使用 NumPy 从零开始实现神经网络
受人脑工作方式启发的机器学习算法中的DNN(深度神经网络) 。 DNN主要用作分类算法。在本文中,我们将介绍如何从头开始在 NumPy(Python库)中实现基本 DNN 算法的逐步方法。
本文的目的是让初学者了解神经网络的工作原理及其实现细节。我们将构建一个三字母(A,B,C)分类器,为简单起见,我们将创建字母(A,B,C)作为 0 和 1 的 NumPy 数组,同时我们将忽略偏差与每个节点相关的术语。
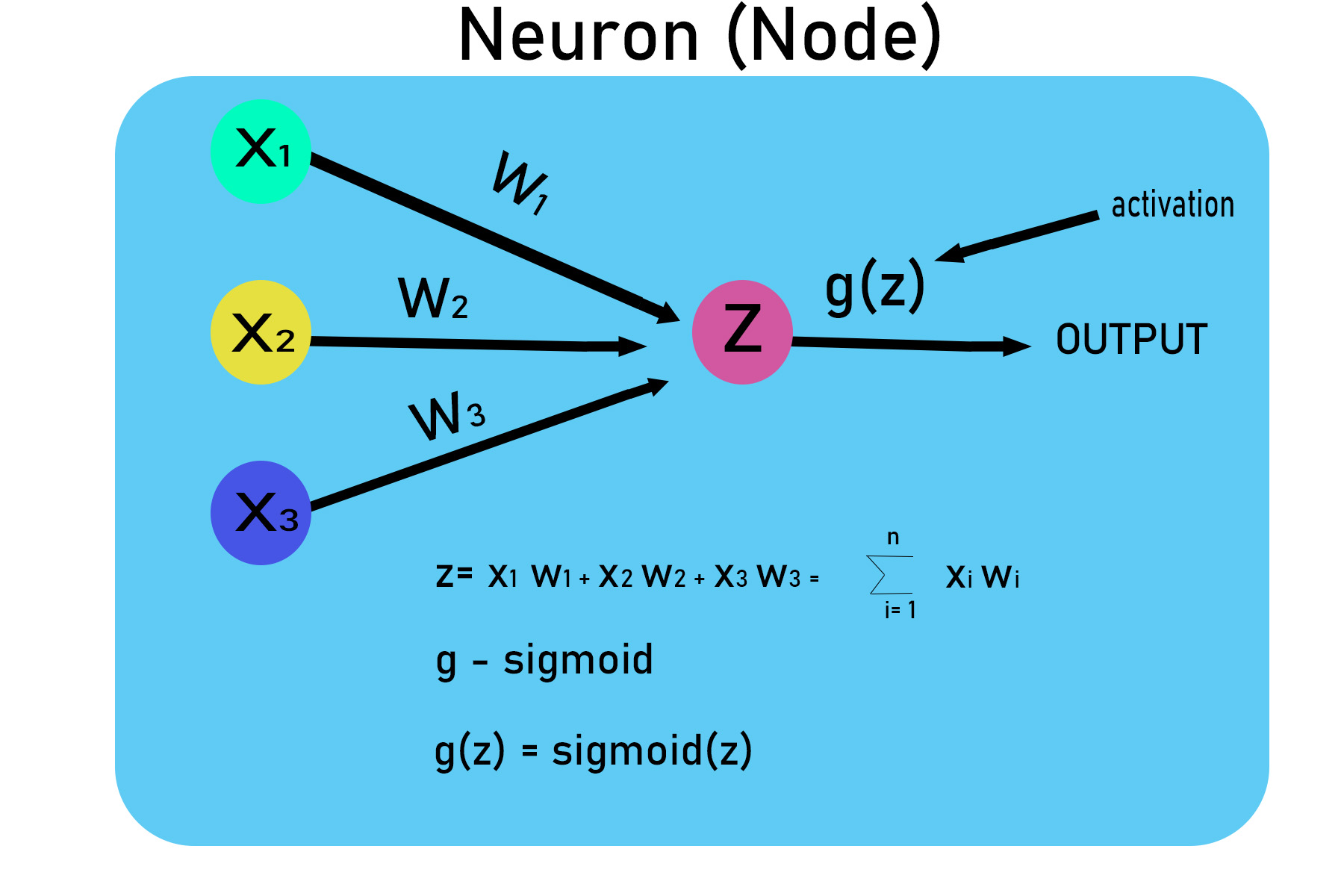
第 1 步:使用 0 和 1 的 numpy 数组创建数据集。
由于图像是矩阵中像素值的集合,我们将为 A、B、C 创建像素矩阵
using 0 and 1
#A
0 0 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0 0 1
#B
0 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 0 0 1 0
0 1 1 1 1 0
#C
0 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 0
#Labels for each Letter
A=[1, 0, 0]
B=[0, 1, 0]
C=[0, 0, 1]代码:
Python3
# Creating data set
# A
a =[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1,
1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
# B
b =[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
# C
c =[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
# Creating labels
y =[[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1]]Python3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# visualizing the data, ploting A.
