OpenGL 中的贝塞尔曲线
OpenGL 是一种跨语言、跨平台的 API,用于渲染 2D 和 3D 矢量图形。它用于使用 OpenGL执行大量设计和动画。在本文中,我们将讨论贝塞尔曲线OpenGL 的概念和实现。
贝塞尔曲线:
- 贝塞尔曲线的概念是由法国工程师皮埃尔·贝塞尔发现的。
- 贝塞尔曲线基本上用于计算机图形绘制形状、CSS 动画以及许多其他地方。
- 这些是在一些其他点(也称为控制点)的控制下生成的曲线。
贝塞尔曲线的性质:
- Bezier 曲线的一个非常重要的特性是它们总是通过第一个和最后一个控制点。
- 定义曲线段的多项式的次数总是比定义多边形点的数量少 1。因此,例如,如果我们有 4 个控制点,则多项式的次数为 3,即三次多项式。
- 在贝塞尔曲线中,移动控制点会改变整条曲线的形状。
- 贝塞尔曲线通常遵循定义多边形的形状。
- 曲线总是在控制点的凸包内。
下面是实现贝塞尔曲线的 C++ 程序:
C++
// C++ program to implement Bezier Curves
#include
#include
#include
#include
int i;
// Function to initialize the Beizer
// curve pointer
void init(void)
{
glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
}
// Function to draw the Bitmap Text
void drawBitmapText(char* string, float x,
float y, float z)
{
char* c;
glRasterPos2f(x, y);
// Traverse the string
for (c = string; *c != '\0'; c++) {
glutBitmapCharacter(
GLUT_BITMAP_TIMES_ROMAN_24, *c);
}
}
// Function to draw the shapes
void draw(GLfloat ctrlpoints[4][3])
{
glShadeModel(GL_FLAT);
glMap1f(GL_MAP1_VERTEX_3, 0.0, 1.0, 3, 4,
&ctrlpoints[0][0]);
glEnable(GL_MAP1_VERTEX_3);
// Fill the color
glColor3f(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);
// Find the coordinates
for (i = 0; i <= 30; i++)
glEvalCoord1f((GLfloat)i / 30.0);
glEnd();
glFlush();
}
// Function to display the curved
// drawn using the Beizer Curve
void display(void)
{
int i;
// Specifying all the control
// points through which the
// curve will pass
GLfloat ctrlpoints[4][3]
= { { -0.00, 2.00, 0.0 },
{ -2.00, 2.00, 0.0 },
{ -2.00, -1.00, 0.0 },
{ -0.00, -1.00, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints);
GLfloat ctrlpoints2[4][3]
= { { 0.0, -1.00, 0.0 },
{ 0.55, -0.65, 0.0 },
{ 0.65, -0.25, 0.0 },
{ 0.00, 0.70, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints2);
GLfloat ctrlpoints3[4][3]
= { { 0.0, 0.70, 0.0 },
{ 0.15, 0.70, 0.0 },
{ 0.25, 0.70, 0.0 },
{ 0.65, 0.700, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints3);
GLfloat ctrlpoints4[4][3]
= { { 0.65, 0.70, 0.0 },
{ 0.65, -0.90, 0.0 },
{ 0.65, -0.70, 0.0 },
{ 0.65, -1.00, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints4);
GLfloat ctrlpoints5[4][3]
= { { 1.00, -1.00, 0.0 },
{ 1.00, -0.5, 0.0 },
{ 1.00, -0.20, 0.0 },
{ 1.00, 1.35, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints5);
GLfloat ctrlpoints6[4][3]
= { { 1.00, 1.35 },
{ 1.10, 1.35, 0.0 },
{ 1.10, 1.35, 0.0 },
{ 1.90, 1.35, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints6);
GLfloat ctrlpoints7[4][3]
= { { 1.00, 0.50, 0.0 },
{ 1.10, 0.5, 0.0 },
{ 1.10, 0.5, 0.0 },
{ 1.90, 0.5, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints7);
GLfloat ctrlpoints8[4][3]
