Python| Pandas DataFrame.to_string
Pandas DataFrame 是一种二维大小可变的、潜在异构的表格数据结构,带有标记的轴(行和列)。算术运算在行标签和列标签上对齐。它可以被认为是 Series 对象的类 dict 容器。这是 Pandas 的主要数据结构。
Pandas DataFrame.to_string()函数将 DataFrame 呈现为控制台友好的表格输出。
Syntax: DataFrame.to_string(buf=None, columns=None, col_space=None, header=True, index=True, na_rep=’NaN’, formatters=None, float_format=None, sparsify=None, index_names=True, justify=None, max_rows=None, max_cols=None, show_dimensions=False, decimal=’.’, line_width=None)
Parameter :
buf : Buffer to write to.
columns : The subset of columns to write. Writes all columns by default.
col_space : The minimum width of each column.
header : Write out the column names. If a list of strings is given, it is assumed to be aliases for the column names.
index : Whether to print index (row) labels.
na_rep : String representation of NAN to use.
formatters : Formatter functions to apply to columns’ elements by position or name.
float_format : Formatter function to apply to columns’ elements if they are floats. The result of this function must be a unicode string.
sparsify : Set to False for a DataFrame with a hierarchical index to print every multiindex key at each row.
index_names : Prints the names of the indexes.
max_rows : Maximum number of rows to display in the console.
max_cols : Maximum number of columns to display in the console.
show_dimensions : Display DataFrame dimensions (number of rows by number of columns).
decimal : Character recognized as decimal separator, e.g. ‘, ’ in Europe.
line_width : Width to wrap a line in characters.
Returns : str (or unicode, depending on data and options)
示例 #1:使用DataFrame.to_string()函数将给定的 DataFrame 呈现为控制台友好的表格输出。不要在输出中包含索引标签。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Weight':[45, 88, 56, 15, 71],
'Name':['Sam', 'Andrea', 'Alex', 'Robin', 'Kia'],
'Age':[14, 25, 55, 8, 21]})
# Create the index
index_ = pd.date_range('2010-10-09 08:45', periods = 5, freq ='H')
# Set the index
df.index = index_
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
输出 : 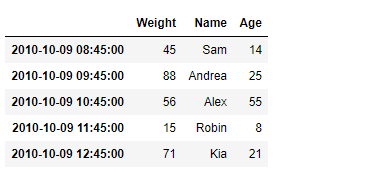
现在我们将使用DataFrame.to_string()函数将给定的 DataFrame 渲染到控制台友好的表格输出。
# print in tabular format
result = df.to_string(index = False)
# Print the result
print(result)
输出 : 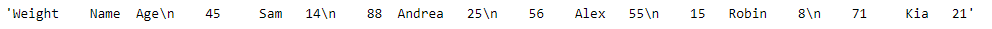
正如我们在输出中看到的那样, DataFrame.to_string()函数已成功地将给定的数据帧呈现到控制台友好的表格输出中。示例 #2:使用DataFrame.to_string()函数将给定的 DataFrame 呈现到控制台友好的表格输出。用字符串'Missing' 表示给定 Dataframe 中的缺失值。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, None, 1],
"B":[7, 2, 54, 3, None],
"C":[20, 16, 11, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, None, 2, 6]})
# Create the index
index_ = ['Row_1', 'Row_2', 'Row_3', 'Row_4', 'Row_5']
# Set the index
df.index = index_
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
输出 : 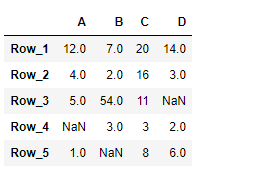
现在我们将使用DataFrame.to_string()函数将给定的 DataFrame 渲染到控制台友好的表格输出。
# print in tabular format
result = df.to_string(na_rep = 'Missing')
# Print the result
print(result)
输出 : 
正如我们在输出中看到的那样, DataFrame.to_string()函数已成功地将给定的数据帧呈现到控制台友好的表格输出中。