plt.imshow(np.array(a).reshape(5, 6))
plt.show()Python3
# converting data and labels into numpy array
"""
Convert the matrix of 0 and 1 into one hot vector
so that we can directly feed it to the neural network,
these vectors are then stored in a list x.
"""
x =[np.array(a).reshape(1, 30), np.array(b).reshape(1, 30),
np.array(c).reshape(1, 30)]
# Labels are also converted into NumPy array
y = np.array(y)
print(x, "\n\n", y)Python3
# activation function
def sigmoid(x):
return(1/(1 + np.exp(-x)))
# Creating the Feed forward neural network
# 1 Input layer(1, 30)
# 1 hidden layer (1, 5)
# 1 output layer(3, 3)
def f_forward(x, w1, w2):
# hidden
z1 = x.dot(w1)# input from layer 1
a1 = sigmoid(z1)# out put of layer 2
# Output layer
z2 = a1.dot(w2)# input of out layer
a2 = sigmoid(z2)# output of out layer
return(a2)
# initializing the weights randomly
def generate_wt(x, y):
l =[]
for i in range(x * y):
l.append(np.random.randn())
return(np.array(l).reshape(x, y))
# for loss we will be using mean square error(MSE)
def loss(out, Y):
s =(np.square(out-Y))
s = np.sum(s)/len(y)
return(s)
# Back propagation of error
def back_prop(x, y, w1, w2, alpha):
# hidden layer
z1 = x.dot(w1)# input from layer 1
a1 = sigmoid(z1)# output of layer 2
# Output layer
z2 = a1.dot(w2)# input of out layer
a2 = sigmoid(z2)# output of out layer
# error in output layer
d2 =(a2-y)
d1 = np.multiply((w2.dot((d2.transpose()))).transpose(),
(np.multiply(a1, 1-a1)))
# Gradient for w1 and w2
w1_adj = x.transpose().dot(d1)
w2_adj = a1.transpose().dot(d2)
# Updating parameters
w1 = w1-(alpha*(w1_adj))
w2 = w2-(alpha*(w2_adj))
return(w1, w2)
def train(x, Y, w1, w2, alpha = 0.01, epoch = 10):
acc =[]
losss =[]
for j in range(epoch):
l =[]
for i in range(len(x)):
out = f_forward(x[i], w1, w2)
l.append((loss(out, Y[i])))
w1, w2 = back_prop(x[i], y[i], w1, w2, alpha)
print("epochs:", j + 1, "======== acc:", (1-(sum(l)/len(x)))*100)
acc.append((1-(sum(l)/len(x)))*100)
losss.append(sum(l)/len(x))
return(acc, losss, w1, w2)
def predict(x, w1, w2):
Out = f_forward(x, w1, w2)
maxm = 0
k = 0
for i in range(len(Out[0])):
if(maxmPython3
w1 = generate_wt(30, 5)
w2 = generate_wt(5, 3)
print(w1, "\n\n", w2)Python3
"""The arguments of train function are data set list x,
correct labels y, weights w1, w2, learning rate = 0.1,
no of epochs or iteration.The function will return the
matrix of accuracy and loss and also the matrix of
trained weights w1, w2"""
acc, losss, w1, w2 = train(x, y, w1, w2, 0.1, 100)Python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt1
# ploting accuraccy
plt1.plot(acc)
plt1.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt1.xlabel("Epochs:")
plt1.show()
# plotting Loss
plt1.plot(losss)
plt1.ylabel('Loss')
plt1.xlabel("Epochs:")
plt1.show()Python3
# the trained weigths are
print(w1, "\n", w2)Python3
"""
The predict function will take the following arguments:
1) image matrix
2) w1 trained weights
3) w2 trained weights
"""
predict(x[1], w1, w2)第 2 步:数据集的可视化
Python3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# visualizing the data, ploting A.