= { { 3.50, 2.00, 0.0 },
{ 1.50, 2.00, 0.0 },
{ 1.50, -1.00, 0.0 },
{ 3.50, -1.00, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints8);
GLfloat ctrlpoints9[4][3]
= { { 3.50, -1.00, 0.0 },
{ 4.05, -0.65, 0.0 },
{ 4.15, -0.25, 0.0 },
{ 3.50, 0.70, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints9);
GLfloat ctrlpoints10[4][3]
= { { 3.50, 0.70, 0.0 },
{ 3.65, 0.70, 0.0 },
{ 3.75, 0.70, 0.0 },
{ 4.15, 0.700, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints10);
GLfloat ctrlpoints11[4][3]
= { { 4.15, 0.70, 0.0 },
{ 4.15, -0.90, 0.0 },
{ 4.15, -0.70, 0.0 },
{ 4.15, -1.00, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints11);
GLfloat ctrlpoints12[4][3]
= { { -2.0, 2.50, 0.0 },
{ 2.05, 2.50, 0.0 },
{ 3.15, 2.50, 0.0 },
{ 4.65, 2.50, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints12);
GLfloat ctrlpoints13[4][3]
= { { -2.0, -1.80, 0.0 },
{ 2.05, -1.80, 0.0 },
{ 3.15, -1.80, 0.0 },
{ 4.65, -1.80, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints13);
GLfloat ctrlpoints14[4][3]
= { { -2.0, -1.80, 0.0 },
{ -2.0, 1.80, 0.0 },
{ -2.0, 1.90, 0.0 },
{ -2.0, 2.50, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints14);
GLfloat ctrlpoints15[4][3]
= { { 4.650, -1.80, 0.0 },
{ 4.65, 1.80, 0.0 },
{ 4.65, 1.90, 0.0 },
{ 4.65, 2.50, 0.0 } };
draw(ctrlpoints15);
// Specifying the colour of
// text to be displayed
glColor3f(1, 0, 0);
drawBitmapText("Bezier Curves "
"Implementation",
-1.00, -3.0, 0);
glFlush();
}
// Function perform the reshaping
// of the curve
void reshape(int w, int h)
{
glViewport(0, 0, (GLsizei)w,
(GLsizei)h);
// Matrix mode
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
if (w <= h)
glOrtho(-5.0, 5.0, -5.0
* (GLfloat)h / (GLfloat)w,
5.0 * (GLfloat)h / (GLfloat)w, -5.0, 5.0);
else
glOrtho(-5.0 * (GLfloat)w / (GLfloat)h,
5.0 * (GLfloat)w / (GLfloat)h,
-5.0, 5.0,
-5.0, 5.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
}
// Driver Code
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(
GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);
// Specifies the window size
glutInitWindowSize(500, 500);
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100);
// Creates the window as
// specified by the user
glutCreateWindow(argv[0]);
init();
// Links display event with the
// display event handler(display)
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutReshapeFunc(reshape);
// Loops the current event
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
} 输出:
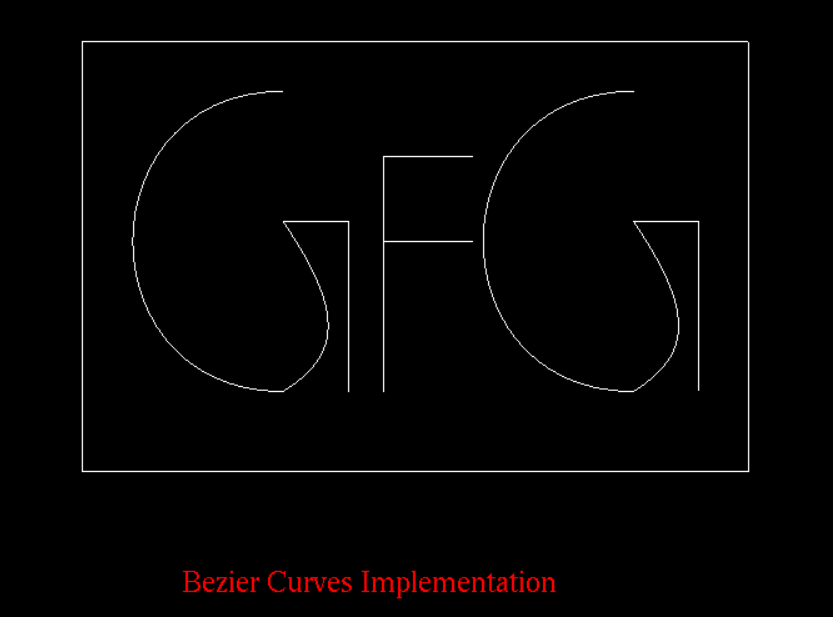
想要从精选的视频和练习题中学习,请查看C++ 基础课程,从基础到高级 C++ 和C++ STL 课程,了解基础加 STL。要完成从学习语言到 DS Algo 等的准备工作,请参阅完整的面试准备课程。