Scrapy – 项目管道
Scrapy是一个网页抓取库,用于抓取、解析和收集网页数据。对于所有这些函数,我们有一个pipelines.py文件,用于通过按顺序执行的各种组件(称为class )处理抓取的数据。
在本文中,我们将学习为此管道文件定义的方法,并将展示它的不同示例。
设置项目
让我们首先创建一个scrapy项目。为此,请确保系统中安装了Python和 PIP。然后一一运行下面给定的命令来创建一个类似于我们将在本文中使用的项目的scrapy项目。
步骤 1:让我们首先在名为 GFGScrapy 的文件夹中创建一个虚拟环境,并在那里激活该虚拟环境。
# To create a folder named GFGScrapy
mkdir GFGScrapy
cd GFGScrapy
# making virtual env there.
virtualenv
cd scripts
# activating it
activate
cd..因此,在运行所有这些命令后,我们将得到如下所示的输出:
创建虚拟环境
第 2 步:现在是时候创建一个 scrapy 项目了。为此确保系统中是否安装了scrapy。如果未安装,请使用下面给定的命令安装它。
pip install scrapy现在创建一个scrapy项目,使用下面给出的命令并创建一个蜘蛛。
# projEct name is scrapytutorial
scrapy startproject scrapytutorial
cd scrapytutorial
scrapy genspider spider_to_crawl https://quotes.toscrape.com然后项目目录的输出看起来像图像中给出的那个。 (如果你想了解更多关于一个scrapy项目并熟悉它,请参考这个)。
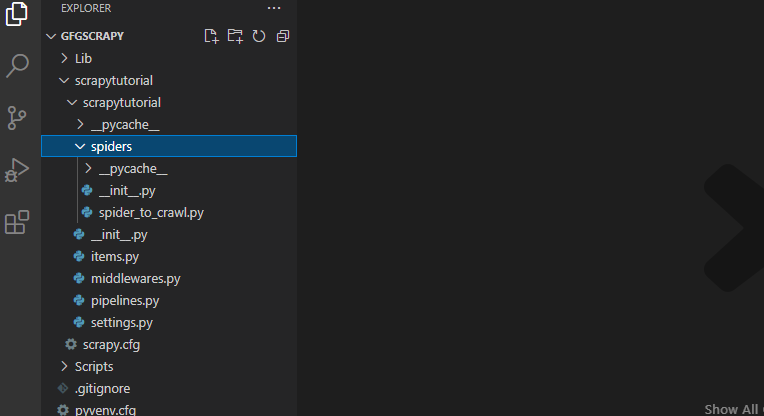
目录结构
让我们看看蜘蛛文件夹中的spider_to_crawl.py文件。这是我们编写蜘蛛必须抓取的 URL 的文件,还有一个名为 parse() 的方法,用于描述应该对蜘蛛抓取的数据做什么。
这个文件是由上面使用的“ scrapy genspider ”命令自动生成的。该文件以蜘蛛的名字命名。下面给出的是生成的默认文件。
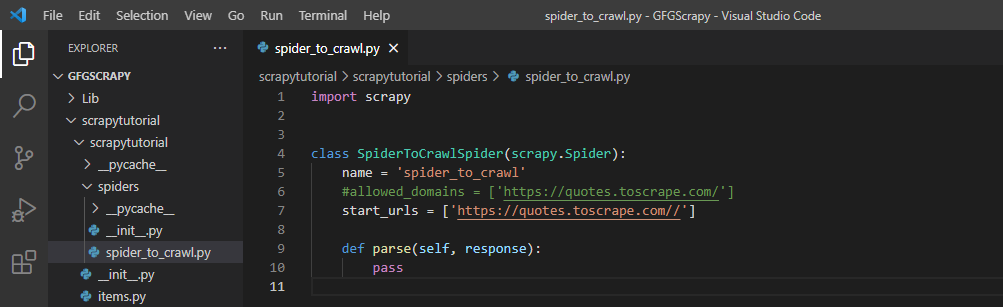
Spider_to_crawl.py
项目管道是一种管道方法,它写在 pipelines.py 文件中,用于对抓取的数据按顺序执行下面给出的操作。下面列出了我们可以对抓取的项目执行的各种操作:
- 解析抓取的文件或数据。
- 将抓取的数据存储在数据库中。
- 验证和检查获得的数据。
- 将文件从一种格式转换为另一种格式。例如到 JSON。
我们将在下面的示例中执行其中一些操作。
操作按顺序执行,因为我们使用settings.py文件来描述操作的执行顺序。即我们可以提到首先执行哪个操作,接下来执行哪个操作。这通常在我们对项目执行多个操作时完成。
我们先来看看默认管道文件的内部结构。下面是该文件中提到的默认类。

默认 pipelines.py 文件
为了对项目执行不同的操作,我们必须声明一个单独的组件(文件中的类),它由各种方法组成,用于执行操作。默认的管道文件有一个以项目名称命名的类。我们还可以创建自己的类来编写它们必须执行的操作。如果任何管道文件包含多个类,那么我们应该明确提及它们的执行顺序。组件的结构定义如下:
每个组件(类)必须有一个名为process_item() 的默认函数。这是始终在管道文件的类或组件内调用的默认方法。
Syntax: process_item( self, item, spider )
Parameters:
- self : This is reference to the self object calling the method.
- item : These are the items list scraped by the spider
- spider : mentions the spider used to scrape.
The return type of this method is the modified or unmodified item object or an error will be raised if any fault is found in item.
This method is also used to call other method in this class which can be used to modify or store data.
附加方法:这些方法与上述自对象方法一起使用以获得对项目的额外控制。 Spider object which is opened and a reference to self object are the parameters. ( These are default cases of python language). Returns nothing except the fact that it is used to either make some changes or open a file or close a file. Spider object which is closed and a reference to self-object. It also either is used to modify the file or open or close it. Crawler object that is specified. This method is used to give pipeline accessibility to all the core components of the scrapy settings so that pipelines can enhance their functionality,Method Description open_spider(self,spider) close_spider(self,spider) from_crawler(cls, crawler)
