遍历Java中的HashMap
HashMap 将数据存储在 (Key, Value) 对中,您可以通过另一种类型的索引来访问它们。 HashMap 类实现了 Map 接口,它允许我们存储密钥。 hashMap 是自Java 1.2 以来出现的Java集合框架的一部分。它在内部使用非常快的散列技术。
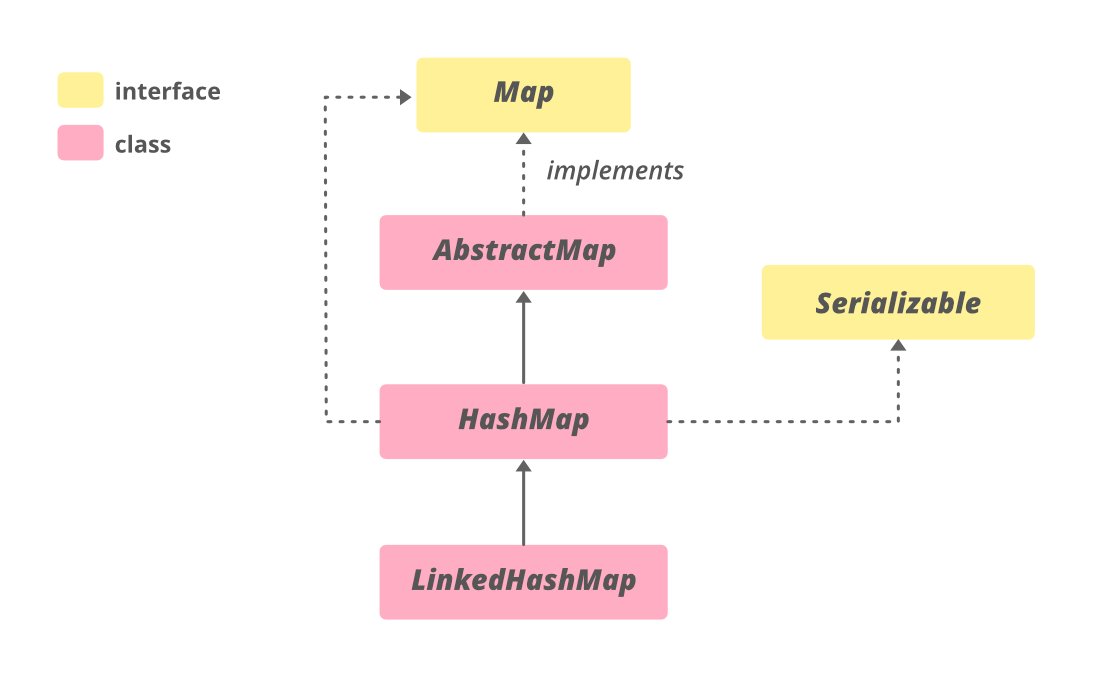
句法:
public class HashMap
extends AbstractMap
implements Map, Clonnable, Serial 不同的遍历方式
我们可以迭代下面列出的键和值对的映射,稍后将描述如下:
方法:
- 使用迭代器
- 使用增强的 for 循环(for-each 循环)
- 使用 forEach() 方法
方法一:使用迭代器
Iterator 是Java.util 包中的一个接口,用于遍历集合。因此,讨论迭代器没有什么特别的,所以我们将提出迭代器接口的方法,用于遍历 HashMap。
- hm.entrySet()用于检索称为 Map.Entries 的所有键值对并在内部存储到集合中。
- hm.entrySet().iterator()返回一个迭代器,它充当光标并指向集合的第一个元素并一直移动到最后。
- hmIterator.hasNext()检查集合中的下一个元素并返回一个布尔值
- hmIterator.next( ) 从集合中返回下一个元素(Map.Entry)。
- mapElement.getKey()返回关联 Map.Entry 的键
- mapElement.getValue()返回关联 Map.Entry 的值
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Traverse through HashMap
// Using Iterator
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an Hashmap of string-integer pairs
// It contains student name and their marks
HashMap hm
= new HashMap();
// Adding mappings to above HashMap
// using put() method
hm.put("GeeksforGeeks", 54);
hm.put("A computer portal", 80);
hm.put("For geeks", 82);
// Printing all elements of HashMap
System.out.println("Created hashmap is" + hm);
// Getting an iterator
Iterator hmIterator = hm.entrySet().iterator();
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"HashMap after adding bonus marks:");
// Iterating through Hashmap and
// adding some bonus marks for every student
while (hmIterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry mapElement
= (Map.Entry)hmIterator.next();
int marks = ((int)mapElement.getValue() + 10);
// Printing mark corresponding to string entries
System.out.println(mapElement.getKey() + " : "
+ marks);
}
}
} Java
// Java program for Traversing through HashMap
// Using for-each Loop
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating an empty HashMap of string and integer
// pairs Mappings denotes Student name and marks
HashMap hm
= new HashMap();
// Adding mappings to HashMap
// using put() method
hm.put("GeeksforGeeks", 54);
hm.put("A computer portal", 80);
hm.put("For geeks", 82);
// Printing all elements of above Map
System.out.println("Created hashmap is" + hm);
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"HashMap after adding bonus marks:");
// Looping through the HashMap
// Using for-each loop
for (Map.Entry mapElement : hm.entrySet()) {
String key = (String)mapElement.getKey();
// Adding some bonus marks to all the students
int value = ((int)mapElement.getValue() + 10);
// Printing above marks corresponding to
// students names
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
} Java
// Java program for traversing Through HashMap
// Using forEach() Method