plt.imshow(np.array(a).reshape(5, 6))
plt.show()
输出:

步骤 3 :由于数据集是列表形式,我们将其转换为 numpy 数组。
Python3
# converting data and labels into numpy array
"""
Convert the matrix of 0 and 1 into one hot vector
so that we can directly feed it to the neural network,
these vectors are then stored in a list x.
"""
x =[np.array(a).reshape(1, 30), np.array(b).reshape(1, 30),
np.array(c).reshape(1, 30)]
# Labels are also converted into NumPy array
y = np.array(y)
print(x, "\n\n", y)
输出:
[array([[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]]),
array([[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]]),
array([[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]])]
[[1 0 0]
[0 1 0]
[0 0 1]]第 4 步:定义深度神经网络的架构或结构。这包括确定层数和每层中的节点数。我们的神经网络将具有以下结构。
1st layer: Input layer(1, 30)
2nd layer: Hidden layer (1, 5)
3rd layer: Output layer(3, 3)
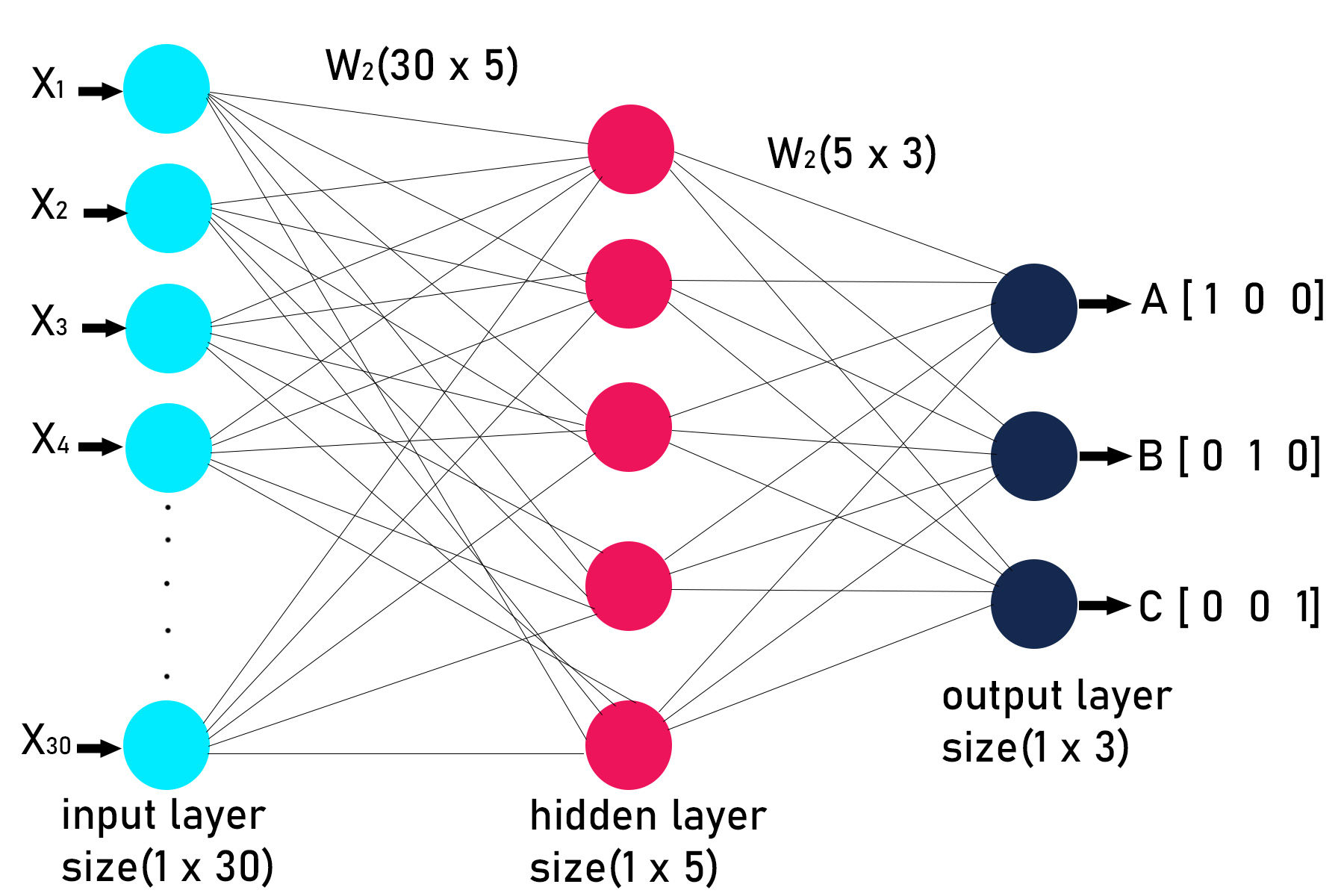
第 5 步:声明和定义构建深度神经网络的所有函数。
Python3
# activation function
def sigmoid(x):
return(1/(1 + np.exp(-x)))
# Creating the Feed forward neural network
# 1 Input layer(1, 30)
# 1 hidden layer (1, 5)
# 1 output layer(3, 3)
def f_forward(x, w1, w2):
# hidden
z1 = x.dot(w1)# input from layer 1
a1 = sigmoid(z1)# out put of layer 2
# Output layer
z2 = a1.dot(w2)# input of out layer
a2 = sigmoid(z2)# output of out layer
return(a2)
# initializing the weights randomly
def generate_wt(x, y):
l =[]
for i in range(x * y):
l.append(np.random.randn())
return(np.array(l).reshape(x, y))
# for loss we will be using mean square error(MSE)
def loss(out, Y):
s =(np.square(out-Y))
s = np.sum(s)/len(y)
return(s)
# Back propagation of error
def back_prop(x, y, w1, w2, alpha):
# hidden layer
z1 = x.dot(w1)# input from layer 1
a1 = sigmoid(z1)# output of layer 2
# Output layer
z2 = a1.dot(w2)# input of out layer
a2 = sigmoid(z2)# output of out layer
# error in output layer
d2 =(a2-y)
d1 = np.multiply((w2.dot((d2.transpose()))).transpose(),
(np.multiply(a1, 1-a1)))
# Gradient for w1 and w2
w1_adj = x.transpose().dot(d1)
w2_adj = a1.transpose().dot(d2)
# Updating parameters
w1 = w1-(alpha*(w1_adj))
w2 = w2-(alpha*(w2_adj))
return(w1, w2)
def train(x, Y, w1, w2, alpha = 0.01, epoch = 10):
acc =[]
losss =[]
for j in range(epoch):
l =[]
for i in range(len(x)):
out = f_forward(x[i], w1, w2)
l.append((loss(out, Y[i])))
w1, w2 = back_prop(x[i], y[i], w1, w2, alpha)
print("epochs:", j + 1, "======== acc:", (1-(sum(l)/len(x)))*100)
