检查给定链表的所有元素是否对应于给定二叉树中任何节点的向下路径
给定二叉树的根和链表的头,任务是检查链表的所有元素是否对应于给定二叉树中任何节点的向下路径。
例子:
Input: Tree in the image below, list = {3, 6, 8}
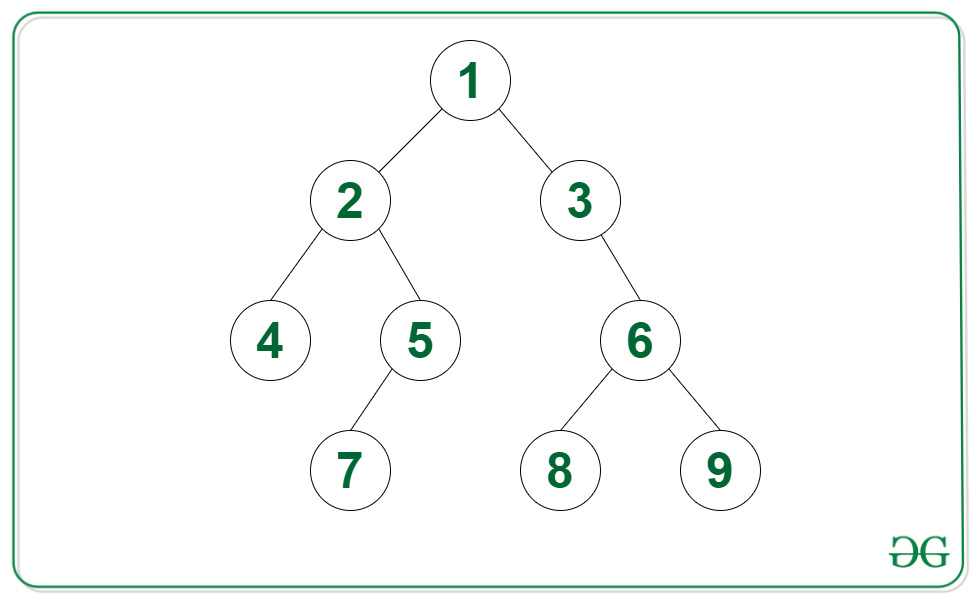
Output: Yes
Explanation: There exists a downward path in the given Binary Tree, having all the elements of the linked list in the same order.
Input: Tree in the image below, list = {1, 2, 5, 7}
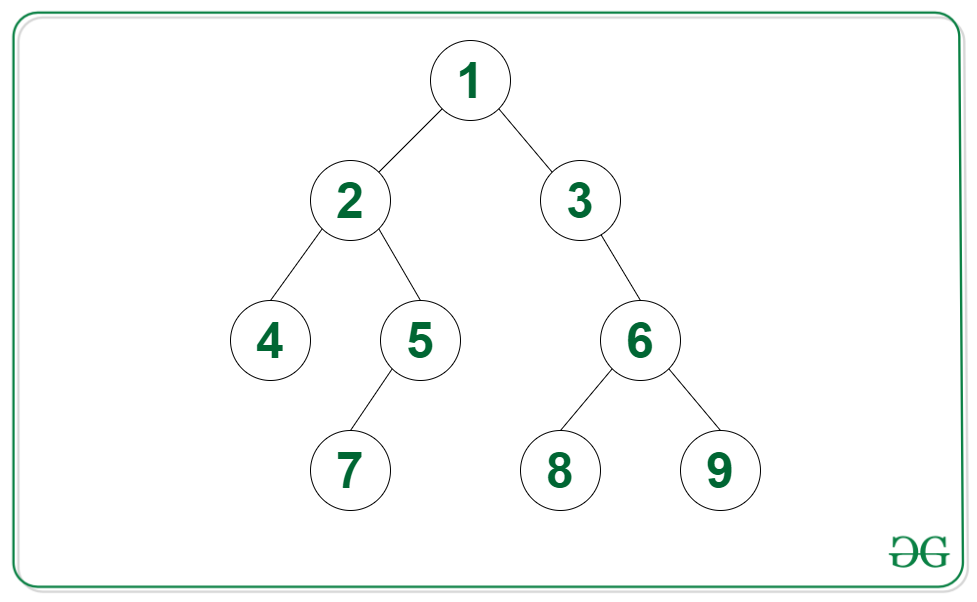
Output: Yes
方法:给定的问题可以借助二叉树的 DFS 遍历来解决。在DFS遍历过程中,如果二叉树的任意一个节点等于链表的头部,则可以调用递归函数isPathUntil()递归检查链表的其他元素是否也作为该节点的路径存在.如果遍历了完整的链表,则存在有效的必需路径,因此返回true 。否则,返回false 。请按照以下步骤解决给定的问题:
- 声明一个函数,比如isSubPathUtil(root, head) ,并在这个函数中执行以下步骤:
- 如果根为NULL ,则返回false 。
- 如果head为NULL,则返回true。
- 如果当前根节点的值与LL当前头的值相同,则递归调用isSubPathUtil(root->left, head->next)和isSubPathUtil(root->right, head->next)如果这些递归调用之一返回的值为真,则返回真。否则,返回false 。
- 声明一个函数,比如isSubPath(root, head) ,并在这个函数中执行以下步骤:
- 如果根为NULL ,则返回false 。
- 如果head为NULL ,则返回 true。
- 如果当前根节点的值与LL当前头的值相同,则递归调用isSubPath(root->left, head->next)和isSubPath(root->right, head->next)如果这些递归调用之一返回的值为真,则返回真。否则,递归调用isSubPath(root->left, head)和isSubPath(root->right, head)返回值。
- 经过上述步骤,如果函数isSubPath(root, head)返回的值为true ,则打印Yes 。否则,打印No 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Node of the Linked list
struct listNode {
int val;
struct listNode* next;
// Constructor
listNode(int data)
{
this->val = data;
next = NULL;
}
};
// Node of the Binary Search tree
struct treeNode {
int val;
treeNode* right;
treeNode* left;
// Constructor
treeNode(int data)
{
this->val = data;
this->left = NULL;
this->right = NULL;
}
};
// Recursive function to check if there
// exist a path from the node curTree
// having the LL from the node curList
bool isPathUtil(listNode* curList,
treeNode* curTree)
{
// If the complete linked list
// is traversed
if (curList == NULL)
return true;
// If the tree node doesnot exist
if (curTree == NULL)
return false;
if (curList->val == curTree->val) {
// Recursively calling for the
// next element
return isPathUtil(curList->next,
curTree->left)
|| isPathUtil(curList->next,
curTree->right);
}
else {
// If not found, return false
return false;
}
}
// Function to check if the linked list
// exist as a downward path in Binary tree
// using the DFS Traversal of the Tree
bool isPath(listNode* head, treeNode* root)
{
// If the current node of the
// tree is Null
if (root == NULL)
return false;
// If the complete linked list
// has been found
if (head == NULL)
return true;
// Stores if there exist the
// required path
bool isPossible = false;
if (root->val == head->val) {
// Recursively calling to
// check the next node of
// the linked list
isPossible = isPathUtil(
head->next, root->left)
|| isPathUtil(
head->next, root->right);
}
// Recursive calling for the next
// elements of of the binary tree
return isPossible || isPath(head, root->left)
|| isPath(head, root->right);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
treeNode* root = new treeNode(1);
root->left = new treeNode(2);
root->right = new treeNode(3);
root->left->left = new treeNode(4);
root->left->right = new treeNode(5);
root->left->right->left = new treeNode(7);
root->right->right = new treeNode(6);
root->right->right->left = new treeNode(8);
root->right->right->right = new treeNode(9);
listNode* head = new listNode(3);
head->next = new listNode(6);
head->next->next = new listNode(8);
// Function Call
cout << (isPath(head, root) ? "Yes" : "No");
