回合:我
数组arr = {7、7、8、8、9、1、1、4、2、2}的数字出现两次或一次。重复项每次并排出现。可能一次只能出现几个数字,仅假设这是一个向右旋转的数组(可以说一个数组可以向右旋转k次)。目的是识别在数组中出现一次的数字。
#include
int main()
{
int a[] = { 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 1, 1, 4, 2, 2 }, i = 1, m = 10;
// int a[]={7, 8, 8, 9, 1, 1, 4, 2, 2, 7}, i=1, m=10;
if (a[0] == a[m - 1]) {
i = 2;
m = m - 1;
}
else
printf("%d\n", a[m - 1]); // For cases like { 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 1, 1, 4, 2, 3 }, a[] = { 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 1, 1, 4, 4, 2 }
for (; i < m; i++)
if (a[i] == a[i - 1])
i++;
else
printf("%d\n", a[i - 1]);
return 0;
}
输入:
7,7,8,8,9,1,1,4,2,2
输出:
9
4
第二轮:
在第二轮中,询问了有关BST的问题。 BST的单个路径中的关键元素的总和(仅说此总和为path_ weight)和阈值路径权重作为输入给出。如果任何路径权重小于超卖的路径权重,则应将其从树中删除。
例子 :
输入:
将下面的树视为输入,并且阈值路径权重为110。 
输出:
以下是输入树可以创建的路径数
路径1:50-> 30-> 20,总和= 100
路径1:50-> 30-> 40,总和= 120
路径1:50-> 70-> 60,总和= 180
路径1:50-> 70-> 80,总和= 200
在当前场景中,路径小于阈值路径权重(100 <110),因此我们必须销毁路径1。
破坏路径后的树1。 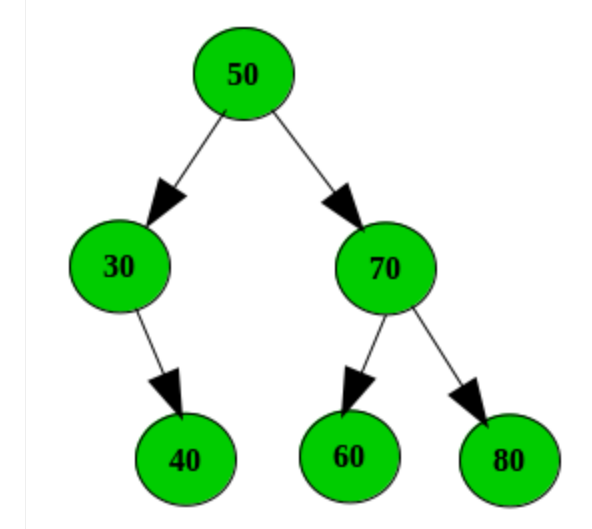
以上任务的程序:
#include
#include
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node* newnode(int element)
{
struct node* temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = element;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
struct node* insert(struct node* root, int element)
{
if (root == NULL)
return newnode(element);
if (element < root->key)
root->left = insert(root->left, element);
else if (element > root->key)
root->right = insert(root->right, element);
return root;
}
void inorder(struct node* mynode)
{
if (mynode != NULL) {
inorder(mynode->left);
printf("%d\t", mynode->key);
inorder(mynode->right);
}
}
struct node* minValueNode(struct node* node)
{
struct node* current = node;
/* loop down to find the leftmost leaf */
while (current->left != NULL)
current = current->left;
return current;
}
struct node* deleteNode(struct node* root, int key)
{
// base case
if (root == NULL)
return root;
// If the key to be deleted is smaller than the root's key,
// then it lies in left subtree
if (key < root->key)
root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);
// If the key to be deleted is greater than the root's key,
// then it lies in right subtree
else if (key > root->key)
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);
// if key is same as root's key, then This is the node
// to be deleted
else {
// node with only one child or no child
if (root->left == NULL) {
struct node* temp = root->right;
free(root);
return temp;
}
else if (root->right == NULL) {
struct node* temp = root->left;
free(root);
return temp;
}
// node with two children: Get the inorder successor (smallest
// in the right subtree)
struct node* temp = minValueNode(root->right);
// Copy the inorder successor's content to this node
root->key = temp->key;
// Delete the inorder successor
root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key);
}
return root;
}
/** Function : checkpathCost(int pathweight, int thresoldPathWeight,
struct node *currentNode, struct node *root)
This function will sum the all individual elements in a every
path and lets say it as pathweight and if the sum less than
key then the path will be deleted.
Arguments:
pathweight : Sum of all elements in a path. As we are
traversing in recursive mode we the sum of
previews elements.
thresoldPathWeight : Threshold value to compare the path weight
currentNode : CUrrent node in the tree.
root : root of the tree, used while deleting the node.
Output : will delete paths which not satisfy the condition
(pathweightkey;
// Check the conditionh if current node is a leaf node.
if ((currentNode->left == NULL) && (currentNode->right == NULL)) {
// If pathweight is less that thresoldPathWeight delete the path
if (pathweight < thresoldPathWeight) {
// we need to delete the node, so there is no necessity
// in maintaining the current->key in pathweight.
pathweight = pathweight - currentNode->key;
printf("need to Delete %d.\n", currentNode->key);
deleteNode(root, currentNode->key);
checkpathCost(0, thresoldPathWeight, root, root);
}
else
// If currentNode->key satisfies the condition
// (pathweight > thresoldPathWeight), need to backtrack
// back to check with other paths and no necessity in
// maintaining the current->key in pathweight.
pathweight = pathweight - currentNode->key;
}
// If currentNode is not a leaf traverse all the
// possible paths.
if (currentNode->left != NULL) {
checkpathCost(pathweight, thresoldPathWeight,
currentNode->left, root);
}
if (currentNode->right != NULL) {
checkpathCost(pathweight, thresoldPathWeight,
currentNode->right, root);
}
}
int main()
{
int thresoldPathWeight = 110;
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
struct node* root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 30);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 40);
root = insert(root, 70);
root = insert(root, 60);
root = insert(root, 80);
printf("Inorder traversal of the given tree \n");
inorder(root);
printf("\n");
checkpathCost(0, thresoldPathWeight, root, root);
printf("Inorder traversal of the given tree \n");
inorder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
除了geeksforgeeks及以下函数BST的现有代码外,还将实现上述任务。
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/binary-search-tree-set-2-delete/