除了所有这些方法之外,我们还可以创建自己的方法来执行更多操作,例如如果我们想要存储一些数据,那么我们可以拥有初始化数据库并在其中创建表的组件,另一个组件可能会添加数据到数据库。
在我们继续参考示例之前,需要注意的重要一点是,我们必须在文件夹结构的settings.py中注册pipelines.py文件的所有组件(类)。这样做是为了维护要执行的组件的顺序,从而产生准确的结果。
创建要通过文件传递的项目。
需要注意的另一件事是,我们将需要在items.py文件中描述我们的项目将包含的内容。因此我们的items.py文件包含以下给定的代码:
Python3
# Define here the models for your scraped items
import scrapy
class ScrapytutorialItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
Quote = scrapy.Field() #only one field that it of Quote.Python3
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import json
class ScrapytutorialPipeline:
def process_item(self, item, spider):
# calling dumps to create json data.
line = json.dumps(dict(item)) + "\n"
self.file.write(line)
return item
def open_spider(self, spider):
self.file = open('result.json', 'w')
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.file.close()Python3
import scrapy
from ..items import ScrapytutorialItem
class SpiderToCrawlSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'spider_to_crawl'
start_urls = ['https://quotes.toscrape.com/']
def parse(self, response):
# creating items dictionary
items = ScrapytutorialItem()
Quotes_all = response.xpath('//div/div/div/span[1]')
# These paths are based on the selectors
for quote in Quotes_all: #extracting data
items['Quote'] = quote.css('p::text').extract()
yield itemsPython3
import scrapy
from ..items import ScrapytutorialItem
class SpiderToCrawlSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'spider_to_crawl'
start_urls = ['https://quotes.toscrape.com/']
def parse(self, response):
# creating items dictionary
items = ScrapytutorialItem()
Quotes_all = response.xpath('//div/div/div/span[1]')
# These paths are based on the selectors
# extracting data
for quote in Quotes_all:
items['Quote'] = quote.css('::text').extract()
yield itemsPython3
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import sqlite3
class ScrapytutorialPipeline(object):
# init method to initialize the database
# and create connection and tables
def __init__(self):
self.create_conn()
self.create_table()
# create connection method to create
# database or use database to store scraped data
def create_conn(self):
self.conn = sqlite3.connect("mydata.db")
self.curr = self.conn.cursor()
# Create table method
# using SQL commands to create table
def create_table(self):
self.curr.execute("""DROP TABLE IF EXISTS firsttable""")
self.curr.execute("""create table firsttable(
Quote text
)""")
