到达目的地的决定数
给定一个由 4 种字符组成的网格:'B' '.' “S”和“D”。我们需要从 S 开始到达 D,在每一步我们都可以到达相邻的单元格,即上、下、左和右。具有字符“B”的单元格被阻止,即在任何步骤我们都不能移动到具有“B”的单元格。给定网格以这样的方式具有点,即只有一种方法可以从任何其他单元格到达任何单元格。我们需要告诉我们需要从多个选项中选择多少次,即决定到达 D 的路径。
例子:
Input : Grid = [".BBB.B.BB"
".....B.B."
"B.B.B.BSB"
".DB......"]
Output : 4
In above shown grid we have to decide 4
times to reach destination at (3, 7),
(3, 5), (1, 3) and (1, 1). 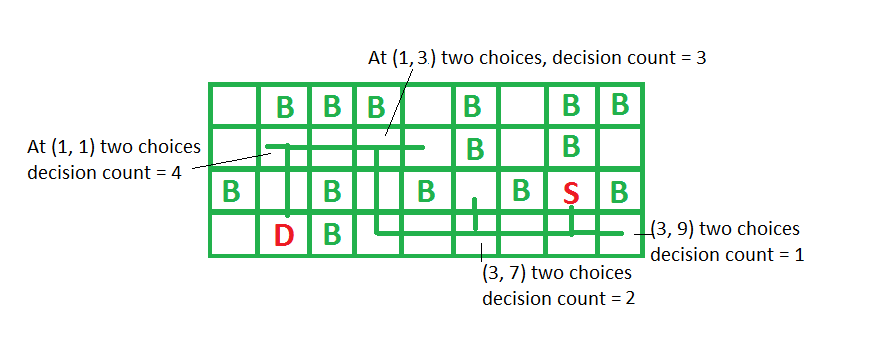
我们可以使用 DFS 解决这个问题。在从源到目的地的路径中,我们可以看到,每当我们有超过 1 个邻居时,我们需要决定我们的路径,所以首先我们做一个 DFS 并将从源到目的地的路径存储为子父数组,然后我们移动从目的地到源,使用父数组逐个单元格,并且在我们有超过 1 个邻居的每个单元格处,我们将把答案增加 1。
请参阅下面的代码以更好地理解。
C++
// C++ program to find decision taken to
// reach destination from source
#include
using namespace std;
// Utility dfs method to fill parent array
void dfs(int u, vector g[], int prt[], bool visit[])
{
visit[u] = true;
// loop over all unvisited neighbors
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++)
{
int v = g[u][i];
if (!visit[v])
{
prt[v] = u;
dfs(v, g, prt, visit);
}
}
}
// method returns decision taken to reach destination
// from source
int turnsToReachDestination(string grid[], int M)
{
int N = grid[0].length();
// storing direction for neighbors
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, -1, 0, 1};
vector g[M*N];
bool visit[M*N] = {0};
int prt[M*N];
int start, dest;
/* initialize start and dest and
store neighbours vector g
If cell index is (i, j), then we can convert
it to 1D as (i*N + j) */
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == 'D')
dest = i*N + j;
if (grid[i][j] == 'S')
start = i*N + j;
g[i*N + j].clear();
if (grid[i][j] != 'B')
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int u = i + dx[k];
int v = j + dy[k];
// if neighboring cell is in boundary
// and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 && u < M && v >= 0 &&
v < N && grid[u][v] != 'B')
g[i*N + j].push_back(u*N + v);
}
}
}
}
// call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit);
int curr = dest;
int res = 0;
// loop from destination cell back to start cell
while (curr != start)
{
/* if current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
then we need to decide our path to reach S
from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (g[curr].size() > 2)
res++;
curr = prt[curr];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
string grid[] =
{
".BBB.B.BB",
".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB",
".DB......"
