给定一组值。任务是使用数组的值实现二进制搜索树,其中每个节点在路径中存储从节点本身开始到树的任何叶结束的最大节点数。
注意:BST中从任何节点到任何叶节点的路径中的最大节点数是根于该节点的子树的高度。
例子:
Input : arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
Output :
data = 1 height = 6
data = 2 height = 5
data = 3 height = 4
data = 4 height = 3
data = 5 height = 2
data = 6 height = 1
data = 7 height = 0
Input : arr[] = {4, 12, 10, 5, 11, 8, 7, 6, 9}
Output :
data = 4 height = 6
data = 5 height = 3
data = 6 height = 0
data = 7 height = 1
data = 8 height = 2
data = 9 height = 0
data = 10 height = 4
data = 11 height = 0
data = 12 height = 5
想法是以BST方式添加节点。父级的高度说P仅在将新节点添加到子树时才更新,这会增加P AND的高度(逻辑),并且在添加新节点后子树的高度也会增加。
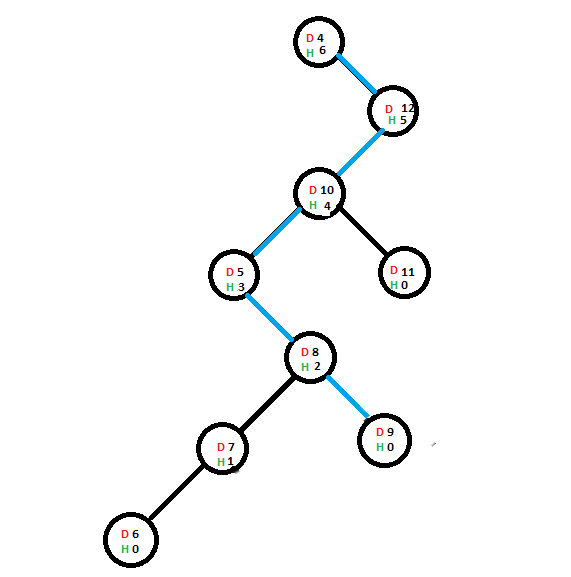
假设存在一棵树(节点的数据为红色,节点的当前高度为绿色):
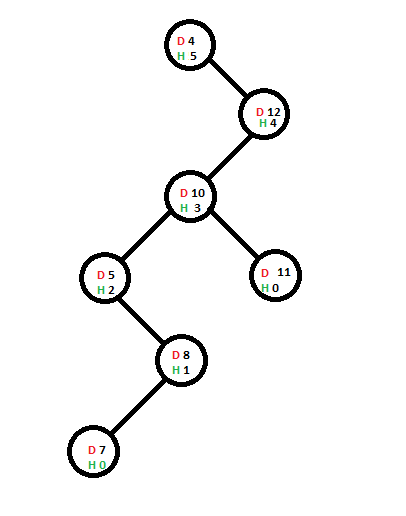
现在,我们将添加一个包含值6的新节点,该节点为了添加而采用的路线已用蓝色突出显示:
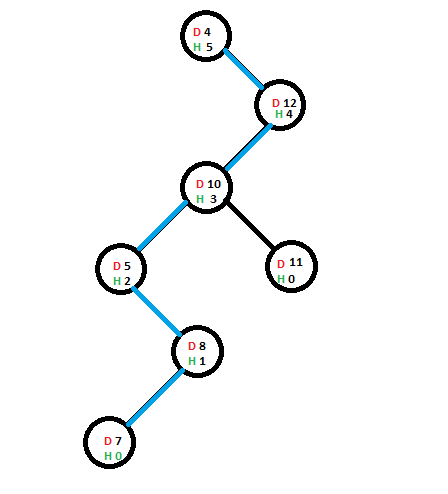
添加新节点后,其直接父节点的高度将增加(仅当包含6个节点的直接父节点的高度受到此添加的影响时-在这种情况下为true)。一旦父级的高度增加,它将检查存在父级的子树是否是该子树作为子级的节点的高度的主要贡献,如果是,则该节点的高度将增加–在如果向上传播,则缩短高度增量。
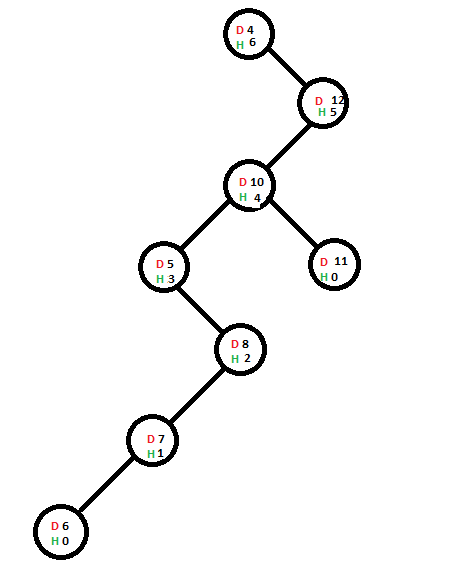
现在,我们将添加另一个包含值9的节点,将其添加到其最终位置所用的路径为蓝色:
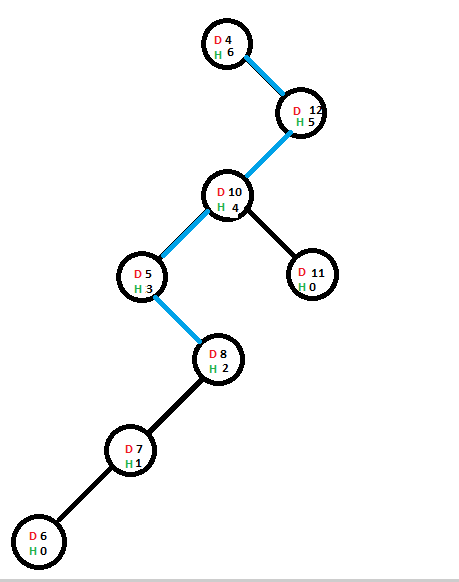
由于包含值9的节点的直接父级的高度不受此加法运算的影响,因此其父级的高度不会受到影响,并且高度增量也不会向上传播。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C
// C implementation of above approach
#include
#include
// Structure containing basic template od a node
struct node {
// Stores the data and current height of the node
int data;
int height;
struct node* right;
struct node* left;
};
int indicator = 0;
void left_insert(struct node*, struct node*);
void right_insert(struct node*, struct node*);
// Inorder traversal of the tree
void traverse(struct node* head)
{
if (head != NULL) {
traverse(head->left);
printf(" data = %d", head->data);
printf(" height = %d\n", head->height);
traverse(head->right);
}
}
// Insertion to the left sub-tree
void left_insert(struct node* head, struct node* temp)
{
// Child node of Current head
struct node* child = NULL;
if (head->data > temp->data) {
if (head->left == NULL) {
indicator = 1;
child = head->left = temp;
}
else {
left_insert(head->left, temp);
child = head->left;
}
}
else {
right_insert(head, temp);
}
if ((indicator == 1) && (child != NULL)) {
if (head->height > child->height) {
// Ending propagation to height of above nodes
indicator = 0;
}
else {
head->height += 1;
}
}
}
// Insertion to the right sub-tree
void right_insert(struct node* head, struct node* temp)
{
// Child node of Current head
struct node* child = NULL;
if (head->data < temp->data) {
if (head->right == NULL) {
indicator = 1;
child = head->right = temp;
}
else {
right_insert(head->right, temp);
child = head->right;
}
}
else {
left_insert(head, temp);
}
if ((indicator == 1) && (child != NULL)) {
if (head->height > child->height) {
// Ending propagation to height of above nodes
indicator = 0;
}
else {
head->height += 1;
}
}
}
// Function to create node and push
// it to its appropriate position
void add_nodes(struct node** head, int value)
