给定完美的二叉树的叶子节点,任务是构造XOR树并打印该树的根节点。
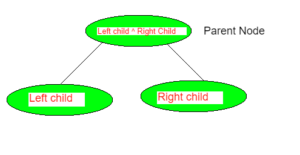
XOR树是其父节点是树的左子节点和右子节点的XOR的树。
父节点=左子节点^右子节点
例子:
Input: arr = {40, 32, 12, 1, 4, 3, 2, 7}
Output: Nodes of the XOR tree
7 5 2 8 13 7 5 40 32 12 1 4 3 2 7
Root: 7
Explanation:
Input: arr = {5, 7, 2, 8, 12, 3, 9, 1}
Output: Nodes of the XOR tree
15 8 7 2 10 15 8 5 7 2 8 12 3 9 1
Root: 15
Input: arr = {4, 2, 10, 1, 14, 30, 21, 7}
Output: Nodes of the XOR tree
15 13 2 6 11 16 18 4 2 10 1 14 30 21 7
Root: 15
Input: arr = {1, 2, 3, 4}
Output: Nodes of the XOR tree
4 3 7 1 2 3 4
Root: 4
Input: arr = {47, 62, 8, 10, 4, 3, 1, 7}
Output: Nodes of the XOR tree
18 19 1 17 2 7 6 47 62 8 10 4 3 1 7
Root: 18
方法:
- 由于它是完美的二叉树,因此总共有2 ^ h-1个节点,其中h是XOR树的高度。
- 由于给出了理想的二叉树的叶节点,因此通过首先递归构建左子树和右子树来构建根节点。
- 左右子树中的每个节点都是通过对其子节点执行XOR操作形成的。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Maximum size for xor tree
int maxsize = 100005;
// Allocating space to xor tree
vector xor_tree(maxsize);
// A recursive function that constructs xor tree
// for vector array[start.....end].
// x is index of current node in XOR tree
void construct_Xor_Tree_Util(vector current,
int start, int end, int x)
{
// If there is one element in vector array, store it
// in current node of XOR tree
if (start == end) {
xor_tree[x] = current[start];
// cout< arr, int n)
{
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// leaf nodes of Perfect Binary Tree
vector leaf_nodes = { 40, 32, 12, 1, 4, 3, 2, 7 };
int n = leaf_nodes.size();
// Build the xor tree
construct_Xor_Tree(leaf_nodes, n);
// Height of xor tree
int x = (int)(ceil(log2(n)));
// Maximum size of xor tree
int max_size = 2 * (int)pow(2, x) - 1;
cout << "Nodes of the XOR Tree:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < max_size; i++) {
cout << xor_tree[i] << " ";
}
// Root node is at index 0 considering
// 0-based indexing in XOR Tree
int root = 0;
// print value at root node
cout << "\nRoot: " << xor_tree[root];
} C
// C program to build xor tree by leaf nodes
// of perfect binary tree and root node value of tree
#include
#include
// maximum size for xor tree
#define maxsize 10005
// Allocating space to xor tree
int xortree[maxsize];
// A recursive function that constructs xor tree
// for array[start.....end].
// x is index of current node in xor tree st
void construct_Xor_Tree_Util(int current[],
int start, int end, int x)
{
// If there is one element in array, store it
// in current node of xor tree and return
if (start == end) {
xortree[x] = current[start];
// printf("%d ", xortree[x]);
return;
}
// for left subtree
int left = x * 2 + 1;
// for right subtree
int right = x * 2 + 2;
// for getting the middle index
// from corner indexes.
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
// Build the left and the right subtrees
// by xor operation
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(current, start, mid, left);
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(current, mid + 1, end, right);
// merge the left and right subtrees by
// XOR operation
xortree[x] = (xortree[left] ^ xortree[right]);
}
// Function to construct XOR tree from given array.
// This function calls construct_Xor_Tree_Util()
// to fill the allocated memory of xort array
void construct_Xor_Tree(int arr[], int n)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < maxsize; i++)
xortree[i] = 0;
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// leaf nodes of Binary Tree
int leaf_nodes[] = { 40, 32, 12, 1, 4, 3, 2, 7 }, i = 0;
int n = sizeof(leaf_nodes) / sizeof(leaf_nodes[0]);
// Build the xor tree
construct_Xor_Tree(leaf_nodes, n);
// Height of xor tree
int x = (int)(ceil(log2(n)));
// Maximum size of xor tree
int max_size = 2 * (int)pow(2, x) - 1;
printf("Nodes of the XOR tree\n");
for (i = 0; i < max_size; i++) {
printf("%d ", xortree[i]);
}
// Root node is at index 0 considering
// 0-based indexing in XOR Tree
int root = 0;
// print value at root node
printf("\nRoot: %d", xortree[root]);
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach
class GFG
{
// Maximum size for xor tree
static int maxsize = 100005;
// Allocating space to xor tree
static int []xor_tree = new int[maxsize];
// A recursive function that constructs xor tree
// for vector array[start.....end].