};
int M = sizeof(grid)/sizeof(grid[0]);
cout << turnsToReachDestination(grid, M) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find decision taken to
// reach destination from source
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Utility dfs method to fill parent array
static void dfs(int u, Vector g[],
int prt[], boolean visit[])
{
visit[u] = true;
// loop over all unvisited neighbors
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++)
{
int v = g[u].get(i);
if (!visit[v])
{
prt[v] = u;
dfs(v, g, prt, visit);
}
}
}
// method returns decision taken to reach destination
// from source
static int turnsToReachDestination(String grid[], int M)
{
int N = grid[0].length();
// storing direction for neighbors
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, -1, 0, 1};
Vector []g = new Vector[M*N];
for (int i = 0; i < M*N; i++)
g[i] = new Vector();
boolean []visit = new boolean[M*N];
int []prt = new int[M*N];
int start = -1, dest = -1;
/* initialize start and dest and
store neighbours vector g
If cell index is (i, j), then we can convert
it to 1D as (i*N + j) */
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (grid[i].charAt(j) == 'D')
dest = i * N + j;
if (grid[i].charAt(j) == 'S')
start = i * N + j;
g[i * N + j].clear();
if (grid[i].charAt(j) != 'B')
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int u = i + dx[k];
int v = j + dy[k];
// if neighboring cell is in boundary
// and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 && u < M && v >= 0 &&
v < N && grid[u].charAt(v) != 'B')
g[i * N + j].add(u * N + v);
}
}
}
}
// call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit);
int curr = dest;
int res = 0;
// loop from destination cell back to start cell
while (curr != start)
{
/* if current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
then we need to decide our path to reach S
from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (g[curr].size() > 2)
res++;
curr = prt[curr];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String grid[] =
{
".BBB.B.BB",
".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB",
".DB......"
};
int M = grid.length;
System.out.print(turnsToReachDestination(grid, M) +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Python3
# Python3 program to find decision taken
# to reach destination from source
# Utility dfs method to fill parent array
def dfs(u, g, prt, visit):
visit[u] = True
# Loop over all unvisited neighbors
for i in range(len(g[u])):
v = g[u][i]
if (not visit[v]):
prt[v] = u
dfs(v, g, prt, visit)
# Method returns decision taken to
# reach destination from source
def turnsToReachDestination(grid, M):
N = len(grid[0])
# Storing direction for neighbors
dx = [ -1, 0, 1, 0 ]
dy = [ 0, -1, 0, 1 ]
g = {}
visit = [0 for i in range(M * N)]
prt = [0 for i in range(M * N)]
start = -1
dest = -1
# Initialize start and dest and
# store neighbours vector g
# If cell index is (i, j), then
# we can convert
# it to 1D as (i*N + j)
for i in range(M):
for j in range(N):
if (grid[i][j] == 'D'):
dest = i * N + j
if (grid[i][j] == 'S'):
start = i * N + j
if (grid[i][j] != 'B'):
for k in range(4):
u = i + dx[k]
v = j + dy[k]
# If neighboring cell is in
# boundary and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 and u < M and
v >= 0 and v < N and
grid[u][v] != 'B'):
if (i * N +j) not in g:
g[i * N + j] = []
g[i * N + j].append(u * N + v)
else:
g[i * N + j].append(u * N + v)
# Call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit)
curr = dest
res = 0
# Loop from destination cell back to start cell
while(curr != start):
# If current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
# then we need to decide our path to reach S
# from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (len(g[curr]) > 2):
res += 1
curr = prt[curr]
return res
# Driver code
grid = [ ".BBB.B.BB", ".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB", ".DB......" ]
M = len(grid)
print(turnsToReachDestination(grid, M))
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155C#
// C# program to find decision taken to
// reach destination from source
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Utility dfs method to fill parent array
static void dfs(int u, List []g,
int []prt, bool []visit)
{
visit[u] = true;
// loop over all unvisited neighbors
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].Count; i++)
{
int v = g[u][i];
if (!visit[v])
{
prt[v] = u;
dfs(v, g, prt, visit);
}
}
}
// method returns decision taken to reach destination
// from source
static int turnsToReachDestination(String []grid, int M)
{
int N = grid[0].Length;
// storing direction for neighbors
int []dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int []dy = {0, -1, 0, 1};
List []g = new List[M*N];
for (int i = 0; i < M*N; i++)
g[i] = new List();
bool []visit = new bool[M*N];
int []prt = new int[M*N];
int start = -1, dest = -1;
/* initialize start and dest and
store neighbours vector g
If cell index is (i, j), then we can convert
it to 1D as (i*N + j) */
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == 'D')
dest = i * N + j;
if (grid[i][j] == 'S')
start = i * N + j;
g[i * N + j].Clear();
if (grid[i][j] != 'B')
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int u = i + dx[k];
int v = j + dy[k];
// if neighboring cell is in boundary
// and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 && u < M && v >= 0 &&
v < N && grid[u][v] != 'B')
g[i * N + j].Add(u * N + v);
}
}
}
}
// call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit);
int curr = dest;
int res = 0;
// loop from destination cell back to start cell
while (curr != start)
{
/* if current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
then we need to decide our path to reach S
from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (g[curr].Count > 2)
res++;
curr = prt[curr];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String []grid =
{
".BBB.B.BB",
".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB",
".DB......"
};
int M = grid.Length;
Console.Write(turnsToReachDestination(grid, M) +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
输出:
4