C++程序是使用特定的模板结构编写的。用C++语言编写的程序的结构如下:
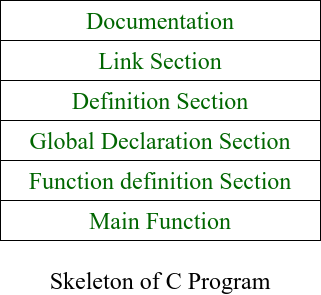
文档部分:
- 本节是第一部分,用于记录程序员要编写代码的程序逻辑。
- 它也可以用于编写程序。
- 在文档部分中所写的都是注释,而不是由编译器编译的。
- 文档部分是可选的,因为程序可以在没有它们的情况下执行。以下是相同的代码段:
C++
/* This is a C++ program to find the
factorial of a number
The basic requirement for writing this
program is to have knowledge of loops
To find the factorial of number
iterate over range from number to one
*/C++
// Function to implement the
// factorial of number num
int factorial(k& num)
{
// Iterate over the loop from
// num to one
for (k i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact *= i;
}
// Return the factorial calculated
return fact;
}C++
// Documentation Section
/* This is a C++ program to find the
factorial of a number
The basic requirement for writing this
program is to have knowledge of loops
To find the factorial of a number
iterate over the range from number to 1
*/
// Linking Section
#include
using namespace std;
// Defination Section
#define msg "FACTORIAL\n"
typedef int k;
// Global Declaration Section
k num = 0, fact = 1, storeFactorial = 0;
// Function Section
k factorial(k& num)
{
// Iterate over the loop from
// num to one
for (k i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact *= i;
}
// Return the factorial
return fact;
}
// Main Function
int main()
{
// Given number Num
k Num = 5;
// Function Call
storeFactorial = factorial(Num);
cout << msg;
// Print the factorial
cout << Num << "! = "
<< storeFactorial << endl;
return 0;
} 链接部分:
链接部分包含两个部分:
头文件:
- 通常,程序包括标准C++库中已定义的各种编程元素,例如内置函数,类,关键字,常量,运算符等。
- 为了在程序中使用这样的预定义元素,必须在程序中包含适当的头。
- 标准头文件是通过预处理程序指令#include在程序中指定的。在图中,使用了iostream标头。当编译器处理指令#include
时 ,它会将流的内容包括在程序中。这使程序员可以使用仅通过中定义的标准流提供的标准输入,输出和错误工具。这些标准流将数据作为字符流进行处理,也就是说,数据将以连续流的形式进行读取和显示。此处列出了 中定义的标准流。
#include
命名空间:
- 命名空间允许以单个名称将各种实体(例如类,对象,函数和各种C++令牌等)分组。
- 任何用户都可以创建自己的独立命名空间,并可以在其他任何程序中使用它们。
- 在以下代码段中,名称空间std包含cout,cin,endl等语句的声明。
using namespace std;- 命名空间可以通过多种方式访问:
- 使用命名空间std;
- 使用std :: cout;
定义部分:
- 它用于声明一些常量并为其分配一些值。
- 在本节中,任何人都可以使用原始数据类型定义自己的数据类型。
- 在#define中,是一个编译器指令,该指令会告诉编译器每当找到该消息时,将其替换为“ Factorial \ n”。
- typedef int K ;该语句告诉编译器,每当遇到K时,将其替换为int,并且已将k声明为数据类型,因此不能将其用作标识符。
全球宣言科:
- 在此声明将在程序中使用的变量和类定义,以使其成为全局变量。
- 在本节中声明的变量的作用域一直持续到整个程序终止。
- 这些变量也可以在用户定义的函数中访问。
函数声明部分:
- 它包含我们主要功能所需的所有功能。
- 通常,此部分包含用户定义的函数。
- 程序的这一部分可以在main函数之后编写,但是为此,请在本节中为该函数编写函数原型,您将在main函数之后编写代码。
C++
// Function to implement the
// factorial of number num
int factorial(k& num)
{
// Iterate over the loop from
// num to one
for (k i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact *= i;
}
// Return the factorial calculated
return fact;
}
主要函数:
- main函数告诉编译器从哪里开始执行程序。程序的执行从main函数开始。
- 所有要执行的语句都写在main函数。
- 编译器执行所有写在大括号{}中的指令,该大括号包含主函数的主体。
- 一旦从主函数的所有指令被执行控制出来的主要函数,并且程序终止的并没有进一步执行发生。
下面是说明此问题的程序:
C++
// Documentation Section
/* This is a C++ program to find the
factorial of a number
The basic requirement for writing this
program is to have knowledge of loops
To find the factorial of a number
iterate over the range from number to 1
*/
// Linking Section
#include
using namespace std;
// Defination Section
#define msg "FACTORIAL\n"
typedef int k;
// Global Declaration Section
k num = 0, fact = 1, storeFactorial = 0;
// Function Section
k factorial(k& num)
{
// Iterate over the loop from
// num to one
for (k i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
fact *= i;
}
// Return the factorial
return fact;
}
// Main Function
int main()
{
// Given number Num
k Num = 5;
// Function Call
storeFactorial = factorial(Num);
cout << msg;
// Print the factorial
cout << Num << "! = "
<< storeFactorial << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
FACTORIAL
5! = 120
想要从精选的最佳视频中学习并解决问题,请查看有关从基础到高级C++的C++基础课程以及有关语言和STL的C++ STL课程。要完成从学习语言到DS Algo等的更多准备工作,请参阅“完整面试准备课程” 。