return 0;
}Java
// Java program for the above approach
//include "bits/stdJava.h"
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Node of the Linked list
static class listNode {
int val;
listNode next;
// Constructor
listNode(int data)
{
this.val = data;
next = null;
}
};
// Node of the Binary Search tree
static class treeNode {
int val;
treeNode right;
treeNode left;
// Constructor
treeNode(int data)
{
this.val = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
};
// Recursive function to check if there
// exist a path from the node curTree
// having the LL from the node curList
static boolean isPathUtil(listNode curList,
treeNode curTree)
{
// If the complete linked list
// is traversed
if (curList == null)
return true;
// If the tree node doesnot exist
if (curTree == null)
return false;
if (curList.val == curTree.val) {
// Recursively calling for the
// next element
return isPathUtil(curList.next,
curTree.left)
|| isPathUtil(curList.next,
curTree.right);
}
else {
// If not found, return false
return false;
}
}
// Function to check if the linked list
// exist as a downward path in Binary tree
// using the DFS Traversal of the Tree
static boolean isPath(listNode head, treeNode root)
{
// If the current node of the
// tree is Null
if (root == null)
return false;
// If the complete linked list
// has been found
if (head == null)
return true;
// Stores if there exist the
// required path
boolean isPossible = false;
if (root.val == head.val) {
// Recursively calling to
// check the next node of
// the linked list
isPossible = isPathUtil(
head.next, root.left)
|| isPathUtil(
head.next, root.right);
}
// Recursive calling for the next
// elements of of the binary tree
return isPossible || isPath(head, root.left)
|| isPath(head, root.right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
treeNode root = new treeNode(1);
root.left = new treeNode(2);
root.right = new treeNode(3);
root.left.left = new treeNode(4);
root.left.right = new treeNode(5);
root.left.right.left = new treeNode(7);
root.right.right = new treeNode(6);
root.right.right.left = new treeNode(8);
root.right.right.right = new treeNode(9);
listNode head = new listNode(3);
head.next = new listNode(6);
head.next.next = new listNode(8);
// Function Call
System.out.print((isPath(head, root) ? "Yes" : "No"));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# Python program for the above approach
# Node of the Linked list
class listNode:
# Constructor
def __init__ (self, data):
self.val = data;
self.next = None;
# Node of the Binary Search tree
class treeNode:
# Constructor
def __init__ (self, data):
self.val = data;
self.left = None;
self.right = None;
# Recursive function to check if there
# exist a path from the node curTree
# having the LL from the node curList
def isPathUtil(curList, curTree):
# If the complete linked list
# is traversed
if (curList == None): return True;
# If the tree node doesnot exist
if (curTree == None): return False;
if (curList.val == curTree.val):
# Recursively calling for the
# next element
return (
isPathUtil(curList.next, curTree.left) or
isPathUtil(curList.next, curTree.right)
);
else:
# If not found, return false
return False;
# Function to check if the linked list
# exist as a downward path in Binary tree
# using the DFS Traversal of the Tree
def isPath(head, root):
# If the current node of the
# tree is None
if (root == None): return False;
