法应用
- 通过搜索索引建立索引
- 用于GPS导航
- 路径查找算法
- 在Ford-Fulkerson算法中查找网络中的最大流量
- 无向图中的循环检测
- 在最小生成树中