给定两个值N和K。查找在框中排列N个不同项目的方式的数量,以便从N个不同的盒子中准确地使用K(K
注意: 1 <= N <= K <= 10 5 。
先决条件:阶乘,计算nCr%p
例子:
Input: N = 5, k = 5
Output: 120
Input: N = 5, k = 3
Output: 1500
方法:我们将使用包含-排除原理来计算方式。
- 让我们假设盒子编号为1到N,现在我们必须选择任意K个盒子并使用它们。进行此操作的方法数量为N CK 。
- 现在,任何项目都可以放入任何选定的盒子中,因此,排列它们的方式为K N。但是,在这里,我们可以计算一些盒子为空的布置。因此,我们将使用包含-排除原理来确保计算所有K盒中至少填充有一个项目的方式。
- 让我们了解包含-排除原理的应用:
- 因此,从K N种方式中,我们减去至少1个盒子(K个中)为空的情况。因此,减去
(K C1 )*((K-1) N ) 。 - 请注意,这里,恰好两个框为空的情况被减去两次(一次是当我们以( K C1 )方式选择第一个元素,然后是当我们以( K C1 )方式选择第二个元素时)。
- 因此,我们一次添加了这些方法进行补偿。因此,我们加上(K C2 )*((K – 2) N ) 。
- 同样,在这里我们需要添加至少3个框为空时的路数,依此类推……
- 因此,从K N种方式中,我们减去至少1个盒子(K个中)为空的情况。因此,减去
- 因此,方法总数:
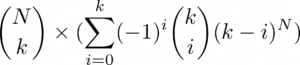
C++
// C++ program to calculate the
// above formula
#include
#define mod 1000000007
#define int long long
using namespace std;
// To store the factorials
// of all numbers
int factorial[100005];
// Function to calculate factorial
// of all numbers
void StoreFactorials(int n)
{
factorial[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
factorial[i] =
(i * factorial[i - 1])
% mod;
}
}
// Calculate x to the power y
// in O(log n) time
int Power(int x, int y)
{
int ans = 1;
while (y > 0) {
if (y % 2 == 1) {
ans = (ans * x) % mod;
}
x = (x * x) % mod;
y /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
// Function to find inverse mod of
// a number x
int invmod(int x)
{
return Power(x, mod - 2);
}
// Calculate (n C r)
int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return (factorial[n]
* invmod((factorial[r]
* factorial[n - r]) % mod))
% mod;
}
int CountWays(int n,int k)
{
StoreFactorials(n);
// Loop to compute the formula
// evaluated
int ans = 0;
for (int i = k; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (i % 2 == k % 2)
{
// Add even power terms
ans = (ans + (Power(i, n)
* nCr(k, i)) % mod)
% mod;
}
else
{
// Subtract odd power terms
ans = (ans + mod - (Power(i, n)
* nCr(k, i)) % mod) % mod;
}
}
// Choose the k boxes which
// were used
ans = (ans * nCr(n, k)) % mod;
return ans;
}
// Driver code
signed main()
{
int N = 5;
int K = 5;
cout << CountWays(N, K) << "\n";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to calculate the
// above formula
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static long mod = 1000000007;
// To store the factorials
// of all numbers
static long factorial[] = new long[100005];
// Function to calculate factorial
// of all numbers
static void StoreFactorials(int n)
{
factorial[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
factorial[i] = (i *
factorial[i - 1]) % mod;
}
}
// Calculate x to the power y
// in O(log n) time
static long Power(long x, long y)
{
long ans = 1;
while (y > 0)
{
if (y % 2 == 1)
{
ans = (ans * x) % mod;
}
x = (x * x) % mod;
y /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
// Function to find inverse mod of
// a number x
static long invmod(long x)
{
return Power(x, mod - 2);
}
// Calculate (n C r)
static long nCr(int n, int r)
{
return (factorial[n] *
invmod((factorial[r] *
factorial[n - r]) % mod)) % mod;
}
static long CountWays(int n,int k)
{
StoreFactorials(n);
// Loop to compute the formula
// evaluated
long ans = 0;
for(int i = k; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (i % 2 == k % 2)
{
// Add even power terms
ans = (ans + (Power(i, n) *
nCr(k, i)) % mod) % mod;
}
else
{
// Subtract odd power terms
ans = (ans + mod - (Power(i, n) *
nCr(k, i)) % mod) % mod;
}
}
// Choose the k boxes which
// were used
ans = (ans * nCr(n, k)) % mod;
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int N = 5;
int K = 5;
System.out.print(CountWays(N, K) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by math_loverPython3
# Python3 program to calculate the
# above formula
mod = 1000000007
# To store the factorials
# of all numbers
factorial = [0 for i in range(100005)]
# Function to calculate factorial
# of all numbers
def StoreFactorials(n):
factorial[0] = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1, 1):
factorial[i] = (i * factorial[i - 1]) % mod
# Calculate x to the power y
# in O(log n) time
def Power(x, y):
ans = 1
while (y > 0):
if (y % 2 == 1):
ans = (ans * x) % mod
x = (x * x) % mod
y //= 2
return ans
# Function to find inverse mod
# of a number x
def invmod(x):
return Power(x, mod - 2)
# Calculate (n C r)
def nCr(n, r):
return ((factorial[n] * invmod((factorial[r] *
factorial[n - r]) %
mod)) % mod)
def CountWays(n, k):
StoreFactorials(n)
# Loop to compute the formula
# evaluated
ans = 0
i = k
while(i >= 0):
if (i % 2 == k % 2):
# Add even power terms
ans = ((ans + (Power(i, n) *
nCr(k, i)) % mod) % mod)
else:
# Subtract odd power terms
ans = ((ans + mod - (Power(i, n) *
nCr(k, i)) %
mod) % mod)
i -= 1
# Choose the k boxes which
# were used
ans = (ans * nCr(n, k)) % mod
return ans
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 5
K = 5
print(CountWays(N, K))
# This code is contributed by Surendra_GangwarC#
// C# program to calculate the
// above formula
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static long mod = 1000000007;
// To store the factorials
// of all numbers
static long []factorial = new long[100005];
// Function to calculate factorial
// of all numbers
static void StoreFactorials(int n)
{
factorial[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
factorial[i] = (i *
factorial[i - 1]) % mod;
}
}
// Calculate x to the power y
// in O(log n) time
static long Power(long x, long y)
{
long ans = 1;
while (y > 0)
{
if (y % 2 == 1)
{
ans = (ans * x) % mod;
}
x = (x * x) % mod;
y /= 2;
}
return ans;
}
// Function to find inverse mod of
// a number x
static long invmod(long x)
{
return Power(x, mod - 2);
}
// Calculate (n C r)
static long nCr(int n, int r)
{
return (factorial[n] *
invmod((factorial[r] *
factorial[n - r]) % mod)) % mod;
}
static long CountWays(int n,int k)
{
StoreFactorials(n);
// Loop to compute the formula
// evaluated
long ans = 0;
for(int i = k; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (i % 2 == k % 2)
{
// Add even power terms
ans = (ans + (Power(i, n) *
nCr(k, i)) % mod) % mod;
}
else
{
// Subtract odd power terms
ans = (ans + mod - (Power(i, n) *
nCr(k, i)) % mod) % mod;
}
}
// Choose the k boxes which
// were used
ans = (ans * nCr(n, k)) % mod;
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main (string[] args)
{
int N = 5;
int K = 5;
Console.Write(CountWays(N, K) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56输出:
120
时间复杂度: O(N * log N)