acc.append((1-(sum(l)/len(x)))*100)
losss.append(sum(l)/len(x))
return(acc, losss, w1, w2)
def predict(x, w1, w2):
Out = f_forward(x, w1, w2)
maxm = 0
k = 0
for i in range(len(Out[0])):
if(maxm第 6 步:初始化权重,因为神经网络有 3 层,所以会有 2 个权重矩阵与之关联。每个矩阵的大小取决于两个连接层中的节点数。
代码:
Python3
w1 = generate_wt(30, 5)
w2 = generate_wt(5, 3)
print(w1, "\n\n", w2)
输出:
[[ 0.75696605 -0.15959223 -1.43034587 0.17885107 -0.75859483]
[-0.22870119 1.05882236 -0.15880572 0.11692122 0.58621482]
[ 0.13926738 0.72963505 0.36050426 0.79866465 -0.17471235]
[ 1.00708386 0.68803291 0.14110839 -0.7162728 0.69990794]
[-0.90437131 0.63977434 -0.43317212 0.67134205 -0.9316605 ]
[ 0.15860963 -1.17967773 -0.70747245 0.22870289 0.00940404]
[ 1.40511247 -1.29543461 1.41613069 -0.97964787 -2.86220777]
[ 0.66293564 -1.94013093 -0.78189238 1.44904122 -1.81131482]
[ 0.4441061 -0.18751726 -2.58252033 0.23076863 0.12182448]
[-0.60061323 0.39855851 -0.55612255 2.0201934 0.70525187]
[-1.82925367 1.32004437 0.03226202 -0.79073523 -0.20750692]
[-0.25756077 -1.37543232 -0.71369897 -0.13556156 -0.34918718]
[ 0.26048374 2.49871398 1.01139237 -1.73242425 -0.67235417]
[ 0.30351062 -0.45425039 -0.84046541 -0.60435352 -0.06281934]
[ 0.43562048 0.66297676 1.76386981 -1.11794675 2.2012095 ]
[-1.11051533 0.3462945 0.19136933 0.19717914 -1.78323674]
[ 1.1219638 -0.04282422 -0.0142484 -0.73210071 -0.58364205]
[-1.24046375 0.23368434 0.62323707 -1.66265946 -0.87481714]
[ 0.19484897 0.12629217 -1.01575241 -0.47028007 -0.58278292]
[ 0.16703418 -0.50993283 -0.90036661 2.33584006 0.96395524]
[-0.72714199 0.39000914 -1.3215123 0.92744032 -1.44239943]
[-2.30234278 -0.52677889 -0.09759073 -0.63982215 -0.51416013]
[ 1.25338899 -0.58950956 -0.86009159 -0.7752274 2.24655146]
[ 0.07553743 -1.2292084 0.46184872 -0.56390328 0.15901276]
[-0.52090565 -2.42754589 -0.78354152 -0.44405857 1.16228247]
[-1.21805132 -0.40358444 -0.65942185 0.76753095 -0.19664978]
[-1.5866041 1.17100962 -1.50840821 -0.61750557 1.56003127]
[ 1.33045269 -0.85811272 1.88869376 0.79491455 -0.96199293]
[-2.34456987 0.1005953 -0.99376025 -0.94402235 -0.3078695 ]
[ 0.93611909 0.58522915 -0.15553566 -1.03352997 -2.7210093 ]]
[[-0.50650286 -0.41168428 -0.7107231 ]
[ 1.86861492 -0.36446849 0.97721539]
[-0.12792125 0.69578056 -0.6639736 ]
[ 0.58190462 -0.98941614 0.40932723]
[ 0.89758789 -0.49250365 -0.05023684]]第 7 步:训练模型。
Python3
"""The arguments of train function are data set list x,
