合并排序通常是对链表进行排序的首选。链表的随机访问性能较慢,使得其他一些算法(例如quicksort)的性能较差,而其他算法(例如堆排序)则完全不可能。
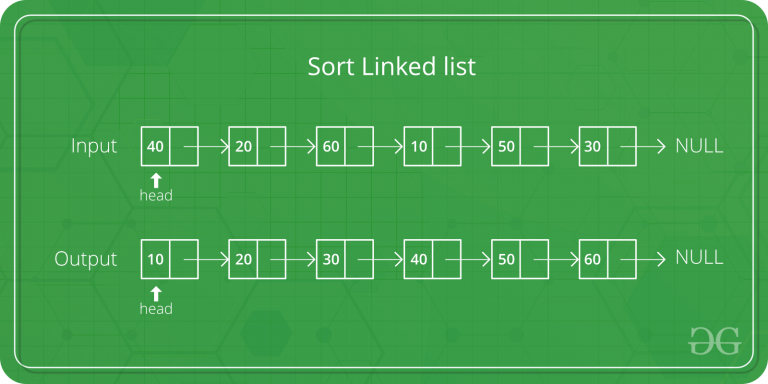
令head为要排序的链表的第一个节点,而headRef为指向head的指针。请注意,我们需要在MergeSort()中引用head,因为以下实现会更改下一个链接以对链接列表进行排序(而不是节点上的数据),因此,如果原始head上的数据不是该节点上的数据,则必须更改head节点。链表中的最小值。
MergeSort(headRef)
1) If the head is NULL or there is only one element in the Linked List
then return.
2) Else divide the linked list into two halves.
FrontBackSplit(head, &a, &b); /* a and b are two halves */
3) Sort the two halves a and b.
MergeSort(a);
MergeSort(b);
4) Merge the sorted a and b (using SortedMerge() discussed here)
and update the head pointer using headRef.
*headRef = SortedMerge(a, b);C++
// C++ code for linked list merged sort
#include
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
/* function prototypes */
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b);
void FrontBackSplit(Node* source,
Node** frontRef, Node** backRef);
/* sorts the linked list by changing next pointers (not data) */
void MergeSort(Node** headRef)
{
Node* head = *headRef;
Node* a;
Node* b;
/* Base case -- length 0 or 1 */
if ((head == NULL) || (head->next == NULL)) {
return;
}
/* Split head into 'a' and 'b' sublists */
FrontBackSplit(head, &a, &b);
/* Recursively sort the sublists */
MergeSort(&a);
MergeSort(&b);
/* answer = merge the two sorted lists together */
*headRef = SortedMerge(a, b);
}
/* See https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/?p=3622 for details of this
function */
Node* SortedMerge(Node* a, Node* b)
{
Node* result = NULL;
/* Base cases */
if (a == NULL)
return (b);
else if (b == NULL)
return (a);
/* Pick either a or b, and recur */
if (a->data <= b->data) {
result = a;
result->next = SortedMerge(a->next, b);
}
else {
result = b;
result->next = SortedMerge(a, b->next);
}
return (result);
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Split the nodes of the given list into front and back halves,
and return the two lists using the reference parameters.
If the length is odd, the extra node should go in the front list.