{
struct node *temp_head = *head, *temp;
if (*head == NULL) {
// When first node is added
*head = malloc(sizeof(**head));
(*head)->data = value;
(*head)->height = 0;
(*head)->right = (*head)->left = NULL;
}
else {
temp = malloc(sizeof(*temp));
temp->data = value;
temp->height = 0;
temp->right = temp->left = NULL;
left_insert(temp_head, temp);
temp_head = *head;
indicator = 0;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct node *head = NULL, *temp_head = NULL;
add_nodes(&head, 4);
add_nodes(&head, 12);
add_nodes(&head, 10);
add_nodes(&head, 5);
add_nodes(&head, 11);
add_nodes(&head, 8);
add_nodes(&head, 7);
add_nodes(&head, 6);
add_nodes(&head, 9);
temp_head = head;
// Traversing the tree to display
// the updated height values
traverse(temp_head);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of above approach
class GFG
{
// Structure containing basic template od a node
static class node
{
// Stores the data and current height of the node
int data;
int height;
node right;
node left;
}
static int indicator = 0;
// Inorder traversal of the tree
static void traverse(node head)
{
if (head != null)
{
traverse(head.left);
System.out.printf(" data = %d", head.data);
System.out.printf(" height = %d\n", head.height);
traverse(head.right);
}
}
// Insertion to the left sub-tree
static void left_insert(node head, node temp)
{
// Child node of Current head
node child = null;
if (head.data > temp.data)
{
if (head.left == null)
{
indicator = 1;
child = head.left = temp;
}
else
{
left_insert(head.left, temp);
child = head.left;
}
}
else
{
right_insert(head, temp);
}
if ((indicator == 1) && (child != null))
{
if (head.height > child.height)
{
// Ending propagation to height of above nodes
indicator = 0;
}
else
{
head.height += 1;
}
}
}
// Insertion to the right sub-tree
static void right_insert(node head, node temp)
{
// Child node of Current head
node child = null;
if (head.data < temp.data)
{
if (head.right == null)
{
indicator = 1;
child = head.right = temp;
}
else
{
right_insert(head.right, temp);
child = head.right;
}
}
else
{
left_insert(head, temp);
}
if ((indicator == 1) && (child != null))
{
if (head.height > child.height)
{
// Ending propagation to height of above nodes
indicator = 0;
}
else
{
head.height += 1;
}
}
}
// Function to create node and push
// it to its appropriate position
static node add_nodes(node head, int value)
{
node temp_head = head, temp;
if (head == null)
{
// When first node is added
head = new node();
(head).data = value;
(head).height = 0;
(head).right = (head).left = null;
}
else
{
temp = new node();
temp.data = value;
temp.height = 0;
temp.right = temp.left = null;
left_insert(temp_head, temp);
temp_head = head;
indicator = 0;
}
return head;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
node head = null, temp_head = null;
head = add_nodes(head, 4);
head = add_nodes(head, 12);
head = add_nodes(head, 10);
