转置图
有向图 G 的转置是同一组顶点上的另一个有向图,其中所有边与 G 中相应边的方向相反。也就是说,如果 G 包含边 (u, v),则相反/ G的转置/反转包含一条边(v,u),反之亦然。
给定一个图(表示为邻接表),我们需要找到另一个图,它是给定图的转置。
例子:
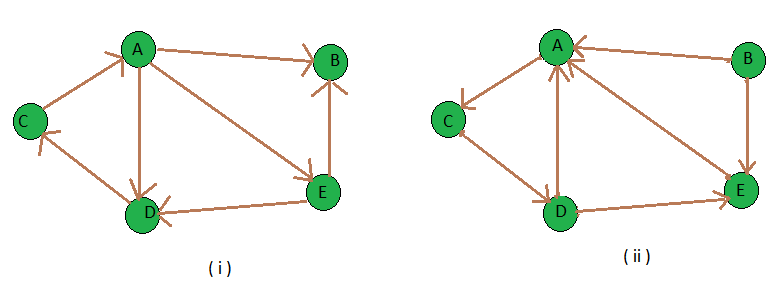
转置图
Input : figure (i) is the input graph.
Output : figure (ii) is the transpose graph of the given graph.
我们遍历邻接表,当我们在顶点 u 的邻接表中找到一个顶点 v 表示主图中从 u 到 v 的一条边时,我们只需在转置图中添加一条从 v 到 u 的边,即在邻接中添加 u新图的顶点 v 列表。因此遍历主图所有顶点的列表,我们可以得到转置图。因此,算法的总时间复杂度为 O(V+E),其中 V 是图的顶点数,E 是图的边数。
注意:获取以邻接矩阵格式存储的图形的转置很简单,您只需要获取该矩阵的转置即可。
C++
// CPP program to find transpose of a graph.
#include
using namespace std;
// function to add an edge from vertex source to vertex dest
void addEdge(vector adj[], int src, int dest)
{
adj[src].push_back(dest);
}
// function to print adjacency list of a graph
void displayGraph(vector adj[], int v)
{
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
cout << i << "--> ";
for (int j = 0; j < adj[i].size(); j++)
cout << adj[i][j] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
}
// function to get Transpose of a graph taking adjacency
// list of given graph and that of Transpose graph
void transposeGraph(vector adj[],
vector transpose[], int v)
{
// traverse the adjacency list of given graph and
// for each edge (u, v) add an edge (v, u) in the
// transpose graph's adjacency list
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < adj[i].size(); j++)
addEdge(transpose, adj[i][j], i);
}
int main()
{
int v = 5;
vector adj[v];
addEdge(adj, 0, 1);
addEdge(adj, 0, 4);
addEdge(adj, 0, 3);
addEdge(adj, 2, 0);
addEdge(adj, 3, 2);
addEdge(adj, 4, 1);
addEdge(adj, 4, 3);
// Finding transpose of graph represented
// by adjacency list adj[]
vector transpose[v];
transposeGraph(adj, transpose, v);
// displaying adjacency list of transpose
// graph i.e. b
displayGraph(transpose, v);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find the transpose of a graph
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Graph
{
// Total number of vertices
private static int vertices = 5;
// Find transpose of graph represented by adj
private static ArrayList[] adj = new ArrayList[vertices];
// Store the transpose of graph represented by tr
private static ArrayList[] tr = new ArrayList[vertices];
// Function to add an edge from source vertex u to
// destination vertex v, if choice is false the edge is added
// to adj otherwise the edge is added to tr
public static void addedge(int u, int v, boolean choice)
{
if(!choice)
adj[u].add(v);
else
tr[u].add(v);
}
// Function to print the graph representation
public static void printGraph()
{
for(int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
{
System.out.print(i + "--> ");
for(int j = 0; j < tr[i].size(); j++)
System.out.print(tr[i].get(j) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
// Function to print the transpose of
// the graph represented as adj and store it in tr
public static void getTranspose()
{
// Traverse the graph and for each edge u, v
// in graph add the edge v, u in transpose
for(int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < adj[i].size(); j++)
addedge(adj[i].get(j), i, true);
}
public static void main (String[] args) throws java.lang.Exception
{
for(int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
{
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
tr[i] = new ArrayList();
}
addedge(0, 1, false);
addedge(0, 4, false);
addedge(0, 3, false);
addedge(2, 0, false);
addedge(3, 2, false);
addedge(4, 1, false);
addedge(4, 3, false);
// Finding transpose of the graph
getTranspose();
// Printing the graph representation
printGraph();
}
}
// This code is contributed by code_freak Python3
# Python3 program to find transpose of a graph.
# function to add an edge from vertex
# source to vertex dest
def addEdge(adj, src, dest):
adj[src].append(dest)
# function to pradjacency list
# of a graph
def displayGraph(adj, v):
for i in range(v):
print(i, "--> ", end = "")
for j in range(len(adj[i])):
print(adj[i][j], end = " ")
print()
# function to get Transpose of a graph
# taking adjacency list of given graph
# and that of Transpose graph
def transposeGraph(adj, transpose, v):
# traverse the adjacency list of given
# graph and for each edge (u, v) add
# an edge (v, u) in the transpose graph's
# adjacency list
for i in range(v):
for j in range(len(adj[i])):
addEdge(transpose, adj[i][j], i)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
v = 5
adj = [[] for i in range(v)]
addEdge(adj, 0, 1)
addEdge(adj, 0, 4)
addEdge(adj, 0, 3)
addEdge(adj, 2, 0)
addEdge(adj, 3, 2)
addEdge(adj, 4, 1)
addEdge(adj, 4, 3)
# Finding transpose of graph represented
# by adjacency list adj[]
transpose = [[]for i in range(v)]
transposeGraph(adj, transpose, v)
# displaying adjacency list of
# transpose graph i.e. b
displayGraph(transpose, v)
# This code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// C# program to find the transpose of a graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Graph
{
// Total number of vertices
private static int vertices = 5;
// Find transpose of graph represented by adj
private static List[] adj = new List[vertices];
// Store the transpose of graph represented by tr
private static List[] tr = new List[vertices];
// Function to add an edge from source vertex u to
// destination vertex v, if choice is false the edge is added
// to adj otherwise the edge is added to tr
public static void addedge(int u, int v, bool choice)
{
if(!choice)
adj[u].Add(v);
else
tr[u].Add(v);
}
// Function to print the graph representation
public static void printGraph()
{
for(int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
{
Console.Write(i + "--> ");
for(int j = 0; j < tr[i].Count; j++)
Console.Write(tr[i][j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Function to print the transpose of
// the graph represented as adj and store it in tr
public static void getTranspose()
{
// Traverse the graph and for each edge u, v
// in graph add the edge v, u in transpose
for(int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < adj[i].Count; j++)
addedge(adj[i][j], i, true);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
{
adj[i] = new List();
tr[i] = new List();
}
addedge(0, 1, false);
addedge(0, 4, false);
addedge(0, 3, false);
addedge(2, 0, false);
addedge(3, 2, false);
addedge(4, 1, false);
addedge(4, 3, false);
// Finding transpose of the graph
getTranspose();
// Printing the graph representation
printGraph();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji 输出:
0--> 2
1--> 0 4
2--> 3
3--> 0 4
4--> 0