correct labels y, weights w1, w2, learning rate = 0.1,
no of epochs or iteration.The function will return the
matrix of accuracy and loss and also the matrix of
trained weights w1, w2"""
acc, losss, w1, w2 = train(x, y, w1, w2, 0.1, 100)
输出:
epochs: 1 ======== acc: 59.24962411875523
epochs: 2 ======== acc: 63.68540644266716
epochs: 3 ======== acc: 68.23850165512243
epochs: 4 ======== acc: 71.30325758406262
epochs: 5 ======== acc: 73.52710796040974
epochs: 6 ======== acc: 75.32860090824263
epochs: 7 ======== acc: 76.8094120430158
epochs: 8 ======== acc: 78.00977196942078
epochs: 9 ======== acc: 78.97728263498026
epochs: 10 ======== acc: 79.76587293092753
epochs: 11 ======== acc: 80.42246589416287
epochs: 12 ======== acc: 80.98214842153129
epochs: 13 ======== acc: 81.4695736928823
epochs: 14 ======== acc: 81.90184308791194
epochs: 15 ======== acc: 82.29094665963427
epochs: 16 ======== acc: 82.64546024973251
epochs: 17 ======== acc: 82.97165532985433
epochs: 18 ======== acc: 83.27421706795944
epochs: 19 ======== acc: 83.55671426703763
epochs: 20 ======== acc: 83.82191341206628
epochs: 21 ======== acc: 84.07199359659367
epochs: 22 ======== acc: 84.30869706017322
epochs: 23 ======== acc: 84.53343682891021
epochs: 24 ======== acc: 84.74737503832276
epochs: 25 ======== acc: 84.95148074055622
epochs: 26 ======== acc: 85.1465730591422
epochs: 27 ======== acc: 85.33335370190892
epochs: 28 ======== acc: 85.51243164226796
epochs: 29 ======== acc: 85.68434197894798
epochs: 30 ======== acc: 85.84956043619462
epochs: 31 ======== acc: 86.0085145818298
epochs: 32 ======== acc: 86.16159256503643
epochs: 33 ======== acc: 86.30914997510234
epochs: 34 ======== acc: 86.45151527443966
epochs: 35 ======== acc: 86.58899414916453
epochs: 36 ======== acc: 86.72187303817682
epochs: 37 ======== acc: 86.85042203982091
epochs: 38 ======== acc: 86.97489734865094
epochs: 39 ======== acc: 87.09554333976325
epochs: 40 ======== acc: 87.21259439177474
epochs: 41 ======== acc: 87.32627651970255
epochs: 42 ======== acc: 87.43680887413676
epochs: 43 ======== acc: 87.54440515197342
epochs: 44 ======== acc: 87.64927495564211
epochs: 45 ======== acc: 87.75162513147157
epochs: 46 ======== acc: 87.85166111297174
epochs: 47 ======== acc: 87.94958829083211
epochs: 48 ======== acc: 88.0456134278342
epochs: 49 ======== acc: 88.13994613312185
epochs: 50 ======== acc: 88.2328004057654