Uses the fast/slow pointer strategy. */
void FrontBackSplit(Node* source,
Node** frontRef, Node** backRef)
{
Node* fast;
Node* slow;
slow = source;
fast = source->next;
/* Advance 'fast' two nodes, and advance 'slow' one node */
while (fast != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
if (fast != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
/* 'slow' is before the midpoint in the list, so split it in two
at that point. */
*frontRef = source;
*backRef = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Function to insert a node at the beginging of the linked list */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* res = NULL;
Node* a = NULL;
/* Let us create a unsorted linked lists to test the functions
Created lists shall be a: 2->3->20->5->10->15 */
push(&a, 15);
push(&a, 10);
push(&a, 5);
push(&a, 20);
push(&a, 3);
push(&a, 2);
/* Sort the above created Linked List */
MergeSort(&a);
cout << "Sorted Linked List is: \n";
printList(a);
return 0;
}
// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
// C code for linked list merged sort
#include
#include
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* function prototypes */
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a, struct Node* b);
void FrontBackSplit(struct Node* source,
struct Node** frontRef, struct Node** backRef);
/* sorts the linked list by changing next pointers (not data) */
void MergeSort(struct Node** headRef)
{
struct Node* head = *headRef;
struct Node* a;
struct Node* b;
/* Base case -- length 0 or 1 */
if ((head == NULL) || (head->next == NULL)) {
return;
}
/* Split head into 'a' and 'b' sublists */
FrontBackSplit(head, &a, &b);
/* Recursively sort the sublists */
MergeSort(&a);
MergeSort(&b);
/* answer = merge the two sorted lists together */
*headRef = SortedMerge(a, b);
}
/* See https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/?p=3622 for details of this
function */
struct Node* SortedMerge(struct Node* a, struct Node* b)
{
struct Node* result = NULL;
/* Base cases */
if (a == NULL)
return (b);
else if (b == NULL)
return (a);
/* Pick either a or b, and recur */
if (a->data <= b->data) {
result = a;
result->next = SortedMerge(a->next, b);
}
else {
result = b;
result->next = SortedMerge(a, b->next);
}
return (result);
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Split the nodes of the given list into front and back halves,
and return the two lists using the reference parameters.
If the length is odd, the extra node should go in the front list.
Uses the fast/slow pointer strategy. */
void FrontBackSplit(struct Node* source,
struct Node** frontRef, struct Node** backRef)
{
struct Node* fast;
struct Node* slow;
slow = source;
fast = source->next;
/* Advance 'fast' two nodes, and advance 'slow' one node */
while (fast != NULL) {
fast = fast->next;
if (fast != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
}
/* 'slow' is before the midpoint in the list, so split it in two
at that point. */
*frontRef = source;
*backRef = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Function to insert a node at the beginging of the linked list */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* res = NULL;
struct Node* a = NULL;
/* Let us create a unsorted linked lists to test the functions
Created lists shall be a: 2->3->20->5->10->15 */
push(&a, 15);
push(&a, 10);
push(&a, 5);
push(&a, 20);
push(&a, 3);
push(&a, 2);
/* Sort the above created Linked List */
MergeSort(&a);
printf("Sorted Linked List is: \n");
printList(a);
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to illustrate merge sorted
// of linkedList
public class linkedList {
node head = null;
// node a, b;
static class node {
int val;
node next;
public node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
}
}
node sortedMerge(node a, node b)
{
node result = null;
/* Base cases */
if (a == null)
return b;
if (b == null)
return a;
/* Pick either a or b, and recur */
if (a.val <= b.val) {
result = a;
result.next = sortedMerge(a.next, b);
}
else {
result = b;
result.next = sortedMerge(a, b.next);
}
return result;
}
node mergeSort(node h)
{
// Base case : if head is null
if (h == null || h.next == null) {
return h;
}
// get the middle of the list
node middle = getMiddle(h);
node nextofmiddle = middle.next;
// set the next of middle node to null
middle.next = null;
// Apply mergeSort on left list
node left = mergeSort(h);
// Apply mergeSort on right list
node right = mergeSort(nextofmiddle);
// Merge the left and right lists
node sortedlist = sortedMerge(left, right);
return sortedlist;
}
// Utility function to get the middle of the linked list
public static node getMiddle(node head)
{
if (head == null)
return head;
node slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
void push(int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
node new_node = new node(new_data);
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
// Utility function to print the linked list
void printList(node headref)
{
while (headref != null) {
System.out.print(headref.val + " ");
headref = headref.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
linkedList li = new linkedList();
/*
* Let us create a unsorted linked list to test the functions
* created. The list shall be a: 2->3->20->5->10->15
*/
li.push(15);
li.push(10);
li.push(5);
li.push(20);
li.push(3);
li.push(2);
// Apply merge Sort
li.head = li.mergeSort(li.head);
System.out.print("\n Sorted Linked List is: \n");
li.printList(li.head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rishabh MahrseePython3
# Python3 program to merge sort of linked list
# create Node using class Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# push new value to linked list
# using append method
def append(self, new_value):
# Allocate new node
new_node = Node(new_value)
# if head is None, initialize it to new node
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
curr_node = self.head
while curr_node.next is not None:
curr_node = curr_node.next
# Append the new node at the end
# of the linked list
curr_node.next = new_node
def sortedMerge(self, a, b):
result = None
# Base cases
if a == None:
return b
if b == None:
