给定两个点A(x1,y1)和B(x2,y2)的坐标,使得x1
- DDA线描算法
- Bresenhams的线条绘制算法简介。
在这篇文章中,讨论了中点画线算法,这是代表上一篇文章中介绍的布雷森汉姆算法的另一种方式。
如上一篇文章中所述,对于任何给定/计算的先前像素P(X p ,Y p ),最接近该行的下一个像素有两个候选项E(X p +1,Y p )和NE(X p + 1,Y p +1)( E代表东方, NE代表东北)。
在中点算法中,我们执行以下操作。
- 找到两个可能的下一个点的中间点。 E(X p +1,Y p )和NE(X p +1,Y p +1)的中间是M(X p + 1 ,Y p +1/2)。
- 如果M在直线上方,则选择E作为下一点。
- 如果M在该线下方,则选择NE作为下一点。
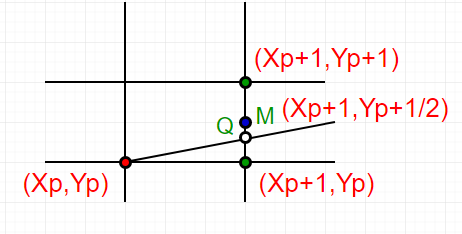
如何找到一个点是在一条线的上方还是一条线的下方?
以下是使算法保持简单的一些假设。
- 我们从左到右画线。
- x1
- 该线的斜率在0到1之间。我们从左下到右上画一条线。
除上述假设以外的其他情况可以通过反思来处理。
Let us consider a line y = mx + B.
We can re-write the equation as :
y = (dy/dx)x + B or
(dy)x + B(dx) - y(dx) = 0
Let F(x, y) = (dy)x - y(dx) + B(dx) -----(1)
Let we are given two end points of a line (under
above assumptions)
-> For all points (x,y) on the line,
the solution to F(x, y) is 0.
-> For all points (x,y) above the line,
F(x, y) result in a negative number.
-> And for all points (x,y) below the line,
F(x, y) result in a positive number. 此关系用于确定相对
M的位置
M =(X p + 1 ,Y p + 1/2)
所以我们的决策参数d是
d = F(M)= F(X p + 1 ,Y p + 1/2)
如何从旧值中有效地找到d的新值?
为了简单起见,让F(x,y)写成ax + by + c。
其中a = dy
b = -dx
c = B * dx
我们从上式(1)得到这些值
情况1:如果选择E,则接下来的要点:
dnew = F(X p +2,Y p + 1/2)
= a(X p +2)+ b(Y p + 1/2)+ c
dold = a(X p +1)+ b(Y p + 1/2)+ c
两个距离的差(或增量):
DELd = dnew – dold
= a(X p +2)-a(X p +1)+ b(Y p + 1/2)-b(Y p + 1/2)+ cc
= a(X p )+ 2a – a(X p )– a
= a。
因此,dnew = dold + dy。 (以a = dy表示)
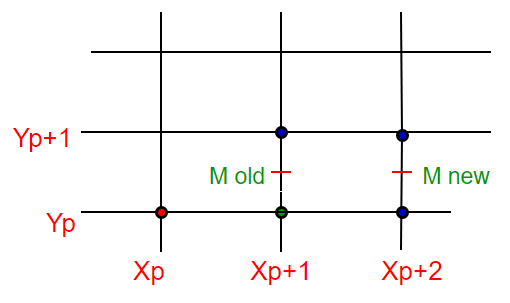
情况2:如果选择NE,则接下来的内容:
dnew = F(X p +2,Y p +3/2)
= a(X p +2)+ b(Y p +3/2)+ c
dold = a(X p +1)+ b(Y p +1/2)+ c
两个距离的差(或增量):
DELd = dnew -dold
= a(X p +2)-a(X p +1)+ b(Y p +3/2)-b(Y p +1/2)+ cc
= a(X p )+ 2a – a(X p )– a + b(Y p )+ 3 / 2b – b(Y p )-1 / 2b
= a + b
因此,dnew = dold + dy – dx。 (如a = dy,b = -dx)
计算对于决策参数d0的初始值:
d0 = F(X1 + 1,Y1 + 1/2)
= a(X1 +1)+ b(Y1 + 1/2)+ c
= aX1 + bY1 + c + a + b / 2
= F(X1,Y1)+ a + b / 2
= a + b / 2(因为F(X1,Y1)= 0)
d0 = dy – dx / 2。 (如a = dy,b = -dx)
算法:
Input (X1,Y1) and (X2,Y2)
dy = Y2- Y1
dx = X2 - X1
// initial value of
// decision parameter d
if(dy<=dx){
d = dy - (dx/2)
x = X1 , y = Y1
// plot initial given point
Plot(x , y)
// iterate through value of X
while(x < X2)
x = x+1
// 'E' is chosen
if (d < 0)
d = d + dy
// 'NE' is chosen
else
d = d + dy - dx
y = y+1
Plot(x,y)}
else if(dx<=dy)
{
d = dx - (dy/2)
x = X1 , y = Y1
// plot initial given point
Plot(x , y)
// iterate through value of X
while(y< Y2)
y= y+1
// 'E' is chosen
if (d < 0)
d = d + dx
// 'NE' is chosen
else
d = d + dx - dy
x= x+1
Plot(x,y)
}下面是上述想法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for Mid-point line generation
#include
using namespace std;
// Header file for including graphics functions
// #include
// midPoint function for line generation
void midPoint(int X1, int Y1, int X2, int Y2)
{
// calculate dx & dy
int dx = X2 - X1;
int dy = Y2 - Y1;
if(dy<=dx){
// initial value of decision parameter d
int d = dy - (dx/2);
int x = X1, y = Y1;
// Plot initial given point
// putpixel(x,y) can be used to print pixel