epochs: 51 ======== acc: 88.32439625156803
epochs: 52 ======== acc: 88.4149613686817
epochs: 53 ======== acc: 88.5047328856618
epochs: 54 ======== acc: 88.59395911861766
epochs: 55 ======== acc: 88.68290129028868
epochs: 56 ======== acc: 88.77183512103412
epochs: 57 ======== acc: 88.86105215751232
epochs: 58 ======== acc: 88.95086064702116
epochs: 59 ======== acc: 89.04158569269322
epochs: 60 ======== acc: 89.13356833768444
epochs: 61 ======== acc: 89.22716312996127
epochs: 62 ======== acc: 89.32273362510695
epochs: 63 ======== acc: 89.42064521532092
epochs: 64 ======== acc: 89.52125466556964
epochs: 65 ======== acc: 89.62489584606081
epochs: 66 ======== acc: 89.73186143973956
epochs: 67 ======== acc: 89.84238093800867
epochs: 68 ======== acc: 89.95659604815005
epochs: 69 ======== acc: 90.07453567327377
epochs: 70 ======== acc: 90.19609371190103
epochs: 71 ======== acc: 90.32101373021872
epochs: 72 ======== acc: 90.44888465704626
epochs: 73 ======== acc: 90.57915066786961
epochs: 74 ======== acc: 90.7111362751668
epochs: 75 ======== acc: 90.84408471463895
epochs: 76 ======== acc: 90.97720484616241
epochs: 77 ======== acc: 91.10971995033672
epochs: 78 ======== acc: 91.24091164815938
epochs: 79 ======== acc: 91.37015369432306
epochs: 80 ======== acc: 91.49693294991012
epochs: 81 ======== acc: 91.62085750782504
epochs: 82 ======== acc: 91.74165396819595
epochs: 83 ======== acc: 91.8591569057493
epochs: 84 ======== acc: 91.97329371114765
epochs: 85 ======== acc: 92.0840675282122
epochs: 86 ======== acc: 92.19154028777587
epochs: 87 ======== acc: 92.29581711003155
epochs: 88 ======== acc: 92.3970327467751
epochs: 89 ======== acc: 92.49534030435096
epochs: 90 ======== acc: 92.59090221343706
epochs: 91 ======== acc: 92.68388325695001
epochs: 92 ======== acc: 92.77444539437016
epochs: 93 ======== acc: 92.86274409885533
epochs: 94 ======== acc: 92.94892593090393
epochs: 95 ======== acc: 93.03312709510452
epochs: 96 ======== acc: 93.11547275630565
epochs: 97 ======== acc: 93.19607692356153
epochs: 98 ======== acc: 93.27504274176297
epochs: 99 ======== acc: 93.35246306044819
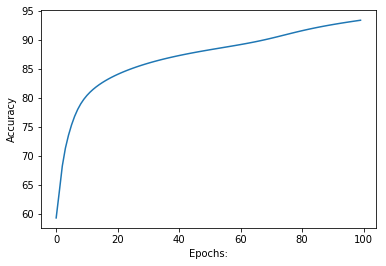
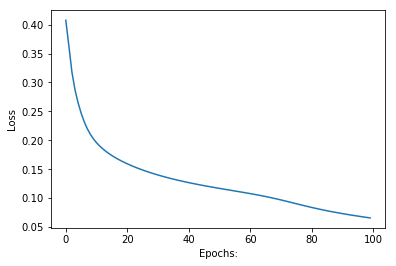
epochs: 100 ======== acc: 93.42842117607569第 8 步:绘制损失和准确度相对于 epoch 数(迭代)的图。
Python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt1
# ploting accuraccy
plt1.plot(acc)