# If the complete linked list
# has been found
if (head == None): return True;
# Stores if there exist the
# required path
isPossible = False;
if (root.val == head.val):
# Recursively calling to
# check the next node of
# the linked list
isPossible = isPathUtil(head.next, root.left) or isPathUtil(head.next, root.right);
# Recursive calling for the next
# elements of of the binary tree
return isPossible or isPath(head, root.left) or isPath(head, root.right);
# Driver Code
root = treeNode(1);
root.left = treeNode(2);
root.right = treeNode(3);
root.left.left = treeNode(4);
root.left.right = treeNode(5);
root.left.right.left = treeNode(7);
root.right.right = treeNode(6);
root.right.right.left = treeNode(8);
root.right.right.right = treeNode(9);
head = listNode(3);
head.next = listNode(6);
head.next.next = listNode(8);
# Function Call
print( "Yes" if isPath(head, root) else "No");
# This code is contributed by saurabh_jaiswal.C#
// C# program for the above approach
//include "bits/stdJava.h"
using System;
public class GFG{
// Node of the Linked list
class listNode {
public int val;
public listNode next;
// Constructor
public listNode(int data)
{
this.val = data;
next = null;
}
};
// Node of the Binary Search tree
class treeNode {
public int val;
public treeNode right;
public treeNode left;
// Constructor
public treeNode(int data)
{
this.val = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
};
// Recursive function to check if there
// exist a path from the node curTree
// having the LL from the node curList
static bool isPathUtil(listNode curList,
treeNode curTree)
{
// If the complete linked list
// is traversed
if (curList == null)
return true;
// If the tree node doesnot exist
if (curTree == null)
return false;
if (curList.val == curTree.val) {
// Recursively calling for the
// next element
return isPathUtil(curList.next,
curTree.left)
|| isPathUtil(curList.next,
curTree.right);
}
else {
// If not found, return false
return false;
}
}
// Function to check if the linked list
// exist as a downward path in Binary tree
// using the DFS Traversal of the Tree
static bool isPath(listNode head, treeNode root)
{
// If the current node of the
// tree is Null
if (root == null)
return false;
// If the complete linked list
// has been found
if (head == null)
return true;
// Stores if there exist the
// required path
bool isPossible = false;
if (root.val == head.val) {
// Recursively calling to
// check the next node of
// the linked list
isPossible = isPathUtil(
head.next, root.left)
|| isPathUtil(
head.next, root.right);
}
// Recursive calling for the next
// elements of of the binary tree
return isPossible || isPath(head, root.left)
|| isPath(head, root.right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
treeNode root = new treeNode(1);
root.left = new treeNode(2);
root.right = new treeNode(3);
root.left.left = new treeNode(4);
root.left.right = new treeNode(5);
root.left.right.left = new treeNode(7);
root.right.right = new treeNode(6);
root.right.right.left = new treeNode(8);
root.right.right.right = new treeNode(9);
listNode head = new listNode(3);
head.next = new listNode(6);
head.next.next = new listNode(8);
// Function Call
Console.Write((isPath(head, root) ? "Yes" : "No"));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
输出:
Yes时间复杂度: O(N * M) 其中 N = 二叉树中的节点数,M = 链表中的节点数。
辅助空间: O(1)