使用 SQLAlchemy 从 Pandas 数据框创建 SQL 表
在本文中,我们将讨论如何使用 SQLAlchemy 从 Pandas 数据框创建 SQL 表。
作为第一步,使用 SQLAlchemy 的 create_engine()函数与现有数据库建立连接。
Syntax:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine = create_engine(dialect+driver://username:password@host:port/database)
Explanation:
- dialect – Name of the DBMS
- driver – Name of the DB API that moves information between SQLAlchemy and the database.
- Username, Password – DB User credentials
- host: port – Specify the type of host and port number.
- Database – Database name
例子:
Python3
engine = create_engine(
'postgresql+psycopg2://scott:tiger@localhost:5432/mydatabase')Python3
# import the necessary packages
import pandas
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# Create the engine to connect to the inbuilt
# sqllite database
engine = create_engine("sqlite+pysqlite:///:memory:")
# Read data from CSV which will be
# loaded as a dataframe object
data = pandas.read_csv('superstore.csv')
# print the sample of a dataframe
data.head()
# Write data into the table in sqllite database
data.to_sql('loan_data', engine)Python3
from sqlalchemy import text
# establish the connection with the engine object
with engine.connect() as conn:
# let's select the column credit_history
# from the loan data table
result = conn.execute(text("SELECT Credit_History FROM loan_data"))
# print the result
for row in result:
print(row.Credit_History)上面的例子创建了一个特定于PostgreSQL的 Dialect 对象和一个Pool对象,当接收到连接请求时,它在localhost:5432建立一个DBAPI连接。
SQLAlchemy 包括许多针对最常见数据库(如Oracle、MS SQL、PostgreSQL、SQLite、MySQL等)的方言实现。要将数据帧加载到任何数据库,SQLAlchemy 提供了一个名为 to_sql() 的函数。
Syntax: pandas.DataFrame.to_sql(table_name, engine_name, if_exists, schema, index, chunksize, dtype)
Explanation:
- table_name – Name in which the table has to be stored
- engine_name – Name of the engine which is connected to the database
- if_exists – By default, pandas throws an error if the table_name already exists. Use ‘REPLACE’ to replace this dataset with the old one or “APPEND” to add the data to the existing table.
- index – (bool), Adds index column to the table that identifies each row uniquely.
对于这个例子,我们可以使用一个内置的、仅在内存中的SQLite数据库,这是测试事物的最简单方法之一,但是对于 SQLAlchemy 支持的所有其他数据库,该过程是相同的。您可以在此处下载示例数据集。
让我们首先导入必要的数据集。现在,让我们与仅内存中的SQLite数据库建立连接,并使用pysqlite驱动程序使其可与Python交互。接下来,我们将使用to_sql()函数加载要推送到SQLite数据库的数据帧,如图所示。
Python3
# import the necessary packages
import pandas
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# Create the engine to connect to the inbuilt
# sqllite database
engine = create_engine("sqlite+pysqlite:///:memory:")
# Read data from CSV which will be
# loaded as a dataframe object
data = pandas.read_csv('superstore.csv')
# print the sample of a dataframe
data.head()
# Write data into the table in sqllite database
data.to_sql('loan_data', engine)
输出:
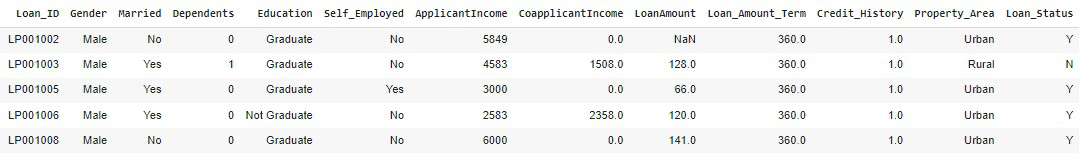
输出
为了检查数据框是否作为表上传,我们可以使用 SQLAlchemy查询表,如下所示,
Python3
from sqlalchemy import text
# establish the connection with the engine object
with engine.connect() as conn:
# let's select the column credit_history
# from the loan data table
result = conn.execute(text("SELECT Credit_History FROM loan_data"))
# print the result
for row in result:
print(row.Credit_History)
输出:
