给定部分填充的9×9矩阵,必须将数字(从1到9)分配给空单元格,以便大小为3×3的每一行,列和子矩阵都恰好包含一个1到9的数字实例。

这里描述了针对此问题的Pure backtracking解决方案。强烈建议读者在继续之前先了解纯回溯解决方案的工作原理。
在纯回溯解决方案中,我们遍历矩阵,每当找到一个空单元格(没有任何数字的单元格)时,我们就为该单元格分配一个数字,该数字在当前列,行和3×3中不存在子矩阵。将数字分配给当前单元格后,我们递归检查此分配是否导致有效的解决方案。如果分配没有找到有效的解决方案,则我们尝试使用当前空单元格的下一个有效数字。并且,如果没有一个数字导致有效的解决方案,则该实例是不可行的。
1. If there is no empty cell in the matrix M:
return true
2. Let (i, j) be an empty cell in the matrix M
3. For i from 1 to 9:
3.1. If i is not present in the row r, in column c, and the 3x3
submatrix of (r, c):
a) M(r, c) = i
b) recursively try fill in remaining empty cells
c) If recursion was successful:
return true
d) M(r, c) = 0
4. return false
- 可以通过遍历相应的行,列和3×3子矩阵来执行步骤(3.1)。但是,我们可以通过在回溯之前对这些数字进行预处理来加快此步骤,这是本文的重点。因此,让我们以下面的矩阵为例:
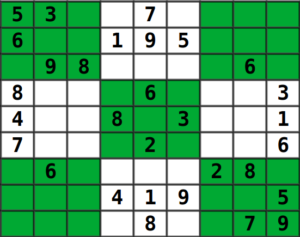
我们可以跟踪整数位中的行,列和3×3子矩阵的数字,例如,考虑上一个矩阵的第一行,我们可以通过以下方式存储这些数字:
bits order - 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 bits - 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0然后在步骤(3.1)中,我们可以使用按位运算来确定数字i是否位于行,列和3×3子矩阵中。假设rowDigits [r]是包含第r行数字的整数,那么我们可以使用以下表达式检查数字i是否在第r行中:
rowsDigits[r] & (1<<(i - 1))如果上面的表达式等于0,则在行r中不存在数字i。例如,如果r = 0,而i = 1,则:
bits order - 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 rowDigits[r] - 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1<<(i - 1) - 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 rowDigits[r]&(1<<(i - 1)) - 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 - 一旦步骤(3.1)的条件为真,就执行步骤(3.1a),然后我们需要在rowDigits,columnDigits和subMatrixDigits中插入数字i,我们可以使用以下表达式进行操作:
rowsDigits[r] | (1<<(i - 1))例如,如果r = 0,而i = 1,则:
bits order - 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 rowDigits[r] - 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1<<(i - 1) - 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 rowDigits[r]|(1<<(i - 1)) - 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 - 如果步骤(3.1c)的条件为false,则执行步骤(3.1d),然后我们需要从rowDigits,columnDigits和subMatrixDigits中删除数字i,我们可以使用以下表达式进行操作:
rowsDigits[r] & ~(1<<(i - 1))例如,如果r = 0,而i = 1,则:
bits order - 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 rowDigits[r] - 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1<<(i - 1) - 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 ~(1<<(i - 1)) - 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 rowDigits[r]&~(1<<(i - 1) - 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0
下面是上述方法的实现。
// C++ program to solve sudoku
#include
#include
// N is used for the size of Sudoku grid.
// Size will be NxN
#define N 9
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to print grid */
void printGrid(int grid[N][N])
{
for (int row = 0; row < N; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < N; col++)
cout << grid[row][col] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
/* Takes a partially filled-in grid and attempts
to assign values to all unassigned locations in
such a way to meet the requirements for
Sudoku solution (non-duplication across rows,
columns, and boxes) */
bool solve(int r, int c, int board[9][9],
int submatrixDigits[3][3],
int rowDigits[9],
int columnDigits[9])
{
if (r == 9)
{
return true;
}
if (c == 9)
{
return solve(r + 1, 0, board, submatrixDigits,
rowDigits, columnDigits);
}
if (board[r] == 0) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++)
{
int digit = 1 << (i - 1);
if (!((submatrixDigits[r / 3] & digit)
|| (rowDigits[r] & digit)
|| (columnDigits & digit)))
{
// set digit
submatrixDigits[r / 3] |= digit;
rowDigits[r] |= digit;
columnDigits |= digit;
board[r] = i;
if (solve(r, c + 1, board, submatrixDigits,
rowDigits, columnDigits))
{
return true;
}
else
{
submatrixDigits[r / 3] &= ~digit;
rowDigits[r] &= ~digit;
columnDigits &= ~digit;
board[r] = 0;
}
}
}
return false;
}
return solve(r, c + 1, board, submatrixDigits,
rowDigits, columnDigits);
}
// Function checks if Sudoku can be
// solved or not
bool SolveSudoku(int board[9][9])
{
int submatrixDigits[3][3];
int columnDigits[9];
int rowDigits[9];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
memset(submatrixDigits[i], 0, 3 * sizeof(int));
memset(rowDigits, 0, 9 * sizeof(int));
memset(columnDigits, 0, 9 * sizeof(int));
// get 3x3 submatrix, row and column digits
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++)
if (board[i][j] > 0)
{
int value = 1 << (board[i][j] - '1');
submatrixDigits[i / 3][j / 3] |= value;
rowDigits[i] |= value;
columnDigits[j] |= value;
}
// Backtrack
if (solve(0, 0, board, submatrixDigits,
rowDigits, columnDigits))
return true;
else
return false;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// 0 means unassigned cells
int grid[N][N] = {{3, 0, 6, 5, 0, 8, 4, 0, 0},
{5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 8, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1},
{0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 0, 0, 8, 0},
{9, 0, 0, 8, 6, 3, 0, 0, 5},
{0, 5, 0, 0, 9, 0, 6, 0, 0},
{1, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 5, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7, 4},
{0, 0, 5, 2, 0, 6, 3, 0, 0}};
if (SolveSudoku(grid) == true)
printGrid(grid);
else
cout << "No solution exists";
return 0;
}
输出:
3 1 6 5 2 8 4 3 4
5 2 2 1 3 4 5 6 7
3 8 7 5 6 7 1 3 1
1 2 3 3 1 5 4 8 6
9 3 4 8 6 3 2 1 5
5 5 6 2 9 1 6 7 3
1 3 1 4 5 2 2 5 8
2 4 3 6 1 8 7 7 4
6 5 5 2 7 6 3 2 1