head = add_nodes(head, 5);
head = add_nodes(head, 11);
head = add_nodes(head, 8);
head = add_nodes(head, 7);
head = add_nodes(head, 6);
head = add_nodes(head, 9);
temp_head = head;
// Traversing the tree to display
// the updated height values
traverse(temp_head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduPython3
# Python implementation of above approach
# Structure containing basic template od a node
class node:
def __init__(self) -> None:
# Stores the data and current height of the node
self.data = 0
self.height = 0
self.right = None
self.left = None
# Inorder traversal of the tree
def traverse(head: node) -> None:
if (head != None):
traverse(head.left)
print(" data = {}".format(head.data), end="")
print(" height = {}".format(head.height))
traverse(head.right)
# Insertion to the left sub-tree
def left_insert(head: node, temp: node) -> None:
global indicator
# Child node of Current head
child = None
if (head.data > temp.data):
if (head.left == None):
indicator = 1
child = head.left = temp
else:
left_insert(head.left, temp)
child = head.left
else:
right_insert(head, temp)
if ((indicator == 1) and (child != None)):
if (head.height > child.height):
# Ending propagation to height of above nodes
indicator = 0
else:
head.height += 1
# Insertion to the right sub-tree
def right_insert(head: node, temp: node) -> None:
global indicator
# Child node of Current head
child = None
if (head.data < temp.data):
if (head.right == None):
indicator = 1
child = head.right = temp
else:
right_insert(head.right, temp)
child = head.right
else:
left_insert(head, temp)
if ((indicator == 1) and (child != None)):
if (head.height > child.height):
# Ending propagation to height of above nodes
indicator = 0
else:
head.height += 1
# Function to create node and push
# it to its appropriate position
def add_nodes(head: node, value: int) -> node:
global indicator
temp_head = head
temp = None
if (head == None):
# When first node is added
head = node()
(head).data = value
(head).height = 0
(head).right = (head).left = None
else:
temp = node()
temp.data = value
temp.height = 0
temp.right = temp.left = None
left_insert(temp_head, temp)
temp_head = head
indicator = 0
return head
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
indicator = 0
head = None
temp_head = None
head = add_nodes(head, 4)
head = add_nodes(head, 12)
head = add_nodes(head, 10)
head = add_nodes(head, 5)
head = add_nodes(head, 11)
head = add_nodes(head, 8)
head = add_nodes(head, 7)
head = add_nodes(head, 6)
head = add_nodes(head, 9)
temp_head = head
# Traversing the tree to display
# the updated height values
traverse(temp_head)
# This code is contributed by sanjeev2552data = 4 height = 6
data = 5 height = 3
data = 6 height = 0
data = 7 height = 1
data = 8 height = 2
data = 9 height = 0
data = 10 height = 4
data = 11 height = 0
data = 12 height = 5如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。