Java程序使用优先队列执行两个链表的并集
给定两个链表,你的任务是完成函数make union(),它返回两个链表的并集。这个联合应该只包括所有不同的元素。形成的新列表应按非递减顺序排列。
Input: L1 = 9->6->4->2->3->8
L2 = 1->2->8->6->2
Output: 1 2 3 4 6 8 9方法:
众所周知,有两种类型的堆,即最小堆和最大堆
- 最小堆 - 按升序存储所有元素
- 最大堆 - 按降序存储所有元素
让我们首先使用最小堆进行可视化,以解释程序执行如何进行两个链表的并集,因此我们将列出两个操作来进行可视化:
- 插入
- 移动
插入:插入两个链表的所有不同元素后,
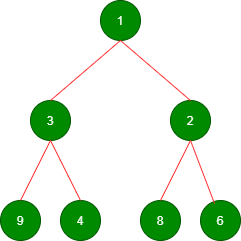
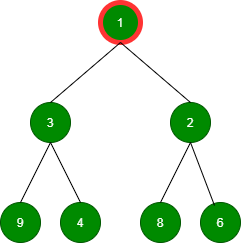
移除:移除根直到 minheap 为空
删除值为 1 的根:
删除值为 2 的根:
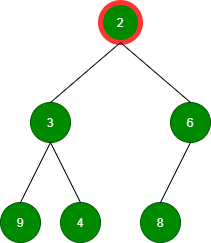
删除值为 3 的根:
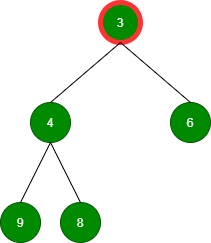
删除值为 4 的根:
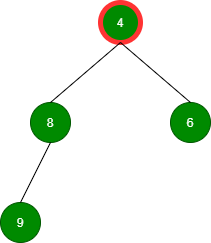
删除值为 6 的根:
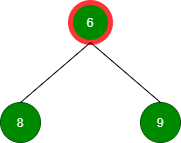
删除值为 8 的根:
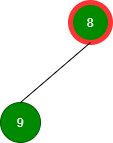
删除值为 9 的根:
![]()
Hence we can conclude that in the min-heap, the smallest element will be at the root of the heap, and in the max heap, the greatest element will be at the root of the heap. While implementing the remove() function on heap, the root element will be removed. Since the output should be in increasing order, Min heap can be used. Priority Queue is used to implement min heap in java.
例子
Java
// JAva Program toIllustrate Union of Two Linked Lists
// Using Priority Queue
// Importing basic reqquired classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Helper class
// Node creation
class Node {
// Data and addressing variable of node
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor to initialize node
Node(int a)
{
data = a;
next = null;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
public class GfG {
// Reading input via Scanner class
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// Method 1
// To create the input list1
public static Node inputList1()
{
// Declaring node variables that is
// Head and tail
Node head, tail;
// Custom input node elements
head = tail = new Node(9);
tail.next = new Node(6);
// Fetching for next node
// using next() method
tail = tail.next;
// Similarly for node 3
tail.next = new Node(4);
tail = tail.next;
// Similarly for node 4
tail.next = new Node(2);
tail = tail.next;
// Similarly for node 5
tail.next = new Node(3);
tail = tail.next;
// Similarly for node 6
tail.next = new Node(8);
tail = tail.next;
// Returning the head
return head;
}
// Method 2
// To create the input List2
// Similar to method 1 but for List2
public static Node inputList2()
{
Node head, tail;
head = tail = new Node(1);
tail.next = new Node(2);
tail = tail.next;
tail.next = new Node(8);
tail = tail.next;
tail.next = new Node(6);
tail = tail.next;
tail.next = new Node(2);
tail = tail.next;
return head;
}
// Method 3
// To print the union list
public static void printList(Node n)
{
// Till there is a node
// condition holds true
while (n != null) {
// Print the node
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
// Moving onto next node
n = n.next;
}
}
// Method 4
// main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Taking input for List 1 and List 2
Node head1 = inputList1();
Node head2 = inputList2();
// Calling
Union obj = new Union();
printList(obj.findUnion(head1, head2));
}
}
// Class 3
// To make the union of two linked list
class Union {
public static Node findUnion(Node head1, Node head2)
{
// Creating a priority queue where
// declaring elements of integer type
PriorityQueue minheap
= new PriorityQueue();
// Setting heads
Node l1 = head1, l2 = head2;
// For List 1
// Inserting elements from linked list1 into
// priority queue
while (l1 != null) {
if (!minheap.contains(l1.data)) {
minheap.add(l1.data);
}
// Move to next element
l1 = l1.next;
}
// For List 2
// Inserting elements from linked list2 into
// priority queue
while (l2 != null) {
if (!minheap.contains(l2.data)) {
minheap.add(l2.data);
}
// Move to next element
l2 = l2.next;
}
Node union = new Node(0), start = union;
// Removing until heap is empty
while (!minheap.isEmpty()) {
Node temp = new Node(minheap.remove());
// Using temp to stoe start
start.next = temp;
start = start.next;
}
// Returning node
return union.next;
}
} 1 2 3 4 6 8 9 Time complexity: O(nlogn), Space complexity: O(n)