// x is index of current node in XOR tree
static void construct_Xor_Tree_Util(int []current,
int start, int end, int x)
{
// If there is one element in vector array, store it
// in current node of XOR tree
if (start == end)
{
xor_tree[x] = current[start];
// System.out.print(xor_tree[x]+" x";
return;
}
// for left subtree
int left = x * 2 + 1;
// for right subtree
int right = x * 2 + 2;
// for getting the middle index from corner indexes.
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
// Build the left and the right subtrees by xor operation
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(current, start, mid, left);
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(current, mid + 1, end, right);
// merge the left and right subtrees by
// XOR operation
xor_tree[x] = (xor_tree[left] ^ xor_tree[right]);
}
// Function to conXOR tree from the given vector array.
// This function calls construct_Xor_Tree_Util() to fill the
// allocated memory of xor_tree vector array
static void construct_Xor_Tree(int []arr, int n)
{
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// leaf nodes of Perfect Binary Tree
int []leaf_nodes = { 40, 32, 12, 1, 4, 3, 2, 7 };
int n = leaf_nodes.length;
// Build the xor tree
construct_Xor_Tree(leaf_nodes, n);
// Height of xor tree
int x = (int)(Math.ceil(Math.log(n)));
// Maximum size of xor tree
int max_size = 2 * (int)Math.pow(2, x) - 1;
System.out.print("Nodes of the XOR Tree:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < max_size; i++)
{
System.out.print(xor_tree[i]+ " ");
}
// Root node is at index 0 considering
// 0-based indexing in XOR Tree
int root = 0;
// print value at root node
System.out.print("\nRoot: " + xor_tree[root]);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992Python
# Python3 implementation of the above approach
from math import ceil,log
# Maximum size for xor tree
maxsize = 100005
# Allocating space to xor tree
xor_tree = [0] * maxsize
# A recursive function that constructs xor tree
# for vector array[start.....end].
# x is index of current node in XOR tree
def construct_Xor_Tree_Util(current, start, end, x):
# If there is one element in vector array, store it
# in current node of XOR tree
if (start == end):
xor_tree[x] = current[start]
# cout<C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Maximum size for xor tree
static int maxsize = 100005;
// Allocating space to xor tree
static int []xor_tree = new int[maxsize];
// A recursive function that constructs xor tree
// for vector array[start.....end].
// x is index of current node in XOR tree
static void construct_Xor_Tree_Util(int []current,
int start, int end, int x)
{
// If there is one element in vector array, store it
// in current node of XOR tree
if (start == end)
{
xor_tree[x] = current[start];
// Console.Write(xor_tree[x]+" x";
return;
}
// for left subtree
int left = x * 2 + 1;
// for right subtree
int right = x * 2 + 2;
// for getting the middle index from corner indexes.
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
// Build the left and the right subtrees by xor operation
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(current, start, mid, left);
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(current, mid + 1, end, right);
// merge the left and right subtrees by
// XOR operation
xor_tree[x] = (xor_tree[left] ^ xor_tree[right]);
}
// Function to conXOR tree from the given vector array.
// This function calls construct_Xor_Tree_Util() to fill the
// allocated memory of xor_tree vector array
static void construct_Xor_Tree(int []arr, int n)
{
construct_Xor_Tree_Util(arr, 0, n - 1, 0);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// leaf nodes of Perfect Binary Tree
int []leaf_nodes = { 40, 32, 12, 1, 4, 3, 2, 7 };
int n = leaf_nodes.Length;
// Build the xor tree
construct_Xor_Tree(leaf_nodes, n);
// Height of xor tree
int x = (int)(Math.Ceiling(Math.Log(n)));
// Maximum size of xor tree
int max_size = 2 * (int)Math.Pow(2, x) - 1;
Console.Write("Nodes of the XOR Tree:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < max_size; i++)
{
Console.Write(xor_tree[i] + " ");
}
// Root node is at index 0 considering
// 0-based indexing in XOR Tree
int root = 0;
// print value at root node
Console.Write("\nRoot: " + xor_tree[root]);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992输出:
Nodes of the XOR Tree:
7 5 2 8 13 7 5 40 32 12 1 4 3 2 7
Root: 7
时间复杂度: O(N)