plt1.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt1.xlabel("Epochs:")
plt1.show()
# plotting Loss
plt1.plot(losss)
plt1.ylabel('Loss')
plt1.xlabel("Epochs:")
plt1.show()
输出:
Python3
# the trained weigths are
print(w1, "\n", w2)
输出:
[[-0.23769169 -0.1555992 0.81616823 0.1219152 -0.69572168]
[ 0.36399972 0.37509723 1.5474053 0.85900477 -1.14106725]
[ 1.0477069 0.13061485 0.16802893 -1.04450602 -2.76037811]
[-0.83364475 -0.63609797 0.61527206 -0.42998096 0.248886 ]
[ 0.16293725 -0.49443901 0.47638257 -0.89786531 -1.63778409]
[ 0.10750411 -1.74967435 0.03086382 0.9906433 -0.9976104 ]
[ 0.48454172 -0.68739134 0.78150251 -0.1220987 0.68659854]
[-1.53100416 -0.33999119 -1.07657716 0.81305349 -0.79595135]
[ 2.06592829 1.25309796 -2.03200199 0.03984423 -0.76893089]
[-0.08285231 -0.33820853 -1.08239104 -0.22017196 -0.37606984]
[-0.24784192 -0.36731598 -0.58394944 -0.0434036 0.58383408]
[ 0.28121367 -1.84909298 -0.97302413 1.58393025 0.24571332]
[-0.21185018 0.29358204 -0.79433164 -0.20634606 -0.69157617]
[ 0.13666222 -0.31704319 0.03924342 0.54618961 -1.72226768]
[ 1.06043825 -1.02009526 -1.39511479 -0.98141073 0.78304473]
[ 1.44167174 -2.17432498 0.95281672 -0.76748692 1.16231747]
[ 0.25971927 -0.59872416 1.01291689 -1.45200634 -0.72575161]
[-0.27036828 -1.36721091 -0.43858778 -0.78527025 -0.36159359]
[ 0.91786563 -0.97465418 1.26518387 -0.21425247 -0.25097618]
[-0.00964162 -1.05122248 -1.2747124 1.65647842 1.15216675]
[ 2.63067561 -1.3626307 2.44355269 -0.87960091 -0.39903453]
[ 0.30513627 -0.77390359 -0.57135017 0.72661218 1.44234861]
[ 2.49165837 -0.77744044 -0.14062449 -1.6659343 0.27033269]
[ 1.30530805 -0.93488645 -0.66026013 -0.2839123 -1.21397584]
[ 0.41042422 0.20086176 -2.07552916 -0.12391564 -0.67647955]
[ 0.21339152 0.79963834 1.19499535 -2.17004581 -1.03632954]
[-1.2032222 0.46226132 -0.68314898 1.27665578 0.69930683]
[ 0.11239785 -2.19280608 1.36181772 -0.36691734 -0.32239543]
[-1.62958342 -0.55989702 1.62686431 1.59839946 -0.08719492]
[ 1.09518451 -1.9542822 -1.18507834 -0.5537991 -0.28901241]]
[[ 1.52837185 -0.33038873 -3.45127838]
[ 1.0758812 -0.41879112 -1.00548735]
[-3.59476021 0.55176444 1.14839625]
[ 1.07525643 -1.6250444 0.77552561]
[ 0.82785787 -1.79602953 1.15544384]]Step9:进行预测。
Python3
"""
The predict function will take the following arguments:
1) image matrix
2) w1 trained weights
3) w2 trained weights
"""
predict(x[1], w1, w2)
输出:
Image is of letter B.