毫升 |使用 Sklearn 实现 L1 和 L2 正则化
先决条件:L2 和 L1 正则化
本文旨在使用Python的Sklearn库的 Ridge 和 Lasso 模块实现线性回归的 L2 和 L1 正则化。
数据集——房价数据集。
第 1 步:导入所需的库
Python3
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, Ridge, Lasso
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score
from statistics import meanPython3
# Changing the working location to the location of the data
cd C:\Users\Dev\Desktop\Kaggle\House Prices
# Loading the data into a Pandas DataFrame
data = pd.read_csv('kc_house_data.csv')
# Dropping the numerically non-sensical variables
dropColumns = ['id', 'date', 'zipcode']
data = data.drop(dropColumns, axis = 1)
# Separating the dependent and independent variables
y = data['price']
X = data.drop('price', axis = 1)
# Dividing the data into training and testing set
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25)Python3
# Building and fitting the Linear Regression model
linearModel = LinearRegression()
linearModel.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluating the Linear Regression model
print(linearModel.score(X_test, y_test))Python3
# List to maintain the different cross-validation scores
cross_val_scores_ridge = []
# List to maintain the different values of alpha
alpha = []
# Loop to compute the different values of cross-validation scores
for i in range(1, 9):
ridgeModel = Ridge(alpha = i * 0.25)
ridgeModel.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores = cross_val_score(ridgeModel, X, y, cv = 10)
avg_cross_val_score = mean(scores)*100
cross_val_scores_ridge.append(avg_cross_val_score)
alpha.append(i * 0.25)
# Loop to print the different values of cross-validation scores
for i in range(0, len(alpha)):
print(str(alpha[i])+' : '+str(cross_val_scores_ridge[i]))Python3
# Building and fitting the Ridge Regression model
ridgeModelChosen = Ridge(alpha = 2)
ridgeModelChosen.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluating the Ridge Regression model
print(ridgeModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test))Python3
# List to maintain the cross-validation scores
cross_val_scores_lasso = []
# List to maintain the different values of Lambda
Lambda = []
# Loop to compute the cross-validation scores
for i in range(1, 9):
lassoModel = Lasso(alpha = i * 0.25, tol = 0.0925)
lassoModel.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores = cross_val_score(lassoModel, X, y, cv = 10)
avg_cross_val_score = mean(scores)*100
cross_val_scores_lasso.append(avg_cross_val_score)
Lambda.append(i * 0.25)
# Loop to print the different values of cross-validation scores
for i in range(0, len(alpha)):
print(str(alpha[i])+' : '+str(cross_val_scores_lasso[i]))Python3
# Building and fitting the Lasso Regression Model
lassoModelChosen = Lasso(alpha = 2, tol = 0.0925)
lassoModelChosen.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluating the Lasso Regression model
print(lassoModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test))Python3
# Building the two lists for visualization
models = ['Linear Regression', 'Ridge Regression', 'Lasso Regression']
scores = [linearModel.score(X_test, y_test),
ridgeModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test),
lassoModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test)]
# Building the dictionary to compare the scores
mapping = {}
mapping['Linear Regression'] = linearModel.score(X_test, y_test)
mapping['Ridge Regression'] = ridgeModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test)
mapping['Lasso Regression'] = lassoModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test)
# Printing the scores for different models
for key, val in mapping.items():
print(str(key)+' : '+str(val))Python3
# Plotting the scores
plt.bar(models, scores)
plt.xlabel('Regression Models')
plt.ylabel('Score')
plt.show()第 2 步:加载和清理数据
Python3
# Changing the working location to the location of the data
cd C:\Users\Dev\Desktop\Kaggle\House Prices
# Loading the data into a Pandas DataFrame
data = pd.read_csv('kc_house_data.csv')
# Dropping the numerically non-sensical variables
dropColumns = ['id', 'date', 'zipcode']
data = data.drop(dropColumns, axis = 1)
# Separating the dependent and independent variables
y = data['price']
X = data.drop('price', axis = 1)
# Dividing the data into training and testing set
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25)
第 3 步:构建和评估不同的模型
a)线性回归:
Python3
# Building and fitting the Linear Regression model
linearModel = LinearRegression()
linearModel.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluating the Linear Regression model
print(linearModel.score(X_test, y_test))
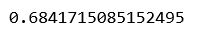
b)岭(L2)回归:
Python3
# List to maintain the different cross-validation scores
cross_val_scores_ridge = []
# List to maintain the different values of alpha
alpha = []
# Loop to compute the different values of cross-validation scores
for i in range(1, 9):
ridgeModel = Ridge(alpha = i * 0.25)
ridgeModel.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores = cross_val_score(ridgeModel, X, y, cv = 10)
avg_cross_val_score = mean(scores)*100
cross_val_scores_ridge.append(avg_cross_val_score)
alpha.append(i * 0.25)
# Loop to print the different values of cross-validation scores
for i in range(0, len(alpha)):
print(str(alpha[i])+' : '+str(cross_val_scores_ridge[i]))

从上面的输出中,我们可以得出结论,数据的最佳 alpha 值为 2。
Python3
# Building and fitting the Ridge Regression model
ridgeModelChosen = Ridge(alpha = 2)
ridgeModelChosen.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluating the Ridge Regression model
print(ridgeModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test))

c) Lasso(L1) 回归:
Python3
# List to maintain the cross-validation scores
cross_val_scores_lasso = []
# List to maintain the different values of Lambda
Lambda = []
# Loop to compute the cross-validation scores
for i in range(1, 9):
lassoModel = Lasso(alpha = i * 0.25, tol = 0.0925)
lassoModel.fit(X_train, y_train)
scores = cross_val_score(lassoModel, X, y, cv = 10)
avg_cross_val_score = mean(scores)*100
cross_val_scores_lasso.append(avg_cross_val_score)
Lambda.append(i * 0.25)
# Loop to print the different values of cross-validation scores
for i in range(0, len(alpha)):
print(str(alpha[i])+' : '+str(cross_val_scores_lasso[i]))

从上面的输出中,我们可以得出结论 lambda 的最佳值为 2。
Python3
# Building and fitting the Lasso Regression Model
lassoModelChosen = Lasso(alpha = 2, tol = 0.0925)
lassoModelChosen.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluating the Lasso Regression model
print(lassoModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test))

第 4 步:比较和可视化结果
Python3
# Building the two lists for visualization
models = ['Linear Regression', 'Ridge Regression', 'Lasso Regression']
scores = [linearModel.score(X_test, y_test),
ridgeModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test),
lassoModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test)]
# Building the dictionary to compare the scores
mapping = {}
mapping['Linear Regression'] = linearModel.score(X_test, y_test)
mapping['Ridge Regression'] = ridgeModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test)
mapping['Lasso Regression'] = lassoModelChosen.score(X_test, y_test)
# Printing the scores for different models
for key, val in mapping.items():
print(str(key)+' : '+str(val))

Python3
# Plotting the scores
plt.bar(models, scores)
plt.xlabel('Regression Models')
plt.ylabel('Score')
plt.show()