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashMap of string-integer
// pairs
HashMap hm
= new HashMap();
// Adding mappings to HashMap
// using put() method
hm.put("GeeksforGeeks", 54);
hm.put("A computer portal", 80);
hm.put("For geeks", 82);
// Printing all elements of above HashMap
System.out.println("Created hashmap is" + hm);
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"HashMap after adding bonus marks:");
// Looping through HashMap and adding bonus marks
// using HashMap.forEach()
hm.forEach((k, v)
-> System.out.println(k + " : "
+ (v + 10)));
}
} 输出
Created hashmap is{GeeksforGeeks=54, A computer portal=80, For geeks=82}
HashMap after adding bonus marks:
GeeksforGeeks : 64
A computer portal : 90
For geeks : 92方法 2:使用 for-each 循环
例子:
Java
// Java program for Traversing through HashMap
// Using for-each Loop
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// creating an empty HashMap of string and integer
// pairs Mappings denotes Student name and marks
HashMap hm
= new HashMap();
// Adding mappings to HashMap
// using put() method
hm.put("GeeksforGeeks", 54);
hm.put("A computer portal", 80);
hm.put("For geeks", 82);
// Printing all elements of above Map
System.out.println("Created hashmap is" + hm);
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"HashMap after adding bonus marks:");
// Looping through the HashMap
// Using for-each loop
for (Map.Entry mapElement : hm.entrySet()) {
String key = (String)mapElement.getKey();
// Adding some bonus marks to all the students
int value = ((int)mapElement.getValue() + 10);
// Printing above marks corresponding to
// students names
System.out.println(key + " : " + value);
}
}
}
输出:
Created hashmap is{GeeksforGeeks=54, A computer portal=80, For geeks=82}
HashMap after adding bonus marks:
GeeksforGeeks : 64
A computer portal : 90
For geeks : 92方法 3:使用 forEach() 方法
forEach() 是Java 8 中引入的 HashMap 的一种方法。它用于遍历 hashmap 并减少代码行数,建议如下:
例子:
Java
// Java program for traversing Through HashMap
// Using forEach() Method
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an empty HashMap of string-integer
// pairs
HashMap hm
= new HashMap();
// Adding mappings to HashMap
// using put() method
hm.put("GeeksforGeeks", 54);
hm.put("A computer portal", 80);
hm.put("For geeks", 82);
// Printing all elements of above HashMap
System.out.println("Created hashmap is" + hm);
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"HashMap after adding bonus marks:");
// Looping through HashMap and adding bonus marks
// using HashMap.forEach()
hm.forEach((k, v)
-> System.out.println(k + " : "
+ (v + 10)));
}
}
输出:
Created hashmap is{GeeksforGeeks=54, A computer portal=80, For geeks=82}
HashMap after adding bonus marks:
GeeksforGeeks : 64
A computer portal : 90
For geeks : 92