// of line in graphics
cout << x << "," << y << "\n";
// iterate through value of X
while (x < X2)
{
x++;
// E or East is chosen
if (d < 0)
d = d + dy;
// NE or North East is chosen
else
{
d += (dy - dx);
y++;
}
// Plot intermediate points
// putpixel(x,y) is used to print pixel
// of line in graphics
cout << x << "," << y << "\n";
}
}
else if(dx Java
// Java program for Mid-point
// line generation
class GFG
{
// midPoint function for line generation
static void midPoint(int X1, int Y1,
int X2, int Y2)
{
// calculate dx & dy
int dx = X2 - X1;
int dy = Y2 - Y1;
// initial value of decision
// parameter d
int d = dy - (dx/2);
int x = X1, y = Y1;
// Plot initial given point
// putpixel(x,y) can be used to
// print pixel of line in graphics
System.out.print(x +"," + y + "\n");
// iterate through value of X
while (x < X2)
{
x++;
// E or East is chosen
if (d < 0)
d = d + dy;
// NE or North East is chosen
else
{
d += (dy - dx);
y++;
}
// Plot intermediate points
// putpixel(x,y) is used to print
// pixel of line in graphics
System.out.print(x +"," + y + "\n");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int X1 = 2, Y1 = 2, X2 = 8, Y2 = 5;
midPoint(X1, Y1, X2, Y2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.Python 3
# Python3 program for Mid-point
# line generation
# midPoint function for line generation
def midPoint(X1,Y1,X2,Y2):
# calculate dx & dy
dx = X2 - X1
dy = Y2 - Y1
# initial value of decision parameter d
d = dy - (dx/2)
x = X1
y = Y1
# Plot initial given point
# putpixel(x,y) can be used to print pixel
# of line in graphics
print(x,",",y,"\n")
# iterate through value of X
while (x < X2):
x=x+1
# E or East is chosen
if(d < 0):
d = d + dy
# NE or North East is chosen
else:
d = d + (dy - dx)
y=y+1
# Plot intermediate points
# putpixel(x,y) is used to print pixel
# of line in graphics
print(x,",",y,"\n")
# Driver program
if __name__=='__main__':
X1 = 2
Y1 = 2
X2 = 8
Y2 = 5
midPoint(X1, Y1, X2, Y2)
# This code is contributed by ash264C#
// C# program for Mid-point
// line generation
using System;
class GFG {
// midPoint function for line
// generation
static void midPoint(int X1, int Y1,
int X2, int Y2)
{
// calculate dx & dy
int dx = X2 - X1;
int dy = Y2 - Y1;
// initial value of decision
// parameter d
int d = dy - (dx/2);
int x = X1, y = Y1;
// Plot initial given point
// putpixel(x,y) can be used
// to print pixel of line in
// graphics
Console.Write(x + "," + y + "\n");
// iterate through value of X
while (x < X2)
{
x++;
// E or East is chosen
if (d < 0)
d = d + dy;
// NE or North East is chosen
else
{
d += (dy - dx);
y++;
}
// Plot intermediate points
// putpixel(x,y) is used to print
// pixel of line in graphics
Console.Write(x + "," + y + "\n");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main ()
{
int X1 = 2, Y1 = 2, X2 = 8, Y2 = 5;
midPoint(X1, Y1, X2, Y2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.PHP
Javascript
输出:
2,2
3,3
4,3
5,4
6,4
7,5
8,5