return a
# pick either a or b and recur..
if a.data <= b.data:
result = a
result.next = self.sortedMerge(a.next, b)
else:
result = b
result.next = self.sortedMerge(a, b.next)
return result
def mergeSort(self, h):
# Base case if head is None
if h == None or h.next == None:
return h
# get the middle of the list
middle = self.getMiddle(h)
nexttomiddle = middle.next
# set the next of middle node to None
middle.next = None
# Apply mergeSort on left list
left = self.mergeSort(h)
# Apply mergeSort on right list
right = self.mergeSort(nexttomiddle)
# Merge the left and right lists
sortedlist = self.sortedMerge(left, right)
return sortedlist
# Utility function to get the middle
# of the linked list
def getMiddle(self, head):
if (head == None):
return head
slow = head
fast = head
while (fast.next != None and
fast.next.next != None):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
# Utility function to print the linked list
def printList(head):
if head is None:
print(' ')
return
curr_node = head
while curr_node:
print(curr_node.data, end = " ")
curr_node = curr_node.next
print(' ')
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
li = LinkedList()
# Let us create a unsorted linked list
# to test the functions created.
# The list shall be a: 2->3->20->5->10->15
li.append(15)
li.append(10)
li.append(5)
li.append(20)
li.append(3)
li.append(2)
# Apply merge Sort
li.head = li.mergeSort(li.head)
print ("Sorted Linked List is:")
printList(li.head)
# This code is contributed by Vikas ChitturiC#
// C# program to illustrate merge sorted
// of linkedList
using System;
public class linkedList {
node head = null;
// node a, b;
public class node {
public int val;
public node next;
public node(int val)
{
this.val = val;
}
}
node sortedMerge(node a, node b)
{
node result = null;
/* Base cases */
if (a == null)
return b;
if (b == null)
return a;
/* Pick either a or b, and recur */
if (a.val <= b.val) {
result = a;
result.next = sortedMerge(a.next, b);
}
else {
result = b;
result.next = sortedMerge(a, b.next);
}
return result;
}
node mergeSort(node h)
{
// Base case : if head is null
if (h == null || h.next == null) {
return h;
}
// get the middle of the list
node middle = getMiddle(h);
node nextofmiddle = middle.next;
// set the next of middle node to null
middle.next = null;
// Apply mergeSort on left list
node left = mergeSort(h);
// Apply mergeSort on right list
node right = mergeSort(nextofmiddle);
// Merge the left and right lists
node sortedlist = sortedMerge(left, right);
return sortedlist;
}
// Utility function to get the
// middle of the linked list
node getMiddle(node h)
{
// Base case
if (h == null)
return h;
node fastptr = h.next;
node slowptr = h;
// Move fastptr by two and slow ptr by one
// Finally slowptr will point to middle node
while (fastptr != null) {
fastptr = fastptr.next;
if (fastptr != null) {
slowptr = slowptr.next;
fastptr = fastptr.next;
}
}
return slowptr;
}
void push(int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
node new_node = new node(new_data);
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
// Utility function to print the linked list
void printList(node headref)
{
while (headref != null) {
Console.Write(headref.val + " ");
headref = headref.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
linkedList li = new linkedList();
/*
* Let us create a unsorted linked list to test the functions
* created. The list shall be a: 2->3->20->5->10->15
*/
li.push(15);
li.push(10);
li.push(5);
li.push(20);
li.push(3);
li.push(2);
// Apply merge Sort
li.head = li.mergeSort(li.head);
Console.Write("\n Sorted Linked List is: \n");
li.printList(li.head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduJava
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int key)
{
this.data = key;
next = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// Function to merge sort
static Node mergeSort(Node head)
{
if (head.next == null)
return head;
Node mid = findMid(head);
Node head2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