# store items to databases.
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.putitemsintable(item)
return item
def putitemsintable(self,item):
self.curr.execute("""insert into firsttable values (?)""",(
item['Quote'][0], # extracting item.
))
self.conn.commit()我们将要求将此文件导入到我们的spider_to_crawl.py文件中。因此,通过这种方式,我们可以创建要传递给管道的项目。我们将主要使用 Wisdom 报价网页,在那里我们可以根据作者和各自的标签获得几个报价,然后我们将在整个示例中修改和使用抓取数据的项目管道。
示例 1:将抓取的数据转换为 JSON 格式
为了将数据转换为 JSON 格式,我们将使用Python 的JSON 库及其 dumps() 方法。
这个想法是我们将在 pipelines.py 文件中获取抓取的数据,然后我们将打开一个名为result.json的文件(如果尚未存在,则它将自动创建)并将所有 JSON 数据写入其中。
- 当蜘蛛开始爬行时,将调用 open_spider() 打开文件(result.json)。
- 当蜘蛛关闭并且抓取结束时,将调用 close_spider() 来关闭文件。
- process_item() 将始终被调用(因为它是默认值)并且主要负责将数据转换为 JSON 格式并将数据打印到文件中。我们将使用Python Web 框架的概念,即它们如何将后端检索到的数据转换为 JSON 和其他格式。
因此,我们的pipelines.py 中的代码如下所示:
蟒蛇3
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import json
class ScrapytutorialPipeline:
def process_item(self, item, spider):
# calling dumps to create json data.
line = json.dumps(dict(item)) + "\n"
self.file.write(line)
return item
def open_spider(self, spider):
self.file = open('result.json', 'w')
def close_spider(self, spider):
self.file.close()
我们的spider_to_crawl.py:
蟒蛇3
import scrapy
from ..items import ScrapytutorialItem
class SpiderToCrawlSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'spider_to_crawl'
start_urls = ['https://quotes.toscrape.com/']
def parse(self, response):
# creating items dictionary
items = ScrapytutorialItem()
Quotes_all = response.xpath('//div/div/div/span[1]')
# These paths are based on the selectors
for quote in Quotes_all: #extracting data
items['Quote'] = quote.css('p::text').extract()
yield items
输出:

解释:
使用命令“scrapy crawl spider_to_crawl”后,将执行以下步骤。
- 由于创建了 result.json 文件,蜘蛛被抓取。现在蜘蛛抓取网页并收集Quotes_all变量中的数据。然后我们将来自这个变量的每个数据一一发送到我们的 pipelines.py 文件。
- 我们从pipelines.py 文件中的spider 接收项目变量,然后使用dumps() 方法将其转换为JSON,然后将输出写入打开的文件中。
这是创建的 JSON 文件:

示例 2:SQLite3 中将数据上传到数据库的管道
现在我们将展示一个项目管道,它将抓取网络内容并将其存储在我们定义的数据库表中。为简单起见,我们将使用 SQLite3 数据库。
所以我们将使用如何在Python实现SQLite3的想法来创建一个管道,该管道将从蜘蛛抓取中接收数据并将该数据插入到创建的数据库中的表中。
Spider_to_crawl.py:
蟒蛇3
import scrapy
from ..items import ScrapytutorialItem
class SpiderToCrawlSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'spider_to_crawl'
start_urls = ['https://quotes.toscrape.com/']
def parse(self, response):
# creating items dictionary
items = ScrapytutorialItem()
Quotes_all = response.xpath('//div/div/div/span[1]')
# These paths are based on the selectors
# extracting data
for quote in Quotes_all:
items['Quote'] = quote.css('::text').extract()
yield items
我们在下面提到的管道方法将写入pipelines.py文件,以便创建数据库:
管道.py文件
蟒蛇3
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import sqlite3
class ScrapytutorialPipeline(object):
# init method to initialize the database
# and create connection and tables
def __init__(self):
self.create_conn()
self.create_table()
# create connection method to create
# database or use database to store scraped data
def create_conn(self):
self.conn = sqlite3.connect("mydata.db")
self.curr = self.conn.cursor()
# Create table method
# using SQL commands to create table
def create_table(self):
self.curr.execute("""DROP TABLE IF EXISTS firsttable""")
self.curr.execute("""create table firsttable(
Quote text
)""")
# store items to databases.
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.putitemsintable(item)
return item
def putitemsintable(self,item):
self.curr.execute("""insert into firsttable values (?)""",(
item['Quote'][0], # extracting item.
))
self.conn.commit()
输出:

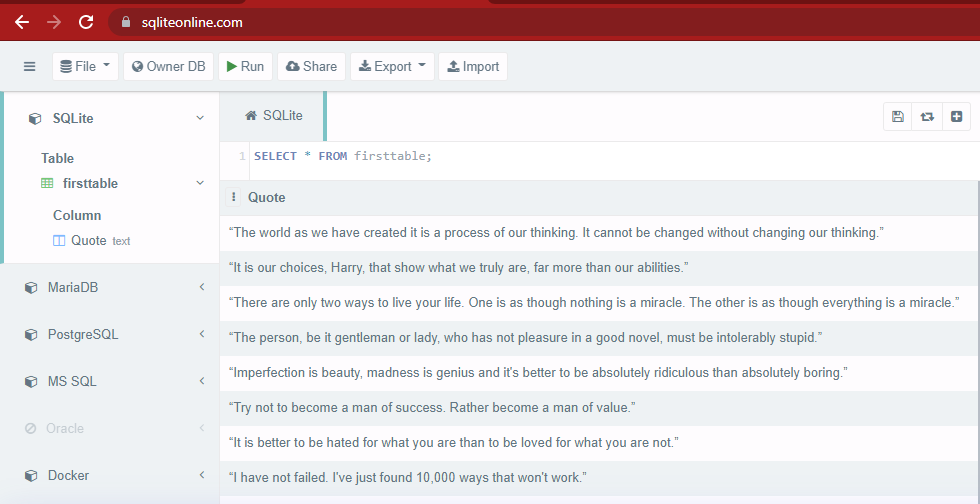
解释:
使用命令“scrapy crawl spider_to_crawl”后,将执行以下步骤
- 在 spider.py 中,我们提到了我们的蜘蛛应该去那个站点并提取 URL 格式中提到的所有数据的代码,然后将创建它的项目列表并将该列表传递给 pipelines.py 文件以进行进一步处理。
- 我们还创建了一个 items 对象来包含要传递的数据,并将其放入目录中的 items.py 文件中。
- 然后当蜘蛛爬行时,它会收集 items 对象中的数据并将其传输到管道,接下来发生的事情已经从上面的代码中清楚地看到了,并在注释中给出了提示。 pipelines.py 文件创建一个数据库并存储所有传入的项目。
- 这里调用了 init() 方法,它在任何Python文件中都被称为默认方法。然后它调用用于创建表和初始化数据库的所有其他方法。
- 然后调用 process_item() 方法,该方法用于调用名为 putitemintable() 的方法,将数据添加到数据库中。然后,在执行此方法后,将引用返回给蜘蛛以传递另一个要操作的项目。