R 编程中的假设检验
研究人员对为任何实验或数据集收集的数据做出假设。假设是研究人员做出的非强制性假设。简而言之,假设是研究人员根据收集的人口数据做出的决定。 R编程中的假设测试是测试研究人员提出的假设或验证假设的过程。为了进行假设检验,从总体中随机抽取数据样本并进行检验。根据检验结果,选择或拒绝假设。这个概念被称为统计推断。在本文中,我们将讨论假设检验的四步过程,一个样本 T 检验,两个样本 T 检验,定向假设,一个样本![]() -测试,两个样本
-测试,两个样本![]() - R 编程中的测试和相关测试。
- R 编程中的测试和相关测试。
假设检验的四步过程
假设检验有 4 个主要步骤:
- 陈述假设——这一步从陈述假设为真的零假设和替代假设开始。
- 制定分析计划并设置决策标准-在此步骤中,设置检验的显着性水平。显着性水平是假设检验中错误拒绝的概率。
- 分析样本数据-在此,使用检验统计量来制定样本均值与总体均值或样本标准差与总体标准差之间的统计比较。
- 解释决策- 检验统计量的值用于根据显着性水平做出决策。例如,如果显着性水平设置为 0.1 概率,那么小于 10% 的样本均值将被拒绝。否则,假设保持为真。
一个样本 T 检验
一种样本 T 测试方法收集大量数据并在随机样本上进行测试。要在 R 中执行 T 检验,需要正态分布的数据。该检验用于检验样本与总体的均值。例如,居住在一个区域的人的身高与居住在其他区域的其他人的身高不同或相同。
Syntax: t.test(x, mu)
Parameters:
x: represents numeric vector of data
mu: represents true value of the mean
要了解t.test()的更多可选参数,请尝试以下命令:
help("t.test")
例子:
# Defining sample vector
x <- rnorm(100)
# One Sample T-Test
t.test(x, mu = 5)
输出:
One Sample t-test
data: x
t = -49.504, df = 99, p-value < 2.2e-16
alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 5
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.1910645 0.2090349
sample estimates:
mean of x
0.008985172
两个样本 T 检验
在两个样本 T 检验中,比较样本向量。如果 var.equal = TRUE,则测试假定两个样本的方差相等。
Syntax: t.test(x, y)
Parameters:
x and y: Numeric vectors
例子:
# Defining sample vector
x <- rnorm(100)
y <- rnorm(100)
# Two Sample T-Test
t.test(x, y)
输出:
Welch Two Sample t-test
data: x and y
t = -1.0601, df = 197.86, p-value = 0.2904
alternative hypothesis: true difference in means is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.4362140 0.1311918
sample estimates:
mean of x mean of y
-0.05075633 0.10175478
方向假设
使用方向假设,可以指定假设的方向,例如,如果用户想知道样本均值低于或大于数据的另一个均值样本。
Syntax: t.test(x, mu, alternative)
Parameters:
x: represents numeric vector data
mu: represents mean against which sample data has to be tested
alternative: sets the alternative hypothesis
例子:
# Defining sample vector
x <- rnorm(100)
# Directional hypothesis testing
t.test(x, mu = 2, alternative = 'greater')
输出:
One Sample t-test
data: x
t = -20.708, df = 99, p-value = 1
alternative hypothesis: true mean is greater than 2
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.2307534 Inf
sample estimates:
mean of x
-0.0651628
一个样品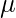 -测试
-测试
当必须对一个样本进行比较并且数据是非参数的时,使用这种类型的测试。它是在 R 编程中使用wilcox.test()函数执行的。
Syntax: wilcox.test(x, y, exact = NULL)
Parameters:
x and y: represents numeric vector
exact: represents logical value which indicates whether p-value be computed
要了解wilcox.test()的更多可选参数,请使用以下命令:
help("wilcox.test")
例子:
# Define vector
x <- rnorm(100)
# one sample test
wilcox.test(x, exact = FALSE)
输出:
Wilcoxon signed rank test with continuity correction
data: x
V = 2555, p-value = 0.9192
alternative hypothesis: true location is not equal to 0
两个样本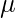 -测试
-测试
执行此测试以比较两个数据样本。
例子:
# Define vectors
x <- rnorm(100)
y <- rnorm(100)
# Two sample test
wilcox.test(x, y)
输出:
Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
data: x and y
W = 5300, p-value = 0.4643
alternative hypothesis: true location shift is not equal to 0
相关性检验
该测试用于比较函数调用中提供的两个向量的相关性或测试配对样本之间的关联。
Syntax: cor.test(x, y)
Parameters:
x and y: represents numeric data vectors
要了解cor.test()函数中的更多可选参数,请使用以下命令:
help("cor.test")例子:
# Using mtcars dataset in R
cor.test(mtcars$mpg, mtcars$hp)
输出:
Pearson's product-moment correlation
data: mtcars$mpg and mtcars$hp
t = -6.7424, df = 30, p-value = 1.788e-07
alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.8852686 -0.5860994
sample estimates:
cor
-0.7761684