Node newHead1 = mergeSort(head);
Node newHead2 = mergeSort(head2);
Node finalHead = merge(newHead1, newHead2);
return finalHead;
}
// Function to merge two linked lists
static Node merge(Node head1, Node head2)
{
Node merged = new Node(-1);
Node temp = merged;
// While head1 is not null and head2
// is not null
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.data < head2.data) {
temp.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
}
else {
temp.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
// While head1 is not null
while (head1 != null) {
temp.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
// While head2 is not null
while (head2 != null) {
temp.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
return merged.next;
}
// Find mid using The Tortoise and The Hare approach
static Node findMid(Node head)
{
Node slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// Function to print list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = new Node(7);
Node temp = head;
temp.next = new Node(10);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(5);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(20);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(3);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(2);
temp = temp.next;
// Apply merge Sort
head = mergeSort(head);
System.out.print("\nSorted Linked List is: \n");
printList(head);
}
}输出:
Sorted Linked List is:
2 3 5 10 15 20时间复杂度: O(n * log n)
空间复杂度: O(n * log n)
方法2:此方法更简单,并使用log n空间。
mergeSort():
- 如果链表的大小为1,则返回头
- 使用“乌龟”和“野兔”方法寻找中点
- 将下一个中点的下一个存储在head2中,即右侧的子链接列表。
- 现在将下一个中点设为空。
- 在左右两个子链表上递归调用mergeSort()并存储左右链表的新标题。
- 给定参数后调用merge()左右子链接列表的新标题,并存储合并后返回的最终标题。
- 返回合并的链表的最后一个头。
merge(head1,head2):
- 用指针说merged将合并的列表存储在其中,并在其中存储一个虚拟节点。
- 取一个指针临时并将其分配给它。
- 如果head1的数据小于head2的数据,则将head1存储在temp的下一个并将head1移到head1的下一个。
- 否则将head2存储在temp的下一个中,并将head2移到head2的下一个中。
- 将温度移到下一个温度。
- 重复步骤3、4和5,直到head1不等于null和head2不等于null。
- 现在,将第一个或第二个链表的所有剩余节点添加到合并的链表中。
- 返回下一个合并的对象(它将忽略该虚拟对象,并返回最后一个合并的链表的头部)
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
// Node Class
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int key)
{
this.data = key;
next = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// Function to merge sort
static Node mergeSort(Node head)
{
if (head.next == null)
return head;
Node mid = findMid(head);
Node head2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
Node newHead1 = mergeSort(head);
Node newHead2 = mergeSort(head2);
Node finalHead = merge(newHead1, newHead2);
return finalHead;
}
// Function to merge two linked lists
static Node merge(Node head1, Node head2)
{
Node merged = new Node(-1);
Node temp = merged;
// While head1 is not null and head2
// is not null
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.data < head2.data) {
temp.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
}
else {
temp.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
// While head1 is not null
while (head1 != null) {
temp.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
// While head2 is not null
while (head2 != null) {
temp.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
return merged.next;
}
// Find mid using The Tortoise and The Hare approach
static Node findMid(Node head)
{
Node slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// Function to print list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = new Node(7);
Node temp = head;
temp.next = new Node(10);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(5);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(20);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(3);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = new Node(2);
temp = temp.next;
// Apply merge Sort
head = mergeSort(head);
System.out.print("\nSorted Linked List is: \n");
printList(head);
}
}
输出:
Sorted Linked List is:
2 3 5 7 10 20 时间复杂度:O(n * log n)
空间复杂度: O(log n)
资料来源:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merge_sort
http://cslibrary.stanford.edu/105/LinkedListProblems.pdf