在 N 叉树中查找给定元素的表兄弟
给定一个 N 数组树根和一个整数K ,任务是打印节点K的所有表亲。
Note: Two nodes are considered to be cousins if they have the same depth (are on the same level) and have different parents.
例子:
Consider the below tree:
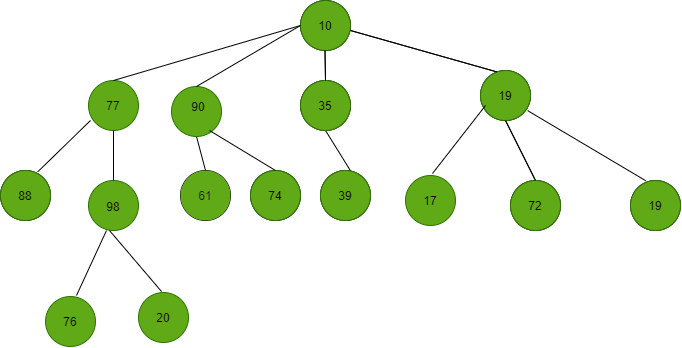
Input: K = 39
Output: 88 98 61 74 17 72 19
Input: K = 17
Output: 88 98 61 74 39
Input: K = 90
Output: NA
方法:这个想法是做一个水平顺序遍历。在遍历过程中,如果我们找到一个其子节点等于给定元素的节点,那么我们将不会推送该节点的子节点。我们将推送其他节点的子节点,当遍历该级别的所有元素时,内部循环将结束。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 如果root等于null,则返回。
- 初始化队列q[]并将根推入队列q[]。
- 将发现的布尔变量初始化为false。
- 将变量qsize初始化为0和节点temp。
- 遍历 while 循环,直到q[]不为空且未找到节点并执行以下任务:
- 将 size qsize设置为队列q[] 的大小。
- 迭代 while 循环直到qsize大于0并执行以下任务:
- 将tempp设置为队列q[] 的前面。
- 从队列q[] 中取出队列。
- 如果found等于true,则将它的所有子代推入队列q[]。
- 使用变量i遍历范围[0, temp->child.size())并执行以下任务:
- 如果 child 不为null并且它的 key 等于value,则将found的值设置为true。
- 如果found为false,则将其所有子代推入队列q[]。
- 将qsize的值减1。
- 如果找到为假,则打印“不可能”。
- 否则,将变量qsize初始化为队列q[] 的大小。
- 如果qsize等于0 ,则打印“No Cousins”。
- 否则,打印队列q[] 的所有元素。
下面是上述方法的实现
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Structure of a node of N-ary tree
struct Node {
int key;
vector child;
};
// New node creation
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the cousins of a
// given node in an N-array tree
void printCousins(Node* root, int value)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return;
queue q;
q.push(root);
// If we find the node
// with value as the key
bool found = false;
int qsize = 0;
Node* tempp;
while (!q.empty() && !found) {
qsize = q.size();
while (qsize) {
// Storing the current node
tempp = q.front();
q.pop();
// If we have already found
// the value as child of a node,
// we need to insert children of other
// node of same level in the queue
if (found == true) {
for (int i = 0; i < tempp->child.size();
i++) {
if (tempp->child[i] != NULL)
q.push(tempp->child[i]);
}
}
// If value is child of tempp node
for (int i = 0; i < tempp->child.size(); i++)
if (tempp->child[i] != NULL
&& tempp->child[i]->key == value)
found = true;
// If value is not the child of tempp node
// then insert all the children
// of the tempp node
if (found == false) {
for (int i = 0; i < tempp->child.size();
i++) {
if (tempp->child[i] != NULL)
q.push(tempp->child[i]);
}
}
qsize--;
}
}
if (found) {
// Queue will contain the cousins
qsize = q.size();
if (qsize == 0)
cout << "NA";
for (int i = 0; i < qsize; i++) {
tempp = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << tempp->key << " ";
}
}
else {
// When value is not in the tree
cout << "Not Possible";
}
cout << "\n";
return;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(10);
(root->child).push_back(newNode(77));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(90));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(35));
(root->child).push_back(newNode(19));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode(88));
(root->child[0]->child).push_back(newNode(98));
(root->child[0]->child[1]->child)
.push_back(newNode(76));
(root->child[0]->child[1]->child)
.push_back(newNode(20));
(root->child[1]->child).push_back(newNode(61));
(root->child[1]->child).push_back(newNode(74));
(root->child[2]->child).push_back(newNode(39));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(17));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(72));
(root->child[3]->child).push_back(newNode(19));
// Find the cousins of value
int value = 39;
printCousins(root, value);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of a node of N-ary tree
static class Node {
int key;
Vector child = new Vector();
};
// New node creation
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the cousins of a
// given node in an N-array tree
static void printCousins(Node root, int value)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
Queue q = new LinkedList();
q.add(root);
// If we find the node
// with value as the key
boolean found = false;
int qsize = 0;
Node tempp;
while (!q.isEmpty() && !found) {
qsize = q.size();
while (qsize > 0) {
// Storing the current node
tempp = q.peek();
q.remove();
// If we have already found
// the value as child of a node,
// we need to insert children of other
// node of same level in the queue
if (found == true) {
for (int i = 0; i < tempp.child.size();
i++) {
if (tempp.child.get(i) != null)
q.add(tempp.child.get(i));
}
}
// If value is child of tempp node
for (int i = 0; i < tempp.child.size(); i++)
if (tempp.child.get(i) != null
&& tempp.child.get(i).key == value)
found = true;
// If value is not the child of tempp node
// then insert all the children
// of the tempp node
if (found == false) {
for (int i = 0; i < tempp.child.size();
i++) {
if (tempp.child.get(i) != null)
q.add(tempp.child.get(i));
}
}
qsize--;
}
}
if (found) {
// Queue will contain the cousins
qsize = q.size();
if (qsize == 0)
System.out.print("NA");
for (int i = 0; i < qsize; i++) {
tempp = q.peek();
q.remove();
System.out.print(tempp.key+ " ");
}
}
else {
// When value is not in the tree
System.out.print("Not Possible");
}
System.out.print("\n");
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(10);
(root.child).add(newNode(77));
(root.child).add(newNode(90));
(root.child).add(newNode(35));
(root.child).add(newNode(19));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode(88));
(root.child.get(0).child).add(newNode(98));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(1).child)
.add(newNode(76));
(root.child.get(0).child.get(1).child)
.add(newNode(20));
(root.child.get(1).child).add(newNode(61));
(root.child.get(1).child).add(newNode(74));
(root.child.get(2).child).add(newNode(39));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode(17));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode(72));
(root.child.get(3).child).add(newNode(19));
// Find the cousins of value
int value = 39;
printCousins(root, value);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput Python3
# Python code for the above approach
# Structure of a node of N-ary tree
class Node:
def __init__ (self, k):
self.key = k;
self.child = [];
# node creation
# Function to find the cousins of a
# given node in an N-array tree
def printCousins(root, value):
# Base case
if (root == None):
return;
q = [];
q.append(root);
# If we find the node
# with value as the key
found = False;
qsize = 0;
tempp = None
while (len(q) != 0 and found != 1):
qsize = len(q);
while (qsize != 0):
# Storing the current node
tempp = q[0];
q.pop(0);
# If we have already found
# the value as child of a node,
# we need to insert children of other
# node of same level in the queue
if (found == True):
for i in range(len(tempp.child)):
if (tempp.child[i] != None):
q.append(tempp.child[i]);
# If value is child of tempp node
for i in range(len(tempp.child)):
if (tempp.child[i] != None and tempp.child[i].key == value):
found = True;
# If value is not the child of tempp node
# then insert all the children
# of the tempp node
if (found == False):
for i in range(len(tempp.child)):
if (tempp.child[i] != None):
q.append(tempp.child[i]);
qsize -= 1
if (found):
# Queue will contain the cousins
qsize = len(q);
if (qsize == 0):
print("NA");
for i in range(qsize):
tempp = q[0];
q.pop(0);
print(tempp.key, end= " ");
else:
# When value is not in the tree
print("Not Possible");
print('')
return;
# Driver Code
root = Node(10);
root.child.append(Node(77));
root.child.append(Node(90));
root.child.append(Node(35));
root.child.append(Node(19));
root.child[0].child.append(Node(88));
root.child[0].child.append(Node(98));
root.child[0].child[1].child.append(Node(76));
root.child[0].child[1].child.append(Node(20));
root.child[1].child.append(Node(61));
root.child[1].child.append(Node(74));
root.child[2].child.append(Node(39));
root.child[3].child.append(Node(17));
root.child[3].child.append(Node(72));
root.child[3].child.append(Node(19));
# Find the cousins of value
value = 39;
printCousins(root, value);
# This code is contributed by gfgkingC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG{
// Structure of a node of N-ary tree
class Node {
public int key;
public List child = new List();
};
// New node creation
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
return temp;
}
// Function to find the cousins of a
// given node in an N-array tree
static void printCousins(Node root, int value)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
Queue q = new Queue();
q.Enqueue(root);
// If we find the node
// with value as the key
bool found = false;
int qsize = 0;
Node tempp;
while (q.Count!=0 && !found) {
qsize = q.Count;
while (qsize > 0) {
// Storing the current node
tempp = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
// If we have already found
// the value as child of a node,
// we need to insert children of other
// node of same level in the queue
if (found == true) {
for (int i = 0; i < tempp.child.Count;
i++) {
if (tempp.child[i] != null)
q.Enqueue(tempp.child[i]);
}
}
// If value is child of tempp node
for (int i = 0; i < tempp.child.Count; i++)
if (tempp.child[i] != null
&& tempp.child[i].key == value)
found = true;
// If value is not the child of tempp node
// then insert all the children
// of the tempp node
if (found == false) {
for (int i = 0; i < tempp.child.Count;
i++) {
if (tempp.child[i] != null)
q.Enqueue(tempp.child[i]);
}
}
qsize--;
}
}
if (found) {
// Queue will contain the cousins
qsize = q.Count;
if (qsize == 0)
Console.Write("NA");
for (int i = 0; i < qsize; i++) {
tempp = q.Peek();
q.Dequeue();
Console.Write(tempp.key+ " ");
}
}
else {
// When value is not in the tree
Console.Write("Not Possible");
}
Console.Write("\n");
return;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(10);
(root.child).Add(newNode(77));
(root.child).Add(newNode(90));
(root.child).Add(newNode(35));
(root.child).Add(newNode(19));
(root.child[0].child).Add(newNode(88));
(root.child[0].child).Add(newNode(98));
(root.child[0].child[1].child)
.Add(newNode(76));
(root.child[0].child[1].child)
.Add(newNode(20));
(root.child[1].child).Add(newNode(61));
(root.child[1].child).Add(newNode(74));
(root.child[2].child).Add(newNode(39));
(root.child[3].child).Add(newNode(17));
(root.child[3].child).Add(newNode(72));
(root.child[3].child).Add(newNode(19));
// Find the cousins of value
int value = 39;
printCousins(root, value);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Javascript
输出
Cousins for the element 39: 88 98 61 74 17 72 19 时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)