潜热
热是相变中的一个重要因素。将固体转化为液相或气相所需的热量称为潜热。根据其相的不同,它有几个名称,例如冷凝热、汽化热等。它也可以指在相变期间接收或释放的热能量。我们将通过本主题中的示例来研究潜热的概念和潜热公式。让我们来看看这个概念!
什么是潜热?
The energy or heat released or absorbed during a phase shift of a material is known as latent heat. It might be from a gas to a liquid or from a liquid to a solid and back again.
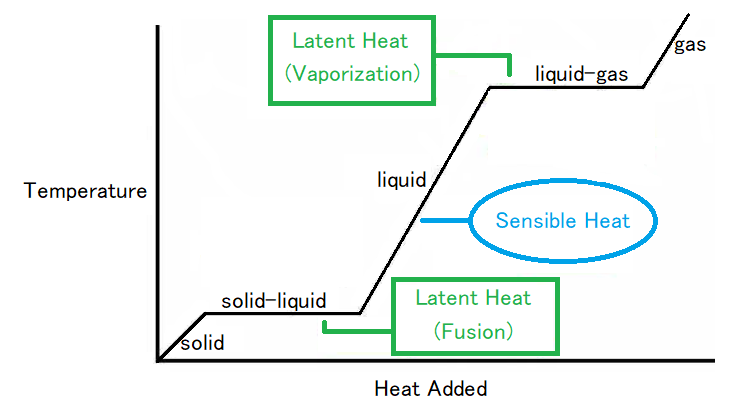
潜热图
焓是与潜热相关的热属性。然而,关于潜热要记住的一个关键因素是材料的温度不会改变。就该过程而言,潜热是克服将物质中的分子和原子保持在一起的吸引力所需的努力。
让我们看一个例子。如果固体转变为液体,它必须吸收能量以将分子推入更大、更多的流体体积。当材料从气体转变为液体时,其密度水平也必须从低到高移动,这需要材料释放或失去能量以使分子更靠近在一起。
当我们在分子水平上观察分子时,我们可以看到气态分子比液态分子具有更多的振动。结果,当我们向液体加热时,分子开始振动。改变分子运动所需的能量将是潜热。每种材料的潜热值不同。
潜热公式
潜热的公式如下:
L = Q ⁄ M
where, L is the latent heat, Q is the amount of heat released or absorbed and M is the mass of substance.
质量为 m 的物体为了改变相位而必须提供或排出的热量 Q 在这个方程中表示。单个潜热用字母 L 表示。
潜热的单位是J ⁄ Kg 。
潜热具有可变值。它取决于正在发生的相变的类型。
- 固体到液体 - 融合
- 液体到气体 - 汽化
- 固体到气体 - 升华
潜热类型
让我们来看看可能出现的多种潜热。
聚变潜热
The heat consumed or emitted when matter melts, changing state from solid to fluid-structure at a constant temperature, is known as latent heat of fusion.
在大气压下将固体转化为流体所需的热能是熔化潜热,而在操作过程中温度保持恒定。任何固体熔化时的焓移称为熔化潜热。
当熔化热以质量单位表示时,称为比熔化热,而摩尔熔化热是指每摩尔材料的焓变。
流体的向内能量大于固态的能量。这意味着必须将能量传递给固体以使其溶解,并且在流体凝固时必须从流体中去除能量,因为流体中的粒子具有更脆弱的分子间力,因此具有更大的势能(一种键-分子间能量的分离能)。
汽化潜热
The heat consumed or expelled as matter disintegrates, changing phase from fluid to gas at a constant temperature, is known as latent heat of vaporization.
水汽化热是最广为人知的。汽化热定义为在不改变流体温度的情况下将 1 g 流体转化为烟雾所需的热量。在物质的温度达到临界点后,需要潜热来将物质的状态从流体状态变为气体状态。
值得注意的是,潜热与温度无关,但与形式变化有关。水的消失具有明显的降温作用,而积聚则具有升温作用,因为汽化热很高。
升华潜热
当暴露在露天环境中时,一些化学物质,如萘,会直接从固体转化为气体。升华潜热是物质从固态转变为气态所需的热量或从气态材料中除去热量以转变为固态所需的热量。
显热
由物体或热力学系统传递的影响物体或系统温度的热量,以及物体或系统除压力或体积以外的一些宏观变量,称为显热。
示例问题
问题一:潜热有哪些应用?
回答:
Some of the applications of the latent heat are given below.
- Quenching fire by using boiling water
- Cooling drinks by the use of cold water and ice
- Melting of ice on road with the help of salt
- Steaming food
问题 2:如果相变的热量为 600 kcal,则计算 20 kg 物质的潜热。
解决方案:
Given:
Q=600 kcal
M=20 Kg
The formula for latent heat is given as:
L=Q⁄M
=600 kcal/20 kg
=30 Kcal/Kg
Hence, the latent heat required for phase change is 30 Kcal / Kg.
问题 3:为什么潜热不能改变物质的温度?
回答:
The increase in kinetic energy of a material causes temperature to rise. However, if the kinetic energy remains constant, the temperature will remain constant. There is no change in kinetic energy when a material absorbs latent heat to produce a liquid. As a result, the temperature remains constant while the condition of matter changes.
问题4:为什么我们在冰冷的装满水的玻璃杯外面看到水滴?
回答:
Water vapor is known to exist in the atmosphere. As a result, as air passes through the glass, the water vapor molecule collides with the cool surface and loses energy. Because when a material loses energy, it reverts to its original condition, water vapor becomes a liquid, and we observe water droplets on the glass’s outer surface.
问题 5:为什么要在烧伤的皮肤区域涂抹冰块?
回答:
The temperature of the wounded skin rises as a result of the burning. When ice is brushed against the skin, the surplus heat is absorbed by the substantial latent heat of fusion of water. As a result, the wounded skin’s temperature drops, and we experience less discomfort.