通过删除 L 形中的元素来计算对角矩阵分解中的总和
给定两个表示方阵维数的整数N和一个用于初始化矩阵的整数A。给定另一个整数mod 。按照给定的步骤计算所需的总和:
- 从最右边的元素开始选择L形所有元素的乘积,将其添加到总和中,然后从矩阵中删除所有元素。
- 将上一步中删除的项与矩阵中剩余的所有其他元素相乘。
- 由于总和可能非常大,请以 modulo mod打印。
例子:
Input: N = 3, A = 3, mod = 1000000007
Output: 953271922
Explanation: 1.2157665459E19 % 1000000007 = 953271922
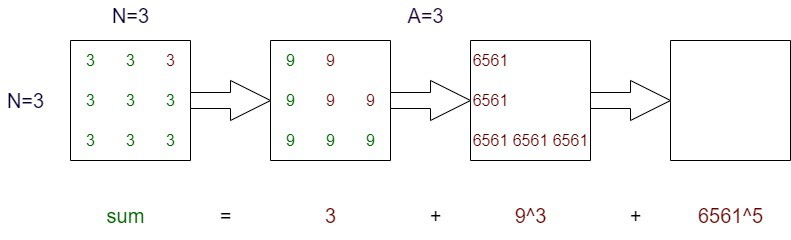
Calculate sum in Diagonal Matrix Decomposition by removing elements in L-shape
Input: N = 2, A = 1, mod = 2
Output: 0
方法:很明显,不能创建大维度的矩阵。此外,可以观察到,每个项都具有奇次幂,其中每个项的底数是前一项的一个幂,指数是每次删除的元素数。按照给定的步骤解决问题:
- 使用Binary Exponentiation的概念创建一个快速的 Modular Exponentiation函数Mod_Power 。
- 将 A 、 2*i-1和 mod 传递给Mod_Power ,其中2*i-1是从1开始的奇次幂,并将结果存储在(比如在变量term中)。
- 通过添加term的所有值来计算总和。
- 将新术语A的基更新为术语和A的乘积。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++14
// C++ code to implement the approach
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
// Function to calculate the power
ll Mod_Power(ll x, ll y, ll m)
{
ll res = 1;
while (y) {
if (y & 1)
res = (res * x) % m;
x = ((x * x) % m + m) % m;
y = y >> 1; // y=y/2
}
return (res % m + m) % m;
}
// Function to get the required sum
ll req_Sum(ll n, ll a, ll m)
{
ll sum = 0, term;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
term = Mod_Power(a, 2 * i - 1, m);
sum += (term % m);
a = ((a * term) % m + m) % m;
}
return (sum % m + m) % m;
}
// driver's code
int main()
{
int N = 3;
int A = 3;
int mod = 1000000007;
cout << req_Sum(N, A, mod);
return 0;
}
// this code is contributed by prophet1999 Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Function to calculate the power
static long Mod_Power(long x, long y, long mod)
{
long res = 1;
while (y > 0) {
if (y % 2 == 1)
res = (res * x) % mod;
x = ((x * x) % mod + mod) % mod;
y = y >> 1;
}
return (res % mod + mod) % mod;
}
// Function to get the required sum
static long req_Sum(long N, long A, long mod)
{
long sum = 0, term;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
term = Mod_Power(A, 2 * i - 1, mod);
sum += (term % mod);
A = ((A * term) % mod + mod) % mod;
}
return (sum % mod + mod) % mod;
}
// Driver's code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Java code to implement the approach
int N = 3;
int A = 3;
int mod = 1000000007;
System.out.print(req_Sum(N, A, mod));
}
}
// this code is contributed by prophet1999Python
# Python code to implement the approach
# Function to calculate the power
def Mod_Power(x, y, m):
res = 1
while (y):
if (y & 1):
res = (res * x) % m
x = ((x * x) % m + m) % m
y = y >> 1 # y=y/2
return (res % m + m) % m
# Function to get the required sum
def req_Sum(n, a, m):
sum = 0
term = 0
for i in range(1, n + 1):
term = Mod_Power(a, 2 * i - 1, m)
sum += (term % m)
a = ((a * term) % m + m) % m
return (sum % m + m) % m
# driver's code
N = 3
A = 3
mod = 1000000007
print(req_Sum(N, A, mod))
# this code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.C#
// C# code to implement the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate the power
static long Mod_Power(long x, long y, long m)
{
long res = 1;
while (y != 0) {
if (y % 2 == 1)
res = (res * x) % m;
x = ((x * x) % m + m) % m;
y = y >> 1; // y=y/2
}
return (res % m + m) % m;
}
// Function to get the required sum
static long req_Sum(long n, long a, long m)
{
long sum = 0, term;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
term = Mod_Power(a, 2 * i - 1, m);
sum += (term % m);
a = ((a * term) % m + m) % m;
}
return (sum % m + m) % m;
}
// driver's code
public static int Main()
{
int N = 3;
int A = 3;
int mod = 1000000007;
Console.Write(req_Sum(N, A, mod));
return 0;
}
}
// This code is contributed by TaranpreetJavascript
输出
953271922时间复杂度: O(N * log (N 2 ))